Abstract
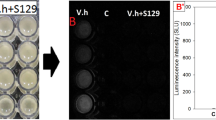
Quorum sensing is an important microbial signaling system that controls the expression of many virulence genes. Maniwamycins C–F, new compounds and quorum-sensing inhibitors, were isolated from the culture broth of Streptomyces sp. TOHO-M025 using a silica gel column and preparative HPLC. The structures of maniwamycins were elucidated by spectroscopic analyses, including NMR. The compounds each have an azoxy moiety. All maniwamycins inhibited violacein synthesis, which is controlled by quorum sensing, in Chromobacterium violaceum CV026.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bassler, B. L. & Losick, R. Bacterially speaking. Cell 125, 237–246 (2006).
McLean, R. J., Whiteley, M, Stickler, D. J. & Fuqua, W. C. Evidence of autoinducer activity in naturally occurring biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 154, 259–263 (1997).
Eberl, L. et al. Involvement of N-acyl-L-hormoserine lactone autoinducers in controlling the multicellular behaviour of Serratia liquefaciens. Mol. Microbiol. 20, 127–136 (1996).
Slater, H., Crow, M., Everson, L. & Salmond, G. P. Phosphate availability regulates biosynthesis of two antibiotics, prodigiosin and carbapenem, in Serratia via both quorum-sensing-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol. Microbiol. 47, 303–320 (2003).
Fineran, P. C., Slater, H., Everson, L., Hughes, K. & Salmond, G. P. Biosynthesis of tripyrrole and beta-lactam secondary metabolites in Serratia: integration of quorum sensing with multiple new regulatory components in the control of prodigiosin and carbapenem antibiotic production. Mol. Microbiol. 56, 1495–1517 (2005).
Falcão, J. P., Sharp, F. & Sperandio, V. Cell-to-cell signaling in intestinal pathogens. Curr. Issues Intest. Microbiol. 5, 9–17 (2004).
Antunes, L. C., Ferreira, R. B., Buckner, M. M. & Finlay, B. B. Quorum sensing in bacterial virulence. Microbiology. 156, 2271–2282 (2010).
Finch, R. G., Pritchard, D. I., Bycroft, B. W., Williams, P. & Stewart, G. S. Quorum sensing: a novel target for anti-infective therapy. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 42, 569–571 (1998).
Cegelski, L., Marshall, G. R., Eldridge, G. R. & Hultgren, S. J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 17–27 (2008).
Baldwin, A., Sokol, P. A., Parkhill, J. & Mahenthiralingam, E. The Burkholderia cepacia epidemic strain marker is part of a novel genomic island encoding both virulence and metabolism-associated genes in Burkholderia cenocepacia. Infect. Immun. 72, 1537–1547 (2004).
Valade, E. et al. The PmlI-PmlR quorum-sensing system in Burkholderia pseudomallei plays a key role in virulence and modulates production of the MprA protease. J. Bacteriol. 186, 2288–2294 (2004).
Nagata, T. et al. Effect of erythromycin on chronic respiratory infection caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa with biofilm formation in an experimental murine model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48, 2251–2259 (2004).
Rasko, D. A. et al. Targeting QseC signaling and virulence for antibiotic development. Science 321, 1078–1080 (2008).
Ooka, K. et al. Novel quorum-sensing inhibitors against Chromobacterium violaceum CV026, from Streptomyces sp. TOHO-Y209 and TOHO-O348. Open J. Med. Chem. 3, 93–99 (2013).
McClean, K. H. et al. Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 143, 3703–3711 (1997).
Nakayama, M. et al. Novel antifungal antibiotics maniwamycins A and B. I. Taxonomy of the producing organism, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 42, 1535–1540 (1989).
Takahashi, Y. et al. Novel antifungal antibiotics maniwamycins A and B. II. Structure determination. J. Antibiot. 42, 1541–1546 (1989).
Blair, L. M. & Sperry, J. Natural products containing a nitrogen-nitrogen bond. J. Nat. Prod. 76, 794–812 (2013).
Haskell, T. H., Ryder, A. & Bartz, Q. R. Elaiomycin, a new tuberculostatic antibiotic; isolation and chemical characterization. Antibiot. Chemother. 4, 141–144 (1954).
McGahren, W. J. & Kunstmann, M. P. A novel alpha, beta-unsaturated azoxy-containing antibiotic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 91, 2808–2810 (1969).
Omura, S. et al. Jietacins A and B, new nematocidal antibiotics from a Streptomyces sp. Taxonomy, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 40, 623–629 (1987).
Bianchi, G., Dallavalle, S., Merlini, L., Nasini, G. & Quaroni, S. A new azoxyalkene from a strain of an actinomadura-like fungus. Planta Med. 69, 574–576 (2003).
Ishiwatari, H. et al Production of azoxy compound. Japanese Patent H07-33730 (1995).
Taylor, K. G. & Tilford, R. Aliphatic azoxy compounds. II. Synthesis of new azoxy compounds by photolytic isomerizations. J. Am. Chem Soc. 94, 250–255 (1972).
Engel, P. S. et al. Photorearrangement of alpha-azoxy ketones and triplet sensitization of azoxy compounds. J. Org. Chem. 70, 2598–2605 (2005).
Bhardwaj, A. K., Vinothkumar, K. & Rajpara, N. Bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors: attractive alternatives for control of infectious pathogens showing multiple drug resistance. Recent Pat. Antiinfect. Drug Discov. 8, 68–83 (2013).
Rasmussen, T. B. et al. Identity and effects of quorumsensing inhibitors produced by Penicillium species. Microbiology 151, 1325–1340 (2005).
Givskov, M. et al. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signalling. J. Bacteriol. 178, 6618–6622 (1996).
Skindersoe, M. E. et al. Effects of antibiotics on quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 52, 3648–3663 (2008).
Tavío, M. M. et al. Quorum-sensing regulator sdiA and marA overexpression is involved in in vitro-selected multidrug resistance of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 65, 1178–1186 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr M. Nakakoshi for NMR experiments and JEOL Ltd. for MS. We also thank Dr Tsukasa Ikeda at Utsunomiya University for kindly providing C. violaceum CV026.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fukumoto, A., Murakami, C., Anzai, Y. et al. Maniwamycins: new quorum-sensing inhibitors against Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 were isolated from Streptomyces sp. TOHO-M025. J Antibiot 69, 395–399 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2015.126
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2015.126
This article is cited by
-
Biotechnological Activities and Applications of Bacterial Pigments Violacein and Prodigiosin
Journal of Biological Engineering (2021)
-
Quorum sensing inhibition and tobramycin acceleration in Chromobacterium violaceum by two natural cinnamic acid derivatives
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2020)
-
Metabolites with Gram-negative bacteria quorum sensing inhibitory activity from the marine animal endogenic fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD08
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2017)
-
Quorum quenching properties of Actinobacteria isolated from Malaysian tropical soils
Archives of Microbiology (2017)
-
A diketopiperazine factor from Rheinheimera aquimaris QSI02 exhibits anti-quorum sensing activity
Scientific Reports (2016)