Abstract
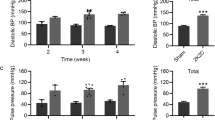
Arterial function after long-term hypertension is characterized by remodeling, endothelial dysfunction and reduction of previously enhanced contractile responses. We investigated whether transient prehypertensive renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) blockade modifies long-term arterial function. Wistar Kyoto rats (WKY) (i) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) (ii) were prehypertensively (week 4–8) treated with losartan (iii) or spironolactone (iv) (20 and 0.5 mg/kg/day, respectively) and investigated at 8 and 72 weeks of age. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was measured intra-arterially. In isolated mesenteric arteries, active wall stress (AWS), relaxation in response to acetylcholine and wall-to-lumen ratio (W/L) were assessed. Western blotting and immunofluorescent staining of whole-mount arterial preparations and two photon laser scanning microscopy (TPLSM) were performed to quantify endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and analyze its intracellular distribution. In 8-week-old SHR treatments were found to have reduced SBP. Relaxation, contractile responses and vascular morphology remained unaffected irrespective of treatment. At 72 weeks, SBP was similar in all SHR groups ((i) 129±6, (ii) 222±10, (iii) 210±16, (iv) 214±9 mmHg). Relaxation and maximum AWS were enhanced after treatments. W/L demonstrated hypertrophy ((i) 0.10±0.01, (ii) 0.16±0.02, (iii) 0.15±0.01, (iv) 0.17±0.01). Untreated SHR (p<0.01), SHR treated with losartan and SHR treated with spironolactone (p<0.05) showed less eNOS as compared to WKY. In treated SHR eNOS was concentrated in a perinuclear endothelial cell compartment. In conclusion, these findings demonstrate that transient prehypertensive blockade results in a long-lasting and blood pressure independent improvement of arterial contractility and endothelium-dependent vasodilatation that persists in aging SHR. This might be associated with an intracellular redistribution of eNOS in the endothelial cell layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Harrap SB, Van der Merwe WM, Griffin SA, Macpherson F, Lever AF : Brief angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor treatment in young spontaneously hypertensive rats reduces blood pressure long-term. Hypertension 1990; 16: 603–614.
Berecek KH, Nagahama S, Oparil S : Effect of central administration of MK-422 (the diacid form of enalapril) on the development of hypertension in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Hypertens Suppl 1984; 2: S63–S66.
Regan CP, Bishop SP, Berecek KH : Early, short-term treatment with captopril permanently attenuates cardiovascular changes in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Clin Exp Hypertens 1997; 19: 1161–1177.
Bergstrom G, Johansson I, Wickman A, Gan L, Thorup C : Brief losartan treatment in young spontaneously hypertensive rats abates long-term blood pressure elevation by effects on renal vascular structure. J Hypertens 2002; 20: 1413–1421.
Nakaya H, Sasamura H, Hayashi M, Saruta T : Temporary treatment of prepubescent rats with angiotensin inhibitors suppresses the development of hypertensive nephrosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2001; 12: 659–666.
Folkow B : Physiological aspects of primary hypertension. Physiol Rev 1982; 62: 347–504.
Weber KT, Brilla CG : Pathological hypertrophy and cardiac interstitium. Fibrosis and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Circulation 1991; 83: 1849–1865.
Neves MF, Virdis A, Schiffrin EL : Resistance artery mechanics and composition in angiotensin II–infused rats: effects of aldosterone antagonism. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 189–198.
Virdis A, Neves MF, Amiri F, Viel E, Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL : Spironolactone improves angiotensin-induced vascular changes and oxidative stress. Hypertension 2002; 40: 504–510.
Morton JJ, Beattie EC, MacPherson F : Angiotensin II receptor antagonist losartan has persistent effects on blood pressure in the young spontaneously hypertensive rat: lack of relation to vascular structure. J Vasc Res 1992; 29: 264–269.
Rizzoni D, Porteri E, Piccoli A, et al: Effects of losartan and enalapril on small artery structure in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1998; 32: 305–310.
Brilla CG, Janicki JS, Weber KT : Cardioreparative effects of lisinopril in rats with genetic hypertension and left ventricular hypertrophy. Circulation 1991; 83: 1771–1779.
Skov K, Fenger-Gron J, Mulvany MJ : Effects of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, a calcium antagonist, and an endothelin receptor antagonist on renal afferent arteriolar structure. Hypertension 1996; 28: 464–471.
van Zandvoort M, Engels W, Douma K, et al: Two-photon microscopy for imaging of the (atherosclerotic) vascular wall: a proof of concept study. J Vasc Res 2004; 41: 54–63.
Endemann D, Touyz RM, Li JS, Deng LY, Schiffrin EL : Altered angiotensin II–induced small artery contraction during the development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 1999; 12: 716–723.
Touyz RM, Endemann D, He G, Li JS, Schiffrin EL : Role of AT2 receptors in angiotensin II–stimulated contraction of small mesenteric arteries in young SHR. Hypertension 1999; 33 ( 1 Pt 2): 366–372.
Baumann M, Smits JFM, Struijker Boudier HAJ : Long-term echocardiographic follow up of brief and early losartan treated SHR reveals sustained cardiac protection. Hypertension 2005; 46: 892 ( Abstract).
Demirci B, McKeown PP, Bayraktutan U : Blockade of angiotensin II provides additional benefits in hypertension- and ageing-related cardiac and vascular dysfunctions beyond its blood pressure–lowering effects. J Hypertens 2005; 23: 2219–2227.
Gillies LK, Lu M, Wang H, Lee RM : AT1 receptor antagonist treatment caused persistent arterial functional changes in young spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1997; 30: 1471–1478.
Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL : Increased generation of superoxide by angiotensin II in smooth muscle cells from resistance arteries of hypertensive patients: role of phospholipase D–dependent NAD(P)H oxidase–sensitive pathways. J Hypertens 2001; 19: 1245–1254.
Rajagopalan S, Kurz S, Munzel T, et al: Angiotensin II–mediated hypertension in the rat increases vascular superoxide production via membrane NADH/NADPH oxidase activation. Contribution to alterations of vasomotor tone. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 1916–1923.
Landmesser U, Dikalov S, Price SR, et al: Oxidation of tetrahydrobiopterin leads to uncoupling of endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase in hypertension. J Clin Invest 2003; 111: 1201–1209.
Wilcox CS : Oxidative stress and nitric oxide deficiency in the kidney: a critical link to hypertension? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2005; 289: R913–R935.
Sanz-Rosa D, Cediel E, de las Heras N, et al: Participation of aldosterone in the vascular inflammatory response of spontaneously hypertensive rats: role of the NFkappaB/IkappaB system. J Hypertens 2005; 23: 1167–1172.
Sanz-Rosa D, Oubina MP, Cediel E, et al: Eplerenone reduces oxidative stress and enhances eNOS in SHR: vascular functional and structural consequences. Antioxid Redox Signal 2005; 7: 1294–1301.
Cosentino F, Savoia C, De Paolis P, et al: Angiotensin II type 2 receptors contribute to vascular responses in spontaneously hypertensive rats treated with angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Am J Hypertens 2005; 18 ( 4 Pt 1): 493–499.
Kanematsu Y, Tsuchiya K, Ohnishi H, et al: Effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade on the systemic blood nitric oxide dynamics in Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester–treated rats. Hypertens Res 2006; 29: 369–374.
Mori Y, Ohyanagi M, Koida S, Ueda A, Ishiko K, Iwasaki T : Effects of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and nitric oxide on endothelial function in femoral resistance arteries of spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertens Res 2006; 29: 187–195.
Mensah GA, Ryan US, Hooper WC, et al: Vascular endothelium summary statement II: Cardiovascular disease prevention and control. Vascul Pharmacol 2007; 46: 318–320.
Cheng C, van Haperen R, de Waard M, et al: Shear stress affects the intracellular distribution of eNOS: direct demonstration by a novel in vivo technique. Blood 2005; 106: 3691–3698.
Zhang Q, Church JE, Jagnandan D, Catravas JD, Sessa WC, Fulton D : Functional relevance of Golgi- and plasma membrane–localized endothelial NO synthase in reconstituted endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: 1015–1021.
Forstermann U, Munzel T : Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace. Circulation 2006; 113: 1708–1714.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumann, M., Megens, R., Bartholome, R. et al. Prehypertensive Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockade in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Ameliorates the Loss of Long-Term Vascular Function. Hypertens Res 30, 853–861 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.853
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.853
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Renal inflammatory markers during the onset of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Hypertension Research (2014)
-
Mineralocorticoid Receptors in Vascular Disease: Connecting Molecular Pathways to Clinical Implications
Current Atherosclerosis Reports (2013)
-
Smooth muscle cell mineralocorticoid receptors: role in vascular function and contribution to cardiovascular disease
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2013)
-
Temporary Treatment With AT1 Receptor Blocker, Valsartan, From Early Stage of Hypertension Prevented Vascular Remodeling
American Journal of Hypertension (2011)