Abstract
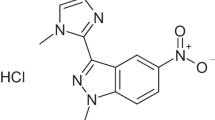
Lincomycin derivatives that have a 5-(2-nitrophenyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl thio moiety at the 7-position were synthesized. 5-Substituted 2-nitrophenyl derivatives showed potent antibacterial activities against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes with erm gene. Antibacterial activities of the 4,5-di-substituted 2-nitrophenyl derivatives were generally comparable to those of telithromycin (TEL) against S. pneumoniae with erm gene and clearly superior to those of TEL against S. pyogenes with erm gene. Compounds 6 and 10c that have a methoxy group at the 5-position of the benzene ring exhibited activities comparable to TEL against Haemophilus influenzae. These results suggest that lincomycin derivatives modified at the 7-position would be promising compounds as a clinical candidate. We would like to dedicate this article to the special issue for late Professor Dr. Hamao Umezawa in The Journal of Antibiotics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Morimoto, S., Takahashi, Y., Watanabe, Y. & Omura, S. Chemical modification of erythromycins. I. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of 6-O-methylerythromycins A. J. Antibiot. 37, 187–189 (1984).
Slobodan, D. et al. Erythromycin series. Part 13. Synthesis and structure elucidation of 10-dihydro-10-deoxo-11-methyl-11-azaerythromycin A. J. Chem. Res. Synop. 1988, 152–153 (1988).
Ajito, K., Miura, T., Furuuchi, T. & Tamura, A. Sixteen-membered macrolides: chemical modifications and future applications. Heterocycles 89, 281–352 (2014).
Sato, T. et al. In vitro antibacterial activity of modithromycin, a novel 6,11-bridged bicyclolide, against respiratory pathogens, including macrolide-resistant Gram-positive cocci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55, 1588–1593 (2011).
Denis, A. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of HMR 3647 a new ketolide highly potent against erythromycin-resistant and susceptible pathogens. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 9, 3075–3080 (1999).
Brueggemann, A. B. et al. In vitro activity of ABT-773, a new ketolide, against recent clinical isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 44, 447–449 (2000).
McGhee, P. et al. In vitro activity of CEM-101 against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes with defined macrolide resistance mechanisms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 54, 230–238 (2010).
Farrell, J. D. et al. In vitro activity of WCK 4873 (Nafithromycin) against resistant subsets of Streptococcus pneumoniae from a global surveillance program (2014). ASM Microbe 2016, Poster Saturday-455 (Boston, USA, (2016).
Clay, K. D. et al. Severe hepatotoxicity of telithromycin: three case reports and literature review. Ann. Intern. Med. 144, 415–420 (2006).
Miura, T. et al. Novel azalides derived from 16-membered macrolides. III. Azalides modified at the C-15 and 4” positions: Improved antibacterial activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 18, 2735–2747 (2010).
Mason, D. J., Dietz, A. & Deboer, C. Lincomycin, a new antibiotic I. Discovery and biological properties. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 554–559 (1962).
Birkenmeyer, R. D. & Kagan, F. Lincomycin. XI. Synthesis and structure of clindamycin. A potent antibacterial agent. J. Med. Chem. 13, 616–619 (1970).
Weisblum, B. Erythromycin resistance by ribosome modification. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 39, 577–585 (1995).
Tsuzuki, K. et al. Motilides, macrolides with gastrointestinal motor stimulating activity. I. O-substituted and tertiary N-substituted derivatives of 8,9-anhydroerythromycin A 6,9-hemiacetal. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 37, 2687–2700 (1989).
Shah, P. J., Vakil, N. & Kabakov, A. Role of intravenous immune globulin in streptococcal toxic shock syndrome and Clostridium difficile infection. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 72, 1013–1019 (2015).
Schlünzen, F. et al. Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature 413, 814–821 (2001).
Sztaricskai, F. et al. Semisynthetic modification of antibiotic lincomycin. J. Antibiot. 49, 941–943 (1996).
Goffic, L. F. Structure activity relationships in lincosamide and streptogramin antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 16 (Suppl A), 13–21 (1985).
Umemura, E. et al. Synthesis of novel lincomycin derivatives and their in vitro antibacterial activities. J. Antibiot. 66, 195–198 (2013).
Wakiyama, Y. et al. Synthesis and structure–activity relationships of novel lincomycin derivatives. Part 1. Newly generated antibacterial activities against Gram-positive bacteria with erm gene by C-7 modification. J. Antibiot. 69, 368–380 (2016).
Wakiyama, Y. et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel lincomycin derivatives. Part 2. Synthesis of 7(S-7-deoxy-7-(4-morpholinocarbonylphenylthio)lincomycin and its 3-dimensional analysis with rRNA. J. Antibiot. 69, 428–439 (2016).
Kumura, K. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial Activity of novel lincomycin derivatives. II. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel lincomycin derivatives. II. Exploring (7 S -7-(5-aryl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl-thio)-7-deoxylincomycin derivatives. J. Antibiot. 70, 655–663 (2017).
Kumura, K. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel lincomycin derivatives. I. Enhancement of antibacterial activities by introduction of substituted azetidines. J. Antibiot. 69, 440–445 (2016).
Houtman, R. L. & Mich, P. (The Upjohn Company), Trimethylsilyl ethers of lincomycin and its compounds. US3418414 (1966).
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr E Shitara, Mr A Tamura, Dr T Okutomi for valuable scientific discussion. We are grateful to Professor Emeritus Dr M Konno for supervision through our in-house drug discovery program in LCM field. We are also grateful to Ms T Miyara, Ms S Miki, Ms K Kaneda, Dr T Murata and Mr S Sato for contribution toward analytical chemistry, Ms K Yamada for biological studies, and Ms M Takagi for manuscript. We also thank Ms M Ishii for direction in intellectual properties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumura, K., Wakiyama, Y., Ueda, K. et al. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of novel lincomycin derivatives. III. Optimization of a phenyl thiadiazole moiety. J Antibiot 71, 104–112 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2017.59
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Version of record:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2017.59
This article is cited by
-
Synthesis and SARs of novel lincomycin derivatives Part 5: optimization of lincomycin analogs exhibiting potent antibacterial activities by chemical modification at the 6- and 7-positions
The Journal of Antibiotics (2018)
-
Synthesis of new chiral 1,3,4-thiadiazole-based di- and tri-arylsulfonamide residues and evaluation of in vitro anti-HIV activity and cytotoxicity
Molecular Diversity (2018)