Abstract
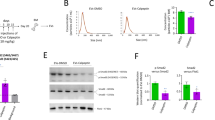
Hemopoietic cells or bone marrow–derived cells contribute to tissue formation, possibly by transdifferentiation into smooth muscle cells (SMCs) or myofibroblasts. In this study our goal is to examine the effects of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) on the transdifferentiation of the monocyte/macrophage lineage into SMC-like cells. Using rat peritoneal exudate macrophages, we investigated the expression of smooth muscle–specific differentiation markers, such as α-smooth muscle actin, embryonic smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, and calponin. The treatment of macrophages with TGF-β1 enhanced the expression of SMC-specific markers at day 4; after 7 days in culture, a higher level of expression (approximately 3- to 5-fold) was detected on Western blots. In contrast, TGF-β1 decreased the expression of CD11b, which is a macrophage marker. Furthermore, we examined the effect of the TGF-β type 1 receptor inhibitor SB-431542 and a replication-defective adenovirus construct expressing Smad7 (Adeno-Smad7), which inhibits TGF-β signaling by interfering with the activation of other Smad proteins. Both SB-431542 and Adeno-Smad7 suppressed the expression of SMC-specific markers. These results indicated that TGF-β signaling is essential for the transdifferentiation of macrophages into SMC-like cells. Elucidating the mechanism by which macrophages transdifferentiate into SMC-like cells may reveal new therapeutic targets for preventing vascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Ross R : Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. New Engl J Med 1999; 340: 115–126.
Libby P : Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002; 420: 868–874.
Yasunari K, Maeda K, Nakamura M, Watanabe T, Yoshikawa J : Benidipine, a long-acting calcium channel blocker, inhibits oxidative stress in polymorphonuclear cells in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 107–112.
Campbell JH, Efendy JL, Han C, Girjes AA, Campbell GR : Haemopoietic origin of myofibroblasts formed in the peritoneal cavity in response to a foreign body. J Vasc Res 2000; 37: 364–371.
Han CI, Campbell GR, Campbell JH : Circulating bone marrow cells can contribute to neointimal formation. J Vasc Res 2001; 38: 113–119.
Hoenig MR, Campbell GR, Rolfe BE, Campbell JH : Tissue-engineered blood vessels: alternative to autologous grafts? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 1128–1134.
Jabs A, Moncada GA, Nichols CE, Waller EK, Wilcox JN : Peripheral blood mononuclear cells acquire myofibroblast characteristics in granulation tissue. J Vasc Res 2005; 42: 174–180.
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, et al: Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 1997; 275: 964–967.
Sata M, Saiura A, Kunisato A, et al: Hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into vascular cells that participate in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Nat Med 2002; 8: 403–409.
Yeh ET, Zhang S, Wu HD, Korbling M, Willerson JT, Estrov Z : Transdifferentiation of human peripheral blood CD34+-enriched cell population into cardiomyocytes, endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells in vivo. Circulation 2003; 108: 2070–2073.
Imanishi T, Hano T, Nishio I : Angiotensin II potentiates vascular endothelial growth factor–induced proliferation and network formation of endothelial progenitor cells. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 101–108.
Lijnen PJ, Petrov VV, Fagard RH : Association between transforming growth factor-β and hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2003; 16: 604–611.
Joki N, Kaname S, Hirakata M, et al: Tyrosine-kinase dependent TGF-β and extracellular matrix expression by mechanical stretch in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertens Res 2000; 23: 91–99.
Diamond JA, Phillips RA : Hypertensive heart disease. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 191–202.
Massague J : TGF-β signal transduction. Annu Rev Biochem 1998; 67: 753–791.
Massague J, Weis-Garcia F : Serine/threonine kinase receptors: mediators of transforming growth factor beta family signals. Cancer Surv 1996; 27: 41–64.
Kobayashi N, Nakano S, Mori Y, et al: Benidipine inhibits expression of ET-1 and TGF-β1 in Dahl salt-sensitive hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 2001; 24: 241–250.
Tahira Y, Fukuda N, Endo M, et al: Transforming growth factor-β expression in cardiovascular organs in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats with the development of hypertension. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 911–918.
Saito K, Ishizaka N, Aizawa T, et al: Role of aberrant iron homeostasis in the upregulation of transforming growth factor-β1 in the kidney of angiotensin II–induced hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 599–607.
Yamashita H, ten Dijke P, Franzen P, Miyazono K, Heldin CH : Formation of hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II receptors for transforming growth factor-β. J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 20172–20178.
Nakao A, Imamura T, Souchelnytskyi S, et al: TGF-β receptor–mediated signalling through Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4. EMBO J 1997; 16: 5353–5362.
Heldin CH, Miyazono K, ten Dijke P : TGF-β signalling from cell membrane to nucleus through SMAD proteins. Nature 1997; 390: 465–471.
Imamura T, Takase M, Nishihara A, et al: Smad6 inhibits signalling by the TGF-β superfamily. Nature 1997; 389: 622–626.
Nakao A, Afrakhte M, Moren A, et al: Identification of Smad7, a TGF β−inducible antagonist of TGF-β signalling. Nature 1997; 389: 631–635.
Chen HB, Rud JG, Lin K, Xu L : Nuclear targeting of transforming growth factor-β−activated Smad complexes. J Biol Chem 2005; 280: 21329–21336.
Fujii M, Takeda K, Imamura T, et al: Roles of bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors and Smad proteins in osteoblast and chondroblast differentiation. Mol Biol Cell 1999; 10: 3801–3813.
Takahashi A, Kureishi Y, Yang J, et al: Myogenic Akt signaling regulates blood vessel recruitment during myofiber growth. Mol Cell Biol 2002; 22: 4803–4814.
Laping NJ, Grygielko E, Mathur A, et al: Inhibition of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1−induced extracellular matrix with a novel inhibitor of the TGF-β type I receptor kinase activity: SB-431542. Mol Pharmacol 2002; 62: 58–64.
Inman GJ, Nicolas FJ, Callahan JF, et al: SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β superfamily type I activin receptor–like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol Pharmacol 2002; 62: 65–74.
Watabe T, Nishihara A, Mishima K, et al: TGF-β receptor kinase inhibitor enhances growth and integrity of embryonic stem cell–derived endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 2003; 163: 1303–1311.
Mattey DL, Dawes PT, Nixon NB, Slater H : Transforming growth factor β1 and interleukin 4 induced alpha smooth muscle actin expression and myofibroblast-like differentiation in human synovial fibroblasts in vitro: modulation by basic fibroblast growth factor. Ann Rheum Dis 1997; 56: 426–431.
Evans RA, Tian YC, Steadman R, Phillips AO : TGF-β1−mediated fibroblast-myofibroblast terminal differentiation—the role of Smad proteins. Exp Cell Res 2003; 282: 90–100.
Sappino AP, Schurch W, Gabbiani G : Differentiation repertoire of fibroblastic cells: expression of cytoskeletal proteins as marker of phenotypic modulations. Lab Invest 1990; 63: 144–161.
Derynck R, Zhang YE : Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-β family signalling. Nature 2003; 425: 577–584.
Sato M, Kawai-Kowase K, Sato H, et al: c-Src and hydrogen peroxide mediate transforming growth factor-β1−induced smooth muscle cell–gene expression in 10T1/2 cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 341–347.
Mallawaarachchi CM, Weissberg PL, Siow RC : Smad7 gene transfer attenuates adventitial cell migration and vascular remodeling after balloon injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: 1383–1387.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ninomiya, K., Takahashi, A., Fujioka, Y. et al. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Enhances Transdifferentiation of Macrophages into Smooth Muscle–Like Cells. Hypertens Res 29, 269–276 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.269
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.269
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Disease-Relevant Single Cell Photonic Signatures Identify S100β Stem Cells and their Myogenic Progeny in Vascular Lesions
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2021)
-
The significance of macrophage phenotype in cancer and biomaterials
Clinical and Translational Medicine (2014)
-
Extracellular matrix and the mechanics of large artery development
Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology (2012)
-
Monocyte polarization: the relationship of genome-wide changes in H4 acetylation with polarization
Genes & Immunity (2011)
-
Coexpression of myofibroblast and macrophage markers: novel evidence for an in vivo plasticity of chorioamniotic mesodermal cells of the human placenta
Laboratory Investigation (2008)