Abstract
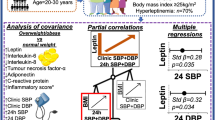
Obesity is often complicated by hypertension, and both conditions are risk factors for atherosclerosis. Leptin has attracted attention as a possible cause of hypertension in obese persons. We investigated the effect of a slow-release α1-receptor blocker, bunazosin hydrochloride, on leptin levels and insulin resistance in obese hypertensive patients with hyperleptinemia. The subjects were 17 patients (12 men and 5 women aged 56.1±12.2 years) with essential hypertension who were not receiving α1-receptor blockers. They had a body mass index (BMI)≥25 kg/m2 and a plasma leptin concentration ≥5 ng/ml. They received oral therapy with bunazosin hydrochloride at doses of up to 9 mg/day. The plasma leptin concentration, body weight, blood pressure, heart rate, fasting blood glucose, plasma insulin concentration, and free fatty acid level were compared between before and after treatment. Although there was no significant change of BMI, there was a significant decrease of plasma leptin after treatment (10.6±5.4 ng/ml vs. 8.7±3.4 ng/ml, p=0.0128), as well as a significant decrease of plasma insulin (9.8±4.8 μU/ml vs. 8.1±4.6 μU/ml, p=0.0494) and HOMA-R (2.9±2.1 vs. 2.2±1.5, p=0.0237). In conclusion, bunazosin hydrochloride reduced the plasma leptin level and improved insulin resistance in hypertensive patients with obesity and hyperleptinemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Adami GF, Papadia F, Carlini F, et al: Effect of biliopancreatic diversion on hypertension in severely obese patients. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 119–123.
Moinat M, Deng C, Muzzin P, et al: Modulation of obese gene expression in rat brown and white adipose tissues. FEBS Lett 1995; 373: 131–134.
Tartagia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, et al: Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 1995; 83: 1263–1271.
Friedman JM, Halaas JL : Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1996; 395: 763–770.
Ogawa Y, Masuzaki H, Isse N, et al: Molecular cloning of rat obese cDNA and augmented gene expression in genetically obese Zucker fatty (fa/fa) rats. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 1647–1652.
Scherrer U, Randin D, Tappy L, Vollenweider P, Jéquier E, Nicod P : Body fat and sympathetic nerve activity in healthy subjects. Circulation 1994; 89: 2634–2640.
Lean ME : Brown adipose tissue in humans. Proc Nutr Soc 1989; 48: 243–256.
Rehnmark S, Kopecky J, Jacobsson A, et al: Brown adipocytes differentiated in vitro can express the gene for the uncoupling protein thermogenin: effects of hypothyroidism and norepinephrine. Exp Cell Res 1989; 182: 75–83.
Satoh N, Ogawa Y, Katsuura G, et al: Sympathetic activation of leptin via the ventromedial hypothalamus: leptin-induced increase in catecholamine secretion. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1787–1793.
Friedman JM : Obesity in the new millennium. Nature 2000; 404: 632–634.
Wang MY, Lee Y, Unger RH : Novel form of lipolysis induced by leptin. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 17541–17544.
Haynes WG, Mogan DA, Walsh SA, Wark AL, Sivitz WI : Receptor mediated regional sympathetic nerve activation by leptin. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 270–278.
Shek EW, Brands MW, Hall JE : Chronic leptin infusion increases arterial pressure. Hypertension 1998; 31: 409–414.
Casto RM, Vaness JM, Overton JM : Effect of central leptin administration on blood pressure in normotensive rats. Neurosci Lett 1998; 246: 29–32.
Ogawa Y, Masuzaki H, Hosoda K, et al: Increased glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in transgenic skinny mice overexpressing leptin. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1822–1829.
Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, Aizawa-Abe M, et al: Glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in transgenic mice overexpressing leptin with lethal yellow agouti mutation: usefulness of leptin for treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1615–1622.
Aizawa-Abe M, Ogawa Y, Masuzaki H, et al: Pathophysiological role of leptin in obesity-related hypertension. J Clin Invest 2000; 105: 1243–1252.
Kaushik RM, Mahajan SK, Rajesh V, Kaushik R : Stress profile in essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 619–624.
Hall JE, Hildebrandt DA, Kuo J : Obesity hypertension: role of leptin and sympathetic nervous system. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 103S–115S.
Hosoda K, Masuzaki H, Ogawa Y, et al: Development of radioimmunoassay for human leptin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1996; 221: 234–239.
Agata J, Masuda A, Takada M, et al: High plasma immunoreactive leptin level in essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1997; 10: 1171–1174.
Leyva F, Goldsland IF, Ghatei M, et al: Hyperleptinemia as a component of a metabolic syndrome of cardiovascular risk. Thromb Vasc Biol 1998; 18: 928–933.
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, et al: Serum immunoreactive leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med 1996; 334: 292–295.
Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, et al: Leptin levels in humans and rodents: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med 1995; 1: 1155–1161.
Lu H, Duanmu Z, Houck C, Jen KC, Buison A, Dunbar JC : Obesity due to a high fat diet decreases the sympathetic nervous and cardiovascular responses to intracerebroventricular leptin in rats. Brain Res Bull 1998; 47: 331–335.
Correia ML, Haynes WG, Rahmouni K, Morgan DA, Sivitz WI : The concept of selective leptin resistance: evidence from agouti yellow obese mice. Diabetes 2002; 51: 439–442.
Paolisso G, Taglimonte MR, Galderisi M, et al: Plasma leptin is associated with myocardial wall thickness in hypertensive insulin-resistant men. Hypertension 1999; 34: 1047–1052.
Söderberg S, Ahren B, Stegmayr B, et al: Leptin is a risk marker for first-ever hemorrhagic stroke in a population-based cohort. Stroke 1999; 30: 328–337.
Söderberg S, Ahren B, Jansson JH, et al: Leptin is associated with increased risk of myocardial infarction. J Intern Med 1999; 426: 409–418.
Takeuchi H, Saitoh S, Takagi S, et al: Metabolic syndrome and cardiac disease in Japanese men: applicability of the concept of metabolic syndrome defined by the National Cholesterol Education Program–Adult Treatment Panel III to Japanese men—the Tanno and Sobetsu study. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 203–208.
Fujiwara T, Saitoh S, Takagi S, et al: Development and progression of atherosclerotic disease in relation to insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 665–670.
Ishizuka N, Ishizaki Y, Toda E, et al: Hypertension is the most common component of metabolic syndrome and the greatest contributor to carotid arteriosclerosis in apparently healthy Japanese individuals. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 27–34.
Bönner G, Schmieder R, Chrosch R, Weidinger G : Effect of bunazosin and atenolol on glucose metabolism in obese, nondiabetic patients with primary hypertension. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 1997; 11: 21–26.
Suzuki M, Hirose J, Asakura Y, et al: Insulin insensitivity in nonobese, nondiabetic essential hypertension and its improvement by an α1-blocker (bunazosin). Am J Hypertens 1992; 5: 869–874.
Matsuda Y : Basic studies on the effects of the α1-blocker bunazosin for lipid metabolism in rats. Akita J Med 1992; 19: 487–502.
Matsunaga A, Hidaka H, Sasaki J, Arakawa K : Bunazosin enhances receptor-mediated endocytosis of low-density lipoproteins. Artery 1992; 19: 307–317.
Pollare T, Lithell H, Selinus I, Berne C : Application of prazosin is associated with an increase of insulin sensitivity in obese patients with hypertension. Diabetologia 1988; 31: 415–420.
Giorda C, Appendino M : Effects of doxazosin, a selective alpha 1-inhibitor, on plasma insulin and blood glucose response to a glucose tolerance test in essential hypertension. Metabolism 1993; 42: 1440–1442.
Fernandez-Real JM, Gutierrez C, Vendrell J, et al: Polymorphism of the tumor necrosis factor-α receptor 2 gene is associated with obesity, leptin levels, and insulin resistance in young subjects and diet-treated type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2000; 23: 831–837.
Mantzoros CS : The role of leptin in human obesity and disease; a review of current evidence. Ann Intern Med 1999; 130: 671–680.
Zhou YT, Wang ZW, Higa M, Newgard CB, Unger RH : Reversing adipocyte differentiation; implications for treatment of obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999; 96: 2391–2395.
Saladin R, De Vos P, Guerre-Millo M, et al: Transient increase in obese gene expression after food intake or insulin administration. Nature 1995; 377: 527–529.
Boden G, Chen X, Kolaczynski JW, Polansky M : Effects of prolonged hyperinsulinemia on serum leptin in normal human subjects. J Clin Invest 1997; 100: 1107–1113.
Müller G, Ertl J, Gerl M, Preibisch G : Leptin impairs metabolic action of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem 1997; 272: 10585–10593.
Kim-Motoyama H, Yamaguchi T, Katakura T, et al: Serum leptin levels are associated with hyperinsulinemia independent of body mass index, but not with visceral obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997; 239: 340–344.
McGarry JD, Dobbins RL : Fatty acids, lipotoxicity and insulin secretion. Diabetologia 1999; 42: 128–138.
Greco AV, Mingrone G, Vettor R, et al: Lowering of circulating free fatty acid levels and reduced expression of leptin in white adipose tissue in postobesity status. J Invest Med 2002; 50: 207–213.
Heptull R, Smitten A, Teague B, Tamborlane WV, Ma YZ, Caprio S : Temporal patterns of circulating leptin levels in lean and obese adolescents: relationships to insulin, growth hormone, and free fatty acids rhythmicity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 86: 90–96.
Merwe MT, Panz VR, Crowther NJ, et al: Free fatty acids and insulin levels-relationship to leptin levels and body composition in various patient groups from South Africa. Int J Obes 1999; 23: 909–917.
Stefan N, Fritsche A, Häring H, Stumvoll M : Acute stimulation of leptin concentrations in humans during hyperglycemia. Int J Obes 2001; 25: 138–142.
Ueshiba H, Miyachi Y : Effect of doxazosin on insulin resistance in hypertensive patients with obesity. Horm Metab Res 2003; 35: 532–536.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ihara, S., Shimamoto, K., Watanabe, H. et al. An α1-Receptor Blocker Reduces Plasma Leptin Levels in Hypertensive Patients with Obesity and Hyperleptinemia. Hypertens Res 29, 805–811 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.805
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.805