Abstract
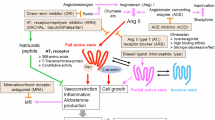
Gitelman's syndrome (GS) is a variant of Bartter's syndrome (BS) characterized by hypokalemic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, hypocalciuria and secondary aldosteronism without hypertension. A 31-year old Japanese man who had suffered from mild hypokalemia for 10 years was admitted to our hospital. He had metabolic alkalosis, hypokalemia and hypocalciuria. Since he had two missense mutations (R261C and L623P) in the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (TSC) gene (SLC12A3), he was diagnosed as having GS. He showed hyperreninism and a high angiotensin I (Ang I) level, whereas his angiotensin II (Ang II) and aldosterone levels were not elevated. His angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) activities were normal, and administration of captopril inhibited the production of Ang II and aldosterone. We evaluated the Ang II–forming activity (AIIFA) of other enzymes in his lymphocytes. Interestingly, chymase-dependent AIIFA was not detected in the lymphocytes. Together, these results suggest that the lack of chymase activity resulted in the manifestation of GS without hyperaldosteronism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Gitelman HJ, Graham JB, Walt LG : A new familial disorder characterized by hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 1966; 79: 221–233.
Cruz DN, Shaer AJ, Bia MJ, Lifton RP, Simon DB : Gitelman's syndrome revisited: an evaluation of symptoms and health-related quality of life. Kidney Int 2001; 59: 710–717.
Bettineli A, Bianchetti MG, Girardin E, et al: Use of calcium excretion values to distinguish two forms of primar renal tubular hypokalemic alkarosis: Bartter and Gitelman syndrome. J Pediatr 1991; 120: 38–43.
Bhandari S, Turney JH : The molecular basis of hypokalemic alkalosis: Bartter's and Gitelman's syndrome. Nephron 1998; 80: 373–379.
Takeuchi K, Kure S, Kato T, et al: Association of a mutation in thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter with familial gitelman's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1996; 81: 4496–4499.
Simon DB, Nelson-Williams C, Bia MJ, et al: Gitelman's variant of Bartter syndrome, inherited hypokalemic alkarosis is caused by mutations in the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter. Nat Genet 1996; 12: 24–30.
Mastroianni N, Bettineli A, Bianchetti M, et al: Novel molecular variants of the Na-Cl cotransporter gene are responsible for Gitelman syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 1996; 59: 1019–1026.
Lemmink HH, Knoers NAVM, Karolyi L, et al: Novel mutations in the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter gene in patients with Gitelman syndrome with predominant localization to the C-terminal domain. Kidney Int 1998; 54: 720–730.
Monkawa T, Kurihara I, Kobayashi K, Hayashi M, Saruta T : Novel mutations in thiazide sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter gene of Gitelman's syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 2000; 11: 65–70.
Yahata K, Tanaka I, Kotani M, et al: Identification of a novel R642C mutation in Na-Cl cotransporter with Gitelman's syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 1999; 34: 845–853.
Boyum A : Separation of white blood cells. Nature 1964; 32: 793–794.
Ferrante A, Thong TH : Optimal conditions for simultaneous purification of mononuclear and polymorphonuclear leucocytes from human blood by the Hypaque-Ficoll method. J Immunol Methods 1980; 36: 109–117.
Akasu M, Urata H, Kinoshita A, Sasaguri M, Ideishi M, Arakawa K : Differences in tissue angiotensin II–forming pathways by species and organs in vitro. Hypertension 1998; 32: 514–520.
Tago N, Kokubo Y, Inamoto N, Naraba H, Tomoike H, Iwai N : A high prevalence of Gitelman's syndrome mutations in Japanese. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 327–331.
Naraba H, Kokubo Y, Tomoike H, Iwai N : Functional confirmation of Gitelman's syndrome mutations in Japanese. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 805–809.
Yamashiki J, Terui K, Hirai Y, et al: Genetic analysis of a case of Gitelman syndrome. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 2002; 91: 3503–3506 ( in Japanese).
Gibbs CJ, Millaer JGB : Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone and kallikrein investigations in a patient with resistant hypomagnesaemia due to Gitelman's syndrome. Ann Clin Biochem 1995; 32: 426–430.
Belova LA : Angiotensin II–generating enzymes. Biochemistry 2000; 65: 1337–1345.
Urata H, Kinoshita A, Misono KS, Bumpus FM, Husain A : Identification of a highly specific chymase as the major angiotensin II forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol Chem 1990; 265: 22348–22357.
Ono K, Kokubo Y, Mannami T, Inamoto N, Shioji K, Iwai N : Heterozygous disruption of CMA1 does not affect blood pressure. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 103–109.
Bergstein JM, Weinberger MH : Hypokalemia, normal blood pressure, and hyperreninemia with hypoaldosteronism. J Pediatr 1981; 99: 561–564.
Umeki S, Ohga R, Ono S, Yasuda T, Moriomto K, Terao A : Angiotensin I level and sporadic hypokalemic periodic paralysis. Arch Intern Med 1986; 146: 1956–1960.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eto, K., Onaka, U., Tsuchihashi, T. et al. A Case of Gitelman's Syndrome with Decreased Angiotensin II–Forming Activity. Hypertens Res 29, 545–549 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.545
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.29.545
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Gitelman syndrome with normocalciuria – a case report
BMC Nephrology (2022)