Abstract
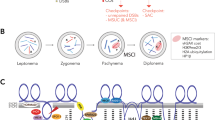
A considerable body of evidence suggests that the deleterious meiotic effects of pericentric inversions in F1 hybrids can be overcome by changes in chiasma location and various means of non-homologous pairing. Such overriding mechanisms may render pericentric inversions benign and increase the likelihood of their fixation in population isolates. It has been argued that overriding mechanisms of this type negate the involvement of pericentric inversions as reproductive isolating mechanisms in speciation. It is suggested, however, that the involvement of pericentric inversions in speciation should be considered on two levels. First, that by reducing meiotic effects in F1 hybrids, overriding mechanisms facilitate the fixation of pericentric inversions. Secondly, when contact hybridization occurs between the chromosomally derived and parental populations second-level effects may be encountered. That is, the recombinational effects of pericentric inversion differences on coadapted gene complexes (sensu Brncic, 1954; Shaw & Coates, 1983) enforce profound inviability barriers in F2 and backcross matings. In this way, multiple pericentric inversions may act as significant post-mating isolating mechanisms, whereas individual inversions with less significant second-level effects may not.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Brncic, D. 1954. Heterosis and the integration of the genotype in geographic populations of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Genetica, 39, 77–88.
Davisson, M T, Poorman, P A, Roderick, R H, and Moses, M J. 1981. A pericentric inversion in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 30, 70–76.
Dobzhansky, T. 1951. Genetics and the Origin of Species, 3rd edn. Columbia University Press, New York.
Fletcher, H L, and Hewitt, G M. 1978. Non-homologous synaptonemal complex formation in a heteromorphic bivalent in Keyacris scurra (Morabinae, Orthoptera). Chromosoma (Berl) 65, 271–281.
Greenbaum, I F, and Reed, M J. 1984. Evidence for heterosynaptic pairing of the inverted segment in pericentric inversion heterozygotes of deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). Cytogenet Cell Genet, 38, 106–111.
Hale, W W. 1986. Heterosynapsis and suppression of chias-mata within heterozygous pericentric inversions of the sitka deer mouse. Chromosoma (Berl), 94, 425–432.
John, B. 1981. Chromosome change and evolutionary change: a critique. In: Atchley, W. R. and Woodruff, D. (eds) Evolution and Speciation Essays in honour of M J D White, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp. 23–51.
John, B, and King, M. 1977. Heterochromatin variation in Cryptobothrus chrysophorus. 1. Chromosome differentiation in natural populations. Chromosoma (Berl), 64, 219–239.
John, B, and King, M. 1980. Heterochromatin variation in Cryptobothrus chrysophorus. III. Synthetic hybrids. Chromosoma (Berl) 78, 165–186.
King, M. 1984. Karyotypic evolution in Gehyra (Gekkonidae, Reptilia). IV. Chromosome change and speciation. Genetica, 64, 101–114.
King, M. 1987. Chromosomal rearrangements, speciation and the theoretical approach. Heredity, 59, 1–6.
Lande, R. 1984. The expected fixation rate of chromosomal inversions. Evolution, 38, 743–752.
Moses, M J. 1977. Microspreading and the synaptonemal complex in cytogenetic studies. Chromosomes Today, 8, 90–103.
Moses, M J, Dresser, M E, and Poorman, P A. 1984. Composition and role of the synaptonemal complex. Symp Soc Exp Biol, 38, 245–270.
Moses, M J, Poorman, P A, Roderick, T H, and Davisson, M T. 1982. Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements. IV. Synapsis and synaptic adjustment in two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma (Berl), 84, 457–474.
Nur, U. 1968. Synapsis and crossing-over within a paracentric inversion in the grasshopper Camnula pellucida. Chromosoma (Berl), 25, 198–214.
Poorman, P A, Moses, M J, Davisson, M T, and Roderick, T H. 1981. Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements. III. Cytogenetic observations on two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma (Berl), 83, 419–429.
Rouhani, S, and Barton, N H. 1987. The probability of peak shifts in founder populations. J Theor Biol, 126, 51–62.
Nur, U. 1968. Synapsis and crossing-over within a paracentric inversion in the grasshopper Camnula pellucida. Chromosoma (Berl), 25, 198–214.
Poorman, P A, Moses, M J, Davisson, M T, and Roderick, T H. 1981. Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements. III. Cytogenetic observations on two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma (Berl), 83, 419–429.
Rouhani, S, and Barton, N H. 1987. The probability of peak shifts in founder populations. J Theor Biol, 126, 51–62.
Schroeder, G L. 1968. Pericentric inversion polymorphism in Trimerotropis helfen (Orthoptera.Acrididae) and its effects on chiasma frequency. PhD thesis University of California at Davis.
Shaw, D D, and Coates, D J. 1983. Chromosomal variation and the concept of the coadapted genome — a direct cytological assessment. In: Bennett, M. and Brandham, P. (eds) Kew Chromosome Conference II. George Allen and Unwin, London, pp. 207–216.
Shaw, D D, Coates, D J, and Wilkinson, P. 1986. Estimating the genic and chromosomal components of reproductive isolation within and between subspecies of the grasshopper Caledia captiva. Can J Genet Cytol, 28, 686–695.
Stack, S, and Anderson, L. 1988. An analysis of synaptic adjustment, length and twisting of synaptonemal complexes in maize. In: Brandham, P. E. (ed.) Kew Chromosome Conference III. HMSO, London, pp. 299–312.
Tease, C, and Fisher, G. 1988. Chromosome pairing in foetal oocytes of mouse inversion heterozygotes. In Brandham, P. E. (ed.) Kew Chromosome Conference III. HMSO, London, pp. 293–298.
Vetukhiv, M. 1953. Viability of hybrids between local populations of Drosophila pseudoobscura. Proc Nat Acad Sci, USA, 39, 30–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, M. A dual level model for speciation by multiple pericentric inversions. Heredity 68, 437–440 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1992.63
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1992.63
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Dugesia hepta and Dugesia benazzii (Platyhelminthes: Tricladida): two sympatric species with occasional sex?
Organisms Diversity & Evolution (2020)
-
Chromosome mapping of repetitive DNAs in sergeant major fishes (Abudefdufinae, Pomacentridae): a general view on the chromosomal conservatism of the genus
Genetica (2016)
-
Emerin deletion reveals a common X-chromosome inversion mediated by inverted repeats
Nature Genetics (1997)