Abstract
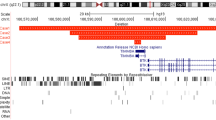
Patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) can present with sensorineural deafness. This can result from a gross deletion that not only involved the Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) gene, but also TIMM8A, mutations in which underlie the Mohr-Tranebjærg syndrome (MTS). We analyzed the genomic break points observed in three XLA–MTS patients and compared these with deletions break points from XLA patients. Patient 1 had a 63-kb deletion with break points in intron 15 of BTK and 4 kb upstream of TAF7L. Patients 2 and 3 had 149.7 and 196 kb deletions comprising BTK, TIMM8A, TAF7L and DRP2. The break points in patients 1 and 3 were located in Alu and endogenous retrovirus (ERV) repeats, whereas the break points in patient 2 did not show involvement of transposable elements. Comparison of gross deletion sizes and involvement of transposable elements in XLA and XLA–MTS patients from the literature showed preferential involvement of Alu elements in smaller deletions (<10 kb). These results show further insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying gross deletions in patients with primary immunodeficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Conley, M. E., Broides, A., Hernadez-Trujillo, V., Howard, V., Kanegane, H., Miyawaki, T. et al. Genetic analysis of patients with defects in early B-cell development. Immunol. Res. 203, 216–234 (2005).
Tsukada, S., Saffran, D. C., Rawlings, D. J., Parolini, O., Allen, R. C., Klisak, I. et al. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell 172, 279–290 (1993).
Vetrie, D., Vořechovský, I., Sideras, P., Holland, J., Davies, A., Flinter, F. et al. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature 361, 226–233 (1993).
Vořechovský, I., Vetrie, D., Holland, J., Bentley, D. R., Thomas, K., Zhou, J. N. et al. Isolation of cosmid and cDNA clones in the region surrounding the BTK gene at Xq21.3-q22. Genomics 21, 517–524 (1994).
Jin, H., May, M., Tranebjærg, L., Kendall, E., Fontán, G., Jackson, J. et al. A novel X-linked gene, DDP, shows mutations in families with deafness (DFN-1), dystonia, mental deficiency and blindness. Nat. Genet. 14, 177–180 (1996).
Tranebjærg, L., Hamel, B. C. J., Gabreels, F. J. M., Renier, W. O. & Van Ghelue, M. A de novo missense mutation in a critical domain of the X-linked DDP gene causes the typical deafness-dystonia-optic atrophy syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 8, 464–467 (2000).
Binder, J., Hofmann, S., Kreisel, S., Wöhrle, J. C., Bäzner, H., Krauss, J. K. et al. Clinical and molecular findings in a patient with a novel mutation in the deafness-dystonia peptide (DDP1) gene. Brain 126, 1814–1820 (2003).
Richter, D., Conley, M. E., Rohrer, J., Myers, L. A., Zahradka, K., Kelecić, J. et al. A contiguous deletion syndrome of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and sensorineural deafness. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 12, 107–111 (2001).
Šedivá, A., Smith, C. I. E., Asplund, A. C., Hadač, J., Janda, A., Zeman, J. et al. Contiguous X-chromosome deletion syndrome encompassing the BTK, TIMM8A, TAF7L and DRP2 genes. J. Clin. Immunol. 27, 640–646 (2007).
Jyonouchi, H., Geng, L., Törüner, G. A., Vinekar, K., Feng, D. & Fitzgerald-Bocarsly, P. Monozygous twins with a microdeletion syndrome involving BTK, DDP1, and two other genes; evidence of intact dendritic cell development and TLR responses. Eur. J. Pediatr. 167, 317–321 (2008).
Hashimoto, S., Tsukada, S., Matsushita, M., Miyawaki, T., Niida, Y., Yachie, A. et al. Identification of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) gene mutations and characterization of the derived proteins in 35 X-linked agammaglobulinemia families: a nationwide study of Btk deficiency in Japan. Blood 88, 561–573 (1996).
Kanegane, H., Futatani, T., Wang, Y., Nomura, K., Shinozaki, K., Matsukura, H. et al. Clinical and mutational characteristics of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and its carrier identified by flow cytometric assessment combined with genetic analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 108, 1012–1020 (2001).
Yamada, M., Arai, T., Oishi, T., Hanano, N., Kobayashi, I., Kubota, M. et al. Determination of the deletion breakpoints in two patients with contiguous gene syndrome encompassing CYBB gene. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 53, 383–388 (2010).
van Zelm, M. C., Geertsema, C., Nieuwenhuis, N., de Ridder, D., Conley, M. E., Schiff, C. et al. Gross deletions involving IGHM, BTK, or Artemis: a model for genomic lesions mediated by transposable elements. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 320–332 (2008).
Kohany, O., Gentles, A. J., Hankus, J. & Jurka, J. Annonation, submission and screening of repetitive elements in Repbase: RepbaseSubmitter and Cancer. BMC Bioinformatics 7, 474 (2006).
Rohrer, J., Minegishi, Y., Richter, D., Eguiguren, J. & Conley, M. E. Unusual mutations in Btk: an insertion, a duplication, an inversion and four large deletions. Clin. Immunol. 90, 28–37 (1999).
Jo, E. K., Wang, Y., Kanegane, H., Futatani, T., Song, C. H., Park, J. K. et al. Identification of mutations in the Bruton's tyrosine kinase gene, including a novel genomic rearrangements resulting in large deletion, in Korean X-linked agammaglobulinemia patients. J. Hum. Genet. 48, 322–326 (2003).
International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921 (2001).
Purandare, S. M. & Patel, P. I. Recombination hot spots and human disease. Genome Res. 7, 773–786 (1997).
Deininger, P. L. & Batzer, M. A. Alu repeats and human disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 67, 183–193 (1999).
Wang, P. J., McCarrey, J. R., Yang, F. & Page, D. C. An abundance of X-linked genes expressed in spermatogonia. Nat. Genet. 27, 422–426 (2001).
Roberts, R. G., Freeman, T. C., Kendall, E., Vetrie, D. L., Dixon, A. K., Shaw-Smith, C. et al. Characterization of DRP2, a novel human dystrophin homologue. Nat. Genet. 13, 223–226 (1996).
Sherman, D. L., Fabrizi, C., Gillespie, C. S. & Brophy, P. J. Specific disruption of a Schwann cell dystrophin-related protein complex in a demyelinating neuropathy. Neuron 30, 677–687 (2001).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and by a grant from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. We thank Chikako Sakai, Hitoshi Moriuchi and Noboru Hosogai for their excellent technical assistance. We are also grateful to the support, cooperation and trust of the patients and their families.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, T., Zhao, M., Kanegane, H. et al. Genetic analysis of contiguous X-chromosome deletion syndrome encompassing the BTK and TIMM8A genes. J Hum Genet 56, 577–582 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.61
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhg.2011.61
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Familial 5.29 Mb deletion in chromosome Xq22.1–q22.3 with a normal phenotype: a rare pedigree and literature review
BMC Medical Genomics (2023)
-
Identification and analysis of deletion breakpoints in four Mohr-Tranebjærg syndrome (MTS) patients
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Phenotype prediction of Mohr-Tranebjaerg syndrome (MTS) by genetic analysis and initial auditory neuropathy
BMC Medical Genetics (2019)
-
Exome sequencing in multiplex autism families suggests a major role for heterozygous truncating mutations
Molecular Psychiatry (2014)
-
Chronic granulomatous disease, the McLeod phenotype and the contiguous gene deletion syndrome-a review
Clinical and Molecular Allergy (2011)