Abstract
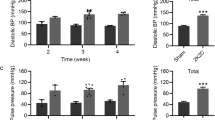
Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are widely used for the treatment of hypertension. It is believed that treatment with an ARB increases the level of plasma angiotensin II (Ang II) because of a lack of negative feedback on renin activity. However, Ichikawa (Hypertens Res 2001; 24: 641–646) reported that long-term treatment of hypertensive patients with olmesartan resulted in a reduction in plasma Ang II level, though the mechanism was not determined. It has been reported that angiotensin 1-7 (Ang-(1-7)) potentiates the effect of bradykinin and acts as an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. It is known that ACE2, which was discovered as a novel ACE-related carboxypeptidase in 2000, hydrolyzes Ang I to Ang-(1-9) and also Ang II to Ang-(1-7). It has recently been reported that olmesartan increases plasma Ang-(1-7) through an increase in ACE2 expression in rats with myocardial infarction. We hypothesized that over-expression of ACE2 may be related to a reduction in Ang II level and the cardioprotective effect of olmesartan. Administration of 0.5 mg/kg/day of olmesartan for 4 weeks to 12-week-old stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRSP) significantly reduced blood pressure and left ventricular weight compared to those in SHRSP given a vehicle. Co-administration of olmesartan and (D-Ala7)−Ang-(1-7), a selective Ang-(1-7) antagonist, partially inhibited the effect of olmesartan on blood pressure and left ventricular weight. Interestingly, co-administration of (D-Ala7)−Ang-(1-7) with olmesartan significantly increased the plasma Ang II level (453.2±113.8 pg/ml) compared to olmesartan alone (144.9±27.0 pg/ml, p<0.05). Moreover, olmesartan significantly increased the cardiac ACE2 expression level compared to that in Wistar Kyoto rats and SHRSP treated with a vehicle. Olmesartan significantly improved cardiovascular remodeling and cardiac nitrite/nitrate content, but co-administration of olmesartan and (D-Ala7)−Ang-(1-7) partially reversed this anti-remodeling effect and the increase in nitrite/nitrate. These findings suggest that olmesartan may exhibit an ACE inhibitory action in addition to an Ang II receptor blocking action, prevent an increase in Ang II level, and protect cardiovascular remodeling through an increase in cardiac nitric oxide production and endogenous Ang-(1-7) via over-expression of ACE2.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Tipnis SR, Hooper NM, Hyde R, Karran E, Christie G, Turner AJ : A human homolog of angiotensin converting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 33238–33243.
Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al: A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme–related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1–9. Circ Res 2000; 87: e1–e9.
Ferrario CM, Chappell MC, Tallant EA, Brosnihan KB, Diz DI : Counterregulatory actions of angiotensin-(1–7). Hypertension 1997; 30: 535–541.
Loot AE, Roks AJ, Henning RH, et al: Angiotenisn-(1–7) attenuates the development of heart failure after myocardial infarction in rats. Circulation 2002; 105: 1548–1550.
Brosnihihan KB, Li P, Ferrario CM : Angiotensin-(1–7) dilates canine coronary arteries through kinins and nitric oxide. Hypertension 1996; 27: 523–528.
Roks AJM, van Geel PP, Pinto YM, et al: Angiotensin-(1–7) is a modulator of the human renin-angiotensin system. Hypertension 1999; 34: 296–301.
Ueda S, Masumori-Maemoto S, Ashino K, et al: Angiotensin-(1–7) attenuates vasoconstriction evoked by angiotensin II but not by noradrenaline in man. Hypertenison 2000; 35: 998–1001.
Gorelik G, Carbini LA, Scicli AG : Angiotensin-(1–7) induces bradykinin-mediated relaxation in porcine coronary artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1998; 286: 403–410.
Deddish PA, Marcic B, Jackman HL, Wang H-Z, Skidgel RA, Erdos EG : N-domain–specific substrate and C-domain inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: angiotenisn-(1–7) and keto-ACE. Hypertension 1998; 31: 912–917.
Minshall RD, Tan F, Nakamura F, et al: Potentiation of the actions of bradykinin by angiotensin B2 recoptors and angiotensin-converting enzyme in CHO cells. Circ Res 1997; 81: 848–856.
Benzing T, Fleming I, Blaukat A, Muller-Esterl W, Busse R : Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ramiprilat interferes with the sequenstration of the B2 kinin receptor within the plasma membrane of native endothelial cells. Circulation 1999; 99: 2034–2040.
Danser AHJ, Tom B, de Vries R, Saxena PR : L-NAME–resistant bradykinin-induced relaxation in porcine coronary arteries is NO-dependent: effect of ACE inhibition. Br J Pharmacol 2000; 131: 195–202.
Ichikawa S, Takayama Y : Long-term effects of olmesartan, an Ang II receptor antagonist, on blood pressure and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 2001; 24: 641–646.
Gavras I, Gavras H, Eprosartan Multinational Study Group: Effects of eprosartan versus enalapril in hypertensive patitents on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone and safety parameters: results from a 26-week, double-blind, multicentre study. Curr Med Res Opin 1999; 15: 15–24.
Grossman E, Peleg E, Carroll J, Shamiss A, Rosenthal T : Hemodynamic and humoral effects of the angiotensin II antagonist losartan in essentioal hypertension. Am J Hypertens 1994; 7: 1041–1044.
Bouer IH, Reams GP, Wu Z, Lau-Sieckman A : Effects of losartan on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis in essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 1995; 9: 237–243.
Ishiyama Y, Gallagher PE, Averill DB, Tallant EA, Brosnihan KB, Ferrario CM : Upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 after myocardial infarction by blockade of angiotensin II receptors. Hypertension 2004; 43: 970–976.
Tom B, de Vries R, Saxena PR, Danser AHJ : Bradykinin potentiation by angiotensin-(1–7) and ACE inhibitors correlates with ACE C- and N-domain blockade. Hypertension 2001; 38: 95–99.
Benter IF, Ferrario CM, Morris M, Diz DI : Antihypertensive actions of angiotensin-(1–7) in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol 1995; 269: H313–H319.
Widdop RE, Sampey DB, Jarrott B : Cardiovascular effects of angiotenisn-(1–7) in conscious spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1999; 34: 964–968.
Kobayashi N, Nishikimi T, Horinaka S, Ishimitsu T, Matsuoka H : Effects of imidapril on NOS expression and myocardial remodeling in failing heart of Dahl-salt sensitive hypertensive rats. Cardiovasc Res 1999; 44: 518–526.
Kobayashi N, Horinaka S, Mita S, et al: Aminoguanidine inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase and improves cardiac performance and cardiovascular remodeling in failing hearts of salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. J Hypertens 2002; 20: 2475–2485.
Turner AJ, Tipnis SR, Guy JL, Rice G, Hooper NM : ACEH/ACE2 is a novel mammalian metallocarboxypeptidase and a monologue of angiotensin-converting enzyme insensitive to ACE inhibitors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2002; 80: 346–353.
Turner AJ, Hooper NM : The angiotensin-converting enzyme gene family: genomics and pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2002; 23: 177–183.
Crackower MA, Sarao R, Oudit GY, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function. Nature 2002; 417: 822–828.
Vickers C, Hales P, Kaushik V, et al: Hydrolysis of biological peptides by human angiotensin-converting enzyme–related carboxypeptidase. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 14838–14843.
Gallagher PE, Chappell MC, Bernish WB, Tallant EA : ACE2 expression in brain: angiotensin II down-regulates ACE2 in astrocytes. Hypertension 2003; 42: 389.
Pool JL, Glazer R, Chiang YT, Gatlin M : Dose-response efficacy of valsartan, a new angiotensin II receptor blocker. J Hum Hypertens 1999; 13: 275–281.
Fogari R, Mugellini A, Zoppi A, et al: Efficacy of losartan, valsartan, and telmisartan in patients with mild to moderate hypertension: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study using ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp 2002; 63: 1–14.
Mendes AC, Ferreira AJ, Pinheiro SV, Santos RA : Chronic infusion of angiotensin-(1–7) reduces heart angiotensin II levels in rats. Regul Pept 2005; 125: 29–34.
Walters PE, Gaspari TA, Widdop RE : Angiotensin-(1–7) acts as a vasodepressor agent via angiotensin II type 2 receptors in conscious rats. Hypertension 2005; 45: 960–966.
Agata J, Chao L, Chao J : Kallikrein gene delivery improves cardiac reserve and attenuates remodeling after myocardial infarction. Hypertension 2002; 40: 653–659.
Santos RA, Simoes e Silva AC, Maric C, et al: Angiotensin-(1–7) is an endogenous ligand for the G protein–coupled receptor Mas. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 2003; 100: 8258–8263.
Taliant EA, Chappell MC, Ferrario CM, Gallagher PE : Inhibition of MAP kinase activity by angiotensin-(1–7) in vascular smooth muscle cells in mediated by the Mas receptor. Hypertension 2004; 43: 1348 ( Abstract).
Strawn WB, Ferrario CM, Tallant EA : Angiotensin-(1–7) reduces smooth muscle growth after vascular injury. Hypertension 1999; 33: 207–211.
Ferreira AJ, Santos RAS, Almeida AP : Angiotensin-(1–7): cardioprotective effect in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Hypertension 2001; 38: 665–668.
Averill DB, Ishiyama Y, Chappell MC, Ferrario CM : Cardiac angiotensin-(1–7) in ischemic cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2003; 108: 2141–2146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agata, J., Ura, N., Yoshida, H. et al. Olmesartan Is an Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker with an Inhibitory Effect on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme. Hypertens Res 29, 865–874 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.865
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.865
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
ACE2 inhibits proliferation of smooth muscle cell through AT1R and its downstream signaling pathway
Journal of Biosciences (2023)
-
A comprehensive evaluation of early potential risk factors for disease aggravation in patients with COVID-19
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Shotgun transcriptome, spatial omics, and isothermal profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals unique host responses, viral diversification, and drug interactions
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Angiotensin-[1–7] attenuates kidney injury in experimental Alport syndrome
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Olmesartan medoxomil/amlodipine/hydrochlorothiazide 20 mg/5 mg/12.5 mg fixed-dose combination in hypertension: a profile of its use
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives (2018)