Abstract
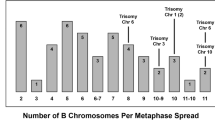
Twenty-eight progeny analyses (PAs) performed on specimens of E. plorans collected from four natural Iberian populations have been informative about the transmission of rare B chromosome types or the de novo origin of some of them. At least 11 rare B-types have been found in addition to the predominant ones: B1 in Daimuz, B2 in Jete and Salobreña, and B5 in Fuengirola. The presence in two controlled crosses of one embryo carrying a B-type which was absent in the parents suggests that these B variants (B2iso and B1f1) have originated de novo. Eleven other PAs suggest that new B derivatives are recurrently arising in these populations. The most frequent B chromosome mutation was centromere misdivision that originated four different B-types (B2m1, B1iso, B2iso and Bmini). Other rearrangements were pericentric inversions (B2i1, B2i2 and B2i3), inverse tandem fusion (B2it1), centric fusion (B1f1) and deletions (B2d1 and B2d2). The four B derivatives produced by centromeric misdivision are significantly eliminated during sexual transmission, most probably owing to deficiencies in the control of chromosome movement by their hemicentromeres. Those derived from translocations showed Mendelian transmission but deletion B variants showed a tendency to elimination. Our results suggest that B chromosome substitution of B1 by B2 in the Salobreña and Jete populations could be achieved by differences in relative transmission efficiency, as in one controlled cross, where the female carried 1 B1 plus 1 B2, B2 was significantly overtransmitted and B1, eliminated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Baverstock, P R, Gelder, M, and Jahnke, A. 1982. Cytogenetic studies of the Australian rodent Uromys caudimaculatus, a species showing extensive heterochromatin variation. Chromosoma, 84, 517–533.
Bougourd, S M, and Parker, J S. 1979. The B chromosome system of Allium schoenoprasum. II. Stability, inheritance and phenotypic effects. Chromosoma, 75, 369–383.
Cabrero, J, Alché, J D, and Camacho, J P M. 1987. Effects of B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans on nucleolar organiser regions activity. Activation of a latent NOR on a B chromosome fused to an autosome. Genome, 29, 116–121.
Fröst, S. 1957. The inheritance of the accessory chromosomes in Centaurea scabiosa. Hereditas, 43, 403–422.
Green, D M. 1990. Muller's Ratchet and the evolution of supernumerary chromosomes. Genome, 33, 818–824.
Henriques-Gil, N, and Arana, P. 1990. Origin and substitution of B chromosomes in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Evolution, 44, 747–753.
Henriques-Gil, N, Arana, P, and Santos, J L. 1983. Spontaneous translocations between B chromosomes and the normal complement in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Chromosoma, 88, 145–148.
Henriques-Gil, N, Santos, J L, and Arana, P. 1984. Evolution of a complex polymorphism in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Chromosoma, 89, 290–293.
Holmes, D S, and Bougourd, S M. 1991. B-chromosome selection in Allium schoenoprasum. II. Experimental populations. Heredity, 67, 117–122.
Jones, R N, and Rees, H. 1982. B Chromosomes. Academic Press, London.
Lima-De-Faria, A. 1963. The evolution of the structural pattern in a rye B chromosome. Evolution, 17, 289–295.
López-León, M D, Cabrero, J, and Camacho, J P M. 1991. Meiotic drive against an autosomal supernumerary segment promoted by the presence of a B chromosome in females of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Chromosoma, 100, 282–287.
López-León, M D, Cabrero, J, Camacho, J P M, Cano, M I, and Santos, J L. 1992. A widespread B chromosome polymorphism maintained without apparent drive. Evolution, 46, 529–539.
López-León, M D, Cabrero, J, Pardo, M C, Viseras, E, and Camacho, J P M. 1993. Paternity displacement in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans. Heredity, in press.
Matsuda, T. 1970. On the accessory chromosomes of Aster. I. The accessory chromosomes of Aster ageratoides. J Sci Hiroshima Univ Ser B Div 2 (Bot), 13, 1–63.
Nur, U. 1977. Maintenance of a ‘parasitic’ B chromosome in the grasshopper Melanoplus femur-rubrum. Genetics, 87, 499–512.
Nur, U, and Brett, B H L. 1988. Genotypes affecting the condensation and transmission of heterochromatic B chromosomes in the mealy bug Pseudococcus affinis. Chromosoma, 96, 205–212.
Parker, J S. 1976. The B chromosome system of Hypochoeris maculata. I. B-distribution, meiotic behaviour and inheritance. Chromosoma, 59, 167–177.
Parker, J S, Jones, G H, Edgar, L, and Whitehouse, C. 1989. The population cytogenetics of Crepis capillaris. II. The stability and inheritance of B chromosomes. Heredity, 63, 19–27.
Parker, J S, Taylor, S, and Ainsworth, C C. 1982. The B chromosome system of Hypochoeris maculata. III. Variation in B-chromosome transmission rates. Chromosoma, 85, 229–310.
Patton, J L. 1977. B chromosome systems in the pocket mouse, Perognathus baileyi: meiosis and C-band studies. Chromosoma, 60, 1–14.
Romera, F, Jiménez, M, and Puertas, M J. 1991. Genetic control of the rate of transmission of rye B chromosomes. I. Effects in 2B × 0B crosses. Heredity, 66, 61–66.
Shaw, M W, and Hewitt, G M. 1990. B chromosomes, selfish DNA and theoretical models: where next? In: Futuyma, D. and Antonovics, J. (eds) Oxford Surveys in Evolutionary Biology, vol. 7, pp. 197–223.
Shaw, M W, Hewitt, G M, and Anderson, D A. 1985. Polymorphism in the rates of meiotic drive acting on the B chromosome of Myrmeleotettix maculatus. Heredity, 55, 61–68.
Webb, G C, and Nehaus, P. 1979. Chromosome organization in the Australian plague locust Chortoicetes terminifera. II. Banding variants of B chromosome. Chromosoma, 70, 205–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
López-León, M., Cabrero, J., Pardo, M. et al. Generating high variability of B chromosomes in Eyprepocnemis plorans (grasshopper). Heredity 71, 352–362 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1993.149
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1993.149
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Out of patterns, the euchromatic B chromosome of the grasshopper Abracris flavolineata is not enriched in high-copy repeats
Heredity (2021)
-
Interpopulation spread of a parasitic B chromosome is unlikely through males in the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans
Heredity (2020)
-
Protein-coding genes in B chromosomes of the grasshopper Eyprepocnemis plorans
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Origin of B chromosomes in the genus Astyanax (Characiformes, Characidae) and the limits of chromosome painting
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2016)
-
Next generation sequencing and FISH reveal uneven and nonrandom microsatellite distribution in two grasshopper genomes
Chromosoma (2015)