Abstract
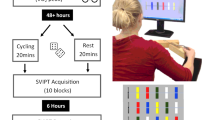
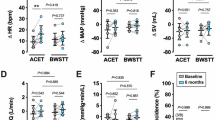
High physical activity or aerobic exercise training increases central arterial distensibility in older humans. However, the effect of a single bout of exercise on central arterial distensibility in older humans is unknown. Furthermore, the effect of exercise training on central arterial distensibility during exercise is unclear. We investigated whether systemic arterial compliance (SAC) changes after acute exercise in older humans, and, if so, whether this change in SAC is enhanced by aerobic exercise training. Seven untrained older women (61–69 years old) participated in a 6-month exercise intervention study. We measured SAC after acute exercise (cycling exercise at 80% of their individual ventilatory threshold for 30 min) before and after 6 months of aerobic exercise training. After exercise training, the individual ventilatory threshold was significantly increased. In addition, both the SAC at rest and that 30 min after acute exercise were significantly increased after the exercise training program. Before exercise training, there was no significant increase in SAC after acute exercise, whereas, after exercise training, the SAC was significantly increased 30 min after acute exercise. The present study suggests that, after aerobic exercise training, SAC increases after acute exercise in older humans, and that the SAC at rest and after acute exercise is enhanced by aerobic exercise training, thereby causing an effective adaptation in increase in cardiac output during exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
Avolio AP, Deng FQ, Li WQ, et al: Effects of aging on arterial distensibility in populations with high and low prevalence of hypertension: comparison between urban and rural communities in China. Circulation 1985; 71: 202–210.
Vaitkevicius PV, Fleg JL, Engel JH, et al: Effects of age and aerobic capacity on arterial stiffness in healthy adults. Circulation 1993; 88: 1456–1462.
Boreham CA, Ferreira I, Twisk JW, Gallagher AM, Savage MJ, Murray LJ : Cardiorespiratory fitness, physical activity, and arterial stiffness: the Northern Ireland Young Hearts Project. Hypertension 2004; 44: 721–726.
Iemitsu M, Maeda S, Otsuki T, et al: Polymorphism in endothelin-related genes limits exercise-induced decreases in arterial stiffness in older subjects. Hypertension 2006; 47: 928–936.
Kakiyama T, Matsuda M, Koseki S : Effect of physical activity on the distensibility of the aortic wall in healthy males. Angiology 1998; 49: 749–757.
Kingwell BA, Cameron JD, Gillies KJ, Jennings GL, Dart AM : Arterial compliance may influence baroreflex function in athletes and hypertensives. Am J Physiol 1995; 268: H411–H418.
Mohiaddin RH, Underwood SR, Bogren HG, et al: Regional aortic compliance studied by magnetic resonance imaging: the effects of age, training, and coronary artery disease. Br Heart J 1989; 62: 90–96.
Otsuki T, Maeda S, Iemitsu M, et al: Vascular endothelium-derived factors and arterial stiffness in strength-and endurance-trained men. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2007; 292: H786–H791.
Tanaka H, DeSouza CA, Seals DR : Absence of age-related increase in central arterial stiffness in physically active women. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1998; 18: 127–132.
Cameron JD, Dart AM : Exercise training increases total systemic arterial compliance in humans. Am J Physiol 1994; 266: H693–H701.
Kakiyama T, Sugawara J, Murakami H, Maeda S, Kuno S, Matsuda M : Effects of short-term endurance training on aortic distensibility in young males. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2005; 37: 267–271.
Sugawara J, Otsuki T, Tanabe T, Hayashi K, Maeda S, Matsuda M : Physical activity duration, intensity, and arterial stiffening in postmenopausal women. Am J Hypertens 2006; 19: 1032–1036.
Tanaka H, Dinenno FA, Monahan KD, Clevenger CM, DeSouza CA, Seals DR : Aging, habitual exercise, and dynamic arterial compliance. Circulation 2000; 102: 1270–1275.
Kingwell BA, Berry KL, Cameron JD, Jennings GL, Dart AM : Arterial compliance increases after moderate-intensity cycling. Am J Physiol 1997; 273: H2186–H2191.
Beaver WL, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ : A new method for detecting anaerobic threshold by gas exchange. J Appl Physiol 1986; 60: 2020–2027.
Davis JA, Frank MH, Whipp BJ, Wasserman K : Anaerobic threshold alterations caused by endurance training in middle-aged men. J Appl Physiol 1979; 46: 1039–1046.
Maeda S, Miyauchi T, Goto K, Matsuda M : Alteration of plasma endothelin-1 by exercise at intensities lower and higher than ventilatory threshold. J Appl Physiol 1994; 77: 1399–1402.
Orr GW, Green HJ, Hughson RL, Bennett GW : A computer linear regression model to determine ventilatory anaerobic threshold. J Appl Physiol 1982; 52: 1349–1352.
Liu Z, Brin KP, Yin FC : Estimation of total arterial compliance: an improved method and evaluation of current methods. Am J Physiol 1986; 251: H588–H600.
Bos WJ, van Goudoever J, van Montfrans GA, van den Meiracker AH, Wesseling KH : Reconstruction of brachial artery pressure from noninvasive finger pressure measurements. Circulation 1996; 94: 1870–1875.
Gizdulich P, Prentza A, Wesseling KH : Models of brachial to finger pulse wave distortion and pressure decrement. Cardiovasc Res 1997; 33: 698–705.
Otsuki T, Maeda S, Kesen Y, et al: Age-related reduction of systemic arterial compliance induces excessive myocardial oxygen consumption during sub-maximal exercise. Hypertens Res 2006; 29: 65–73.
Otsuki T, Maeda S, Sugawara J, et al: Age-related reduction of systemic arterial compliance relates to decreased aerobic capacity during sub-maximal exercise. Hypertens Res 2006; 29: 759–765.
Sugawara J, Tanabe T, Miyachi M, et al: Non-invasive assessment of cardiac output during exercise in healthy young humans: comparison between Modelflow method and Doppler echocardiography method. Acta Physiol Scand 2003; 179: 361–366.
Wesseling KH, Jansen JR, Settels JJ, Schreuder JJ : Computation of aortic flow from pressure in humans using a nonlinear, three-element model. J Appl Physiol 1993; 74: 2566–2573.
Elzinga G, Westerhof N : Pressure and flow generated by the left ventricle against different impedances. Circ Res 1973; 32: 178–186.
Sugawara J, Otsuki T, Tanabe T, et al: The effects of low-intensity single-leg exercise on regional arterial stiffness. Jpn J Physiol 2003; 53: 239–241.
Seals DR : Habitual exercise and the age-associated decline in large artery compliance. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2003; 31: 68–72.
Tanaka H, Safar ME : Influence of lifestyle modification on arterial stiffness and wave reflections. Am J Hypertens 2005; 18: 137–144.
Maeda S, Tanabe T, Otsuki T, et al: Moderate regular exercise increases basal production of nitric oxide in elderly women. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 947–953.
Maeda S, Tanabe T, Miyauchi T, et al: Aerobic exercise training reduces plasma endothelin-1 concentration in older women. J Appl Physiol 2003; 95: 336–341.
Tanabe T, Maeda S, Miyauchi T, et al: Exercise training improves ageing-induced decrease in eNOS expression of the aorta. Acta Physiol Scand 2003; 178: 3–10.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeda, S., Tanabe, T., Otsuki, T. et al. Acute Exercise Increases Systemic Arterial Compliance after 6-Month Exercise Training in Older Women. Hypertens Res 31, 377–381 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.31.377
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.31.377
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vascular adaptations to hypobaric hypoxic training in postmenopausal women
The Journal of Physiological Sciences (2011)