Abstract
Purpose
Analysis of microstructural alterations of corneal and limbal epithelial cells in healthy human corneas and in other ocular conditions.
Patients and methods
Unilateral eyes of three groups of subjects include healthy volunteers (G1, n=5), contact lens wearers (G2, n=5), and patients with dry eyes (G3, n=5) were studied. Imaging of basal (BC) and intermediate (IC) epithelial cells from central cornea (CC), corneal limbus (CL) and scleral limbus (SL) was obtained by in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM). An appropriate image analysis algorithm was used to quantify morphometric parameters including mean cell area, compactness, solidity, major and minor diameter, and maximum boundary distance.
Results
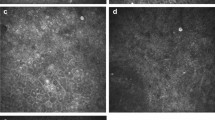
The morphometric parameters of BC and IC demonstrated no significant differences (P>0.05) between groups. Comparison between three corneal locations (CC, CL, and SL) within the groups showed significant differences (P<0.05) with mean values of cell area, compactness, solidity, and major and minor diameter of BC that increase from CC to limbus. The BC were round and regular in the central cornea (P<0.05) compared with CL and SL.
Conclusions
IVCM enables high-quality confocal images from central corneal and limbal epithelium. This quantitative study demonstrated morphological differences in the basal and intermediate epithelium between limbus and central cornea, and found no differences between contact lens wearers, dry eyes, and normal subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Thoft RA, Friend J . The X, Y, Z hypothesis of corneal epithelial maintenance. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1983; 24 (10): 1442–1443.
Tavakoli M, Hossain P, Malik RA . Clinical applications of corneal confocal microscopy. Clin Ophthalmol 2008; 2 (2): 435–445.
Gaujoux T, Touzeau O, Laroche L, Borderie VM . Morphometry of corneal epithelial cells on normal eyes and after anterior lamellar keratoplasty. Cornea 2010; 29 (10): 1118–1124.
Miri A, Al-Aqaba M, Otri AM, Fares U, Said DG, Faraj LA et al. in vivo confocal microscopic features of normal limbus. Br J Ophthalmol 2012; 96 (4): 530–536.
Prakasam RK, Winter K, Schwiede M, Allgeier S, Zhivov A, Köhler B et al. Characteristic quantities of corneal epithelial structures in confocal laser scanning microscopic volume data sets. Cornea 2013; 32 (5): 636–643.
Goldberg MF, Bron AJ . Limbal palisades of Vogt. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1982; 80: 155–171.
Dua HS, Azuara-Blanco A . Limbal stem cells of the corneal epithelium. Surv Ophthalmol 2000; 44 (5): 415–425.
Dua HS, Shanmuganathan VA, Powell-Richards AO, Tighe PJ, Joseph A . Limbal epithelial crypts: a novel anatomical structure and a putative limbal stem cell niche. Br J Ophthalmol 2005; 89 (5): 529–532.
Martin R . Corneal conjunctivalisation in long-standing contact lens wearers. Clin Exp Optom 2007; 90 (1): 26–30.
Beljan J, Beljan K, Beljan Z . Complications caused by contact lens wearing. Coll Antropol 2013; 37 (Suppl 1): 179–187.
Gobbels M, Spitznas M . Influence of artificial tears on corneal epithelium in dry-eye syndrome. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1989; 227 (2): 139–141.
Stave J, Zinser G, Grummer G, Guthoff R . Modified Heidelberg Retinal Tomograph HRT. Initial results of in vivo presentation of corneal structures. Ophthalmologe 2002; 99 (4): 276–280.
Eckard A, Stave J, Guthoff RF . In vivo investigations of the corneal epithelium with the confocal Rostock Laser Scanning Microscope (RLSM). Cornea 2006; 25 (2): 127–131.
Falke K, Prakasam RK, Guthoff RF, Stachs O . In vivo imaging of limbal epithelium and palisades of Vogt. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 2012; 229 (12): 1185–1190.
Patel DV, Sherwin T, McGhee CN . Laser scanning in vivo confocal microscopy of the normal human corneoscleral limbus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2006; 47 (7): 2823–2827.
Romano AC, Espana EM, Yoo SH, Budak MT, Wolosin JM, Tseng SC . Different cell sizes in human limbal and central corneal basal epithelia measured by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003; 44 (12): 5125–5129.
Kobayashi A, Sugiyama K . In vivo corneal confocal microscopic findings of palisades of Vogt and its underlying limbal stroma. Cornea 2005; 24 (4): 435–437.
Bourne WM . The effect of long-term contact lens wear on the cells of the cornea. Clao J 2001; 27 (4): 225–230.
Mathers WD, Sachdev MS, Petroll M, Lemp MA . Morphologic effects of contact lens wear on the corneal surface. Clao J. 1992; 18 (1): 49–52.
Kalogeropoulos G, Chang S, Bolton T, Jalbert I . The effects of short-term lens wear and eye rubbing on the corneal epithelium. Eye Contact Lens 2009; 35 (5): 255–259.
Stapleton F, Kasses S, Bolis S, Keay L . Short term wear of high Dk soft contact lenses does not alter corneal epithelial cell size or viability. Br J Ophthalmol 2001; 85 (2): 143–146.
Mantelli F, Massaro-Giordano M, Macchi I, Lambiase A, Binini S . The cellular mechanisms of dry eye: from pathogenesis to treatment. J Cell Physiol 2013; 228 (12): 2253–2256.
Liu Z, Pflugfelder SC . Corneal surface regularity and the effect of artificial tears in aqueous tear deficiency. Ophthalmology 1999; 106 (5): 939–943.
Benitez del Castillo JM, Wasfy MA, Fernandez C, Garcia-Sanchez J . An in vivo confocal masked study on corneal epithelium and subbasal nerves in patients with dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004; 45 (9): 3030–3035.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by BMBF (RESPONSE) and DFG (KO-4979/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakasam, R., Kowtharapu, B., Falke, K. et al. Quantitative assessment of central and limbal epithelium after long-term wear of soft contact lenses and in patients with dry eyes: a pilot study. Eye 30, 979–986 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.58
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/eye.2016.58