Abstract
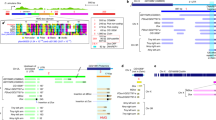
The behaviour of the retrotransposons copia and mdg1 was analysed in hybrids between Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Females of a highly inbred line of D. melanogaster were crossed with D. simulans males from three natural populations. The insertion site profiles for the two elements were determined in F1 hybrid larvae by in situ hybridization to polytene chromosomes, and were compared with that of their parents. No somatic transposition events were detected after this genomic stress of interspecific hybridization for the two transposable elements concerned.
Similar content being viewed by others

Article PDF
References
Ananiev, E V, and Ilyin, Y V. 1981. A comparative study of the location of mobile dispersed genes in salivary gland and midgut polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma, 82, 429–435.
Biemont, C. 1994. Dynamic equilibrium between insertion and excision of P elements in highly inbred lines from an M' strain of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Evol, 39, 466–472.
Biemont, C, and Aouar, A. 1987. Copy-number dependent transpositions and excisions of the mdg-1 mobile element in inbred lines of Drosophila melanogaster. Heredity, 58, 39–47.
Blackman, R H, and Kelbart, W M. 1989. The transposable element hobo of Drosophila melanogaster. In: Berg, D. E. and Howe, M. M. (eds) Mobile DNA, pp. 523–529. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Bock, I R. 1984. Interspecific hybridization in the genus Drosophila. Evol Biol, 18, 41–70.
Coen, E S, Robbins, T P, Almeida, J, Hudson, A, and Carpenter, R. 1989. Consequences and mechanisms of transposition in Antirrhinum majus. In: Berg, D. E. and Howe, M. M. (eds) Mobile DNA, pp. 413–436. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Crow, J F. 1984. The P factor: a transposable element in Drosophila. In: Chu, E. H. Y. and Generoso, W. M. (eds) Mutation, Cancer and Malformation, pp. 257–273. Plenum Press, New York.
Di Franco, C, Pisano, C, Dimitri, P, Gigliotti, S, and Junakovic, N. 1989. Genomic distribution of copia-like transposable elements in somatic tissues and during development of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma, 98, 402–410.
Dunsmuir, P, Brorein, W J, Jr, Simon, M A, and Rubin, G M. 1980. Insertion of the Drosophila transposable element copia generates a 5 base pair duplication. Cell, 21, 575–579.
Emmons, S W, and Yesner, L. 1984. High-frequency excision of transposable element Tel in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell, 36, 599–605.
Evgen'Ev, M B, Yenikolopov, G N, Peunova, N I, and Ilyin, Y V. 1982. Transposition of mobile genetic elements in interspecific hybrids of Drosophila. Chromosoma, 85, 373–386.
Federoff, N V. 1989. Maize transposable elements. In: Berg, D. E. and Howe, M. M. (eds) Mobile DNA, pp. 375–412. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Fontdevila, A. 1993. Genetic instability and rapid speciation: are they coupled? In: MacDonald, J. F. (ed.) Transposable Elements and Evolution, pp. 242–253. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands.
Garcia Guerreiro, M P, and Biemont, C. 1995. Changes in the chromosomal insertion pattern of the copia element during the process of making chromosomes homozygous in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet, 246, 206–211.
Georgiev, P G, Kiselev, S L, Simonova, O B, and Gerasimova, T I. 1990. A novel transposition system in Drosophila melanogaster depending on the Stalker mobile genetic element. EMBO J, 9, 2037–2044.
Gerstel, D U, and Burns, J A. 1966. Chromosomes of unusual length in hybrids between two species of Nicotiana. Today, 1, 41–56.
Getz, D, and Van Schaik, N. 1991. Somatic mutation in the wings of Drosophila melanogaster females dysgenic due to P elements when reared at 29°C. Mutat Res, 248, 187–194.
Hartl, D L. 1989. Transposable element mariner in Drosophila species. In: Berg, D. E. and Howe, M. M. (eds) Mobile DNA, pp. 531–536. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Ilyin, Y V, Chemeliauskaite, V G, and Georgiev, G P. 1980. Double-stranded sequences in RNA of Drosophila melanogaster: relation to mobile dispersed genetic genes. Nucleic Acids Res, 8, 3439–3457.
Kim, A I, and Belyaeva, E S. 1991a. Direct demonstration of the transposition of mobile element mdg4 in the sex and somatic cells of the unstable mutator line of Drosophila melanogaster. Dokl Biol Sci, 314, 595–598.
Kim, A I, and Belyaeva, E S. 1991b. Transposition of mobile elements gypsy (mdg4) and hobo in germ-line and somatic cells of a genetically unstable mutator strain of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet, 229, 437–444.
Labrador, M, and Fontdevila, A. 1994. High transposition rates of Osvaldo, a new Drosophila buzzatii retrotransposon. Mol Gen Genet, 245, 661–674.
Lee, W L. 1978. Temperature sensitive viability of hybrids between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Jap J Genet, 53, 339–344.
Levis, R, Dunsmuir, P, and Rubin, G M. 1980. Terminal repeats of the Drosophila transposable element copia: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. Cell, 21, 581–588.
McDonald, J. 1990. Macroevolution and retroviral elements. Bioscience, 40, 183–191.
Moerman, D G, and Waterson, R H. 1989. Mobile elements in Caenorhabditis elegans and other nematodes. In: Berg, D. E. and Howe, M. M. (eds) Mobile DNA, pp. 537–556. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, DC.
Naveira, H, and Fontdevila, A. 1985. The evolutionary history of Drosophila buzzatii. IX. High frequencies of new chromosome rearrangements induced by introgressive hybridization. Chromosoma, 91, 87–94.
Pasyukova, E G, and Nuzhdin, S V. 1993. Doc and copia instability in an isogenic Drosophila melanogaster stock. Mol Gen Genet, 240, 302–306.
Pasyukova, E G, Belyaeva, E S, Ilyinskaya, L E, and Gvozdev, V A. 1988. Outcross-dependent transpositions of copia-like mobile genetic elements in chromosomes of an inbred Drosophila melanogater stock. Mol Gen Genet, 212, 281–286.
Pontecorvo, G. 1943. Hybrid sterility in artificially produced recombinants between Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Proc R Soc Edinb Sect B, 61, 385–397.
Price, H J. 1988. Nuclear DNA content variation within angiosperm species. Evol Trends Plants, 2, 53–60.
Rayburn, A L, Biradar, D P, Bullock, D G, and McMurphy, L M. 1993. Nuclear DNA content in F1 hybrids of maize. Heredity, 70, 294–300.
Seperack, P K, Strobel, M C, Corrow, D J, Jenkins, N A, and Copeland, N G. 1988. Somatic and germ-line reverse mutation rates of the retrovirus-induced dilute coat-color mutation of DBA mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 85, 189–192.
Sturtevant, A H. 1929. The genetics of Drosophila simulans. Carnegie Inst. Wash. Publ., 399, 1–62.
Sturtevant, A H. 1939. High mutation frequency induced by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 25, 308–310.
Tchurikov, N A, Ilyin, Y V, Skryabin, K G, Ananiev, E V, Bayev, A A, Jr, Lyubomirskaya, N V, and Georgiev, G P. 1980. General properties of mobile dispersed genetic elements in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol, 45, 655–665.
Watanabe, T K, Lee, W H, Inoue, Y, and Kaganishi, M. 1977. Genetic variation of the hybrid crossability between Drosophila melanogaster and Drosophila simulans. Jap J Genet, 52, 1–8.
Woodruff, R C. 1992. Transposable DNA elements and life history traits I. Transposition of P DNA elements in somatic cells reduces the lifespan of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetica, 86, 143–154.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerreiro, M. Behaviour of the transposable elements copia and mdg1 in hybrids between the sibling species Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans. Heredity 77, 40–46 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1996.106
Received:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/hdy.1996.106