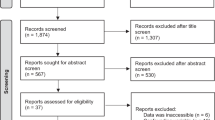
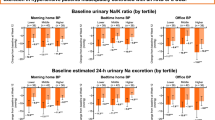
Abstract
Both strict blood pressure control and efferent artery dilatation are critical in reducing proteinuria, which in turn helps to regulate blood pressure. Benidipine, an L- and T-type calcium channel blocker, has the potential for increased effectiveness compared with L-type–dominant calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine. Therefore, we evaluated blood pressure and proteinuria after changeover from amlodipine to benidipine in poorly controlled hypertensive patients. Fifty-eight hypertensive outpatients undergoing amlodipine treatment and unable to achieve optimal blood pressure as determined by Japanese Society of Hypertension Guidelines for the Management of Hypertention (JSH 2004) were changed over to benidipine treatment. We measured blood pressure and pulse rate and assessed urinary protein excretion before and after changeover. Systolic and diastolic blood pressure dropped from 151/90 mmHg to 140/81 mmHg (p<0.0001). Mean blood pressure (p<0.0001) and pulse pressure (p=0.0069) were also reduced, but pulse rate increased from 75 bpm to 78 bpm (p=0.0047). Urinary protein excretion adjusted for urinary creatinine was reduced from 0.35±0.82 to 0.22±0.55 g/g creatinine (p=0.0119). The urinary protein reduction was observed only in patients with renin-angiotensin inhibition (p=0.0216). By switching from amlodipine to benidipine treatment, more than 80% of patients reduced their blood pressure, and more than 40% achieved optimal blood pressure. Higher urinary protein excretion (p<0.0001), lower glomerular filtration rate (p=0.0011) and presence of diabetes (p=0.0284) were correlated with reduction of urinary proteins during changeover. Taken together, our results suggest that benidipine may have greater efficacy than amlodipine in reducing blood pressure and proteinuria.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Peralta CA, Kurella M, Lo JC, Chertow GM : The metabolic syndrome and chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2006; 15: 361–365.
Segura J, Campo C, Gil P, et al: Development of chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular prognosis in essential hypertensive patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 1616–1622.
Nakamura K, Okamura T, Hayakawa T, et al: Chronic kidney disease is a risk factor for cardiovascular death in a community-based population in Japan: NIPPON DATA90. Circ J 2006; 70: 954–959.
De Leeuw PW, Thijs L, Birkenhager WH, et al: Prognostic significance of renal function in elderly patients with isolated systolic hypertension: results from the Syst-Eur trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 2002; 13: 2213–2222.
Marin R, Gorostidi M, Fernandez-Vega F, Alvarez-Navascues R : Systemic and glomerular hypertension and progression of chronic renal disease: the dilemma of nephrosclerosis. Kidney Int Suppl 2005; 99: S52–S56.
Wang T, Takabatake T : Effects of vasopeptidase inhibition on renal function and tubuloglomerular feedback in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 611–618.
Hayashi K, Wakino S, Homma K, Sugano N, Saruta T : Pathophysiological significance of T-type Ca2+ channels: role of T-type Ca2+ channels in renal microcirculation. J Pharmacol Sci 2005; 99: 221–227.
Caldicott WJ, Taub KJ, Margulies SS, Hollenberg NK : Angiotensin receptors in glomeruli differ from those in renal arterioles. Kidney Int 1981; 19: 687–693.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, et al: Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 861–869.
Ruggenenti P, Perna A, Loriga G, et al: Blood-pressure control for renoprotection in patients with non-diabetic chronic renal disease (REIN-2): multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2005; 365: 939–946.
Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic : the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA 2002; 288: 2981–2997.
Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Weber M, et al: Outcomes in hypertensive patients at high cardiovascular risk treated with regimens based on valsartan or amlodipine: the VALUE randomised trial. Lancet 2004; 363: 2022–2031.
Furukawa T, Yamakawa T, Midera T, et al: Selectivities of dihydropyridine derivatives in blocking Ca2+ channel subtypes expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1999; 291: 464–473.
Hayashi K, Nagahama T, Oka K, Epstein M, Saruta T : Disparate effects of calcium antagonists on renal microcirculation. Hypertens Res 1996; 19: 31–36.
Morikawa T, Okumura M, Konishi Y, Okada N, Imanishi M : Effects of benidipine on glomerular hemodynamics and proteinuria in patients with nondiabetic nephropathy. Hypertens Res 2002; 25: 571–576.
Kita T, Suzuki Y, Eto T, Kitamura K : Long-term anti-hypertensive therapy with benidipine improves arterial stiffness over blood pressure lowering. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 959–964.
Makino H, Aoki M, Hashiya N, et al: A calcium-channel blocker, benidipine, improves forearm reactive hyperemia in patients with essential hypertension. Blood Press Suppl 2005; 1: 39–44.
Sanada H, Midorikawa S, Yatabe J, et al: Elevation of serum soluble E- and P-selectin in patients with hypertension is reversed by benidipine, a long-acting calcium channel blocker. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 871–878.
Hoshide S, Kario K, Ishikawa J, Eguchi K, Shimada K : Comparison of the effects of cilnidipine and amlodipine on ambulatory blood pressure. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 1003–1008.
Iino Y, Hayashi M, Kawamura T, et al: Renoprotective effect of losartan in comparison to amlodipine in patients with chronic kidney disease and hypertension—a report of the Japanese Losartan Therapy Intended for the Global Renal Protection in Hypertensive Patients (JLIGHT) study. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 21–30.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, et al: The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003; 289: 2560–2572.
2003 European Society of Hypertension–European Society of Cardiology guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 1011–1053.
Peterson JC, Adler S, Burkart JM, et al: Blood pressure control, proteinuria, and the progression of renal disease. The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study. Ann Intern Med 1995; 123: 754–762.
Yao K, Sato H, Sonoda R, et al: Effects of benidipine and candesartan on kidney and vascular function in hypertensive Dahl rats. Hypertens Res 2003; 26: 569–576.
Yao K, Sato H, Ina Y, et al: Renoprotective effects of benidipine in combination with angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker in hypertensive Dahl rats. Hypertens Res 2003; 26: 635–641.
Poulter NR, Wedel H, Dahlof B, et al: Role of blood pressure and other variables in the differential cardiovascular event rates noted in the Anglo-Scandinavian Cardiac Outcomes Trial—Blood Pressure Lowering Arm (ASCOT-BPLA). Lancet 2005; 366: 907–913.
Ogihara T, Matsuzaki M, Matsuoka H, et al: The combination therapy of hypertension to prevent cardiovascular events (COPE) trial: rationale and design. Hypertens Res 2005; 28: 331–338.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohishi, M., Takagi, T., Ito, N. et al. Renal-Protective Effect of T-and L-Type Calcium Channel Blockers in Hypertensive Patients: An Amlodipine-to-Benidipine Changeover (ABC) Study. Hypertens Res 30, 797–806 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.797
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.797
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Calcium channel blocker in patients with chronic kidney disease
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology (2022)
-
Ion-Channel modulator TH1177 reduces glomerular injury and serum creatinine in chronic mesangial proliferative disease in rats
BMC Nephrology (2020)
-
Amlodipine Compared with Benidipine in the Management of Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention (2020)
-
Pharmacokinetics, Safety and Tolerability of Tylerdipine Hydrochloride, a Novel Dihydropyridine Dual L/T-type Calcium Channel Blocker, after Single and Multiple Oral Doses in Healthy Chinese Subjects
Clinical Drug Investigation (2019)
-
Blood pressure management in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hypertension Research (2017)