Abstract
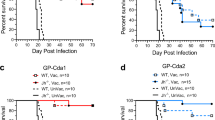
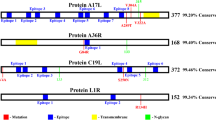
Cholera toxin (CT) B and A2 subunit complementary DNAs (cDNAs) were fused to a rotavirus enterotoxin and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli fimbrial antigen genes and transferred into potato. Immunoblot and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) results indicated that the fusion antigens were synthesized in transformed tuber tissues and assembled into cholera holotoxin-like structures that retained enterocyte-binding affinity. Orally immunized mice generated detectable levels of serum and intestinal antibodies against the pathogen antigens. Elevated levels of interleukin 2 (IL2) and interferon γ (INFγ) detected in immunogen-challenged spleen cells from the immunized mice indicated the presence of a strong Th1 immune response to the three plant-synthesized antigens. This result was supported by flow cytometry analysis of immunized mouse spleen cells that showed a significant increase in CD4+ lymphocyte numbers. Diarrhea symptoms were reduced in severity and duration in passively immunized mouse neonates following rotavirus challenge. The results suggest that food plants can function as vaccines for simultaneous protection against infectious virus and bacterial diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conner M.E. et al. Development of a mucosal rotaviurs vaccine. In Mucosal vaccines. (eds Kiyono, H., Ogra, P.L. & McGhee, J.R.) 325–326 (Academic Press, San Diego, CA; 1996).
Mason, H.S., Lam, D.M. & Arntzen, C.J. Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen in transgenic plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 11745–11749 (1992).
Mason, H.S. et al. Expression of Norwalk virus capsid protein in transgenic tobacco and potato and its immunogenicity in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 5335–5340 (1996).
Arakawa, T., Chong, D.K., Merritt, J.L. & Langridge, W.H. Expression of cholera toxin B subunit ologomers in transgenic potato plants. Transgenic Res. 6, 403–413 (1997).
Modelska, A. et al. Immunization against rabies with plant-derived antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.USA 95, 2481–2485 (1998).
Thanavala, Y., Yang, Y.F., Lyons, P., Mason, H.S. & Arntzen, C.J. Immunogenicity of transgenic plant-derived hepatitis B surface antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3358–3361 (1995).
Haq, T.A., Mason, H.S., Clements, J.D. & Arntzen, C.J. Oral immunization with a recombinant bacterial antigen produced in transgenic plants. Science 268, 714–716 (1995).
Arakawa, T., Chong, D.K. & Langridge, W.H. Efficacy of a food plant-based oral cholera toxin B subunit vaccine. Nat. Biotechnol. 16, 292–297 (1998).
Czerkinsky, C., Russell, M.W., Lycke, N., Lindblad, M. & Holmgren, J. Oral administration of a streptococcal antigen coupled to cholera toxin B subunit evokes strong antibody responses in salivary glands and extramucosal tissues. Infect. Immun. 57, 1072–1077 (1989).
Holmgren, J., Lycke, N. & Czerkinsky, C. Cholera toxin and cholera B subunit as oral-mucosal adjuvant and antigen vector systems. Vaccine 11, 1179–1184 (1993).
Bloom, P.D. & Boedeker, E.C. Mucosal immune responses to intestinal bacterial pathogens. Semin. Gastrointest. Dis. 7, 151–166 (1996).
Cox, D.S. & Taubman, M.A. Oral induction of the secretory antibody response by soluble and particulate antigens. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 75, 126 (1984).
Mackenzie, S.J. & Halsey, J.F. Cholera toxin B subunit as a carrier protein to stimulate a mucosal immune response. J. Immunol. 133, 1818–1824 (1984).
Lycke, N. & Holmgren, J. Strong adjuvant properties of cholera toxin on gut mucosal immune responses to orally presented antigens. Immunology 59, 301–308 (1986).
Jackson, R.J. et al. Optimizing oral vaccines: induction of systemic and mucosal B-cell and antibody responses to tetanus toxoid by use of cholera toxin as an adjuvant. Infect. Immun. 61, 4272–4279 (1993).
Sun, J.B., Holmgren, J. & Czerkinsky, C. Cholera toxin B subunit: An efficient transmucosal carrier-delivery system for induction of peripheral immunological tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 10795–10799 (1994).
Marinaro, M. et al. Use of intranasal IL-12 to target predominantly Th1 responses to nasal and Th2 responses to oral vaccines given with cholera toxin. J. Immunol. 162, 114–121 (1999).
Williams, N.A., Hirst, T.R. & Nashar, T.O. Immune modulation by the cholera-like enterotoxins: from adjuvant to therapeutic. Immunol.Today 20, 95–101 (1999).
Xu-Amano, J. et al. Helper Th1 and Th2 cell responses following mucosal or systemic immunization with cholera toxin. Vaccine 12, 903–911 (1994).
Arakawa, T. et al. A plant-based cholera toxin B subunit–insulin fusion protein protects against the development of autoimmune diabetes. Nat. Biotechnol. 16, 934–938 (1998).
Pascual, D.W. et al. Expression of recombinant enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli colonization factor antigen I by Salmonella typhimurium elicits a biphasic T helper cell response. Infect. Immun. 67, 6249–6256 (1999).
Ball, J.M., Tian, P., Zeng, C.Q.Y., Morris, A.P. & Estes, M.K. Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein. Science 272, 101–104 (1996).
Svennerholm, A.M. et al. Mucosal antitoxic and antibacterial immunity after cholera disease and after immunization with a combined B subunit–whole cell vaccine. J. Infect. Dis. 149, 884–893 (1984).
Horie, Y. et al. Diarrhea induction by rotavirus NSP4 in the homologous mouse model system. Virology 262, 398–407 (1999).
Hajishengallis, G., Hollingshead, A.K., Koga, T. & Russell, M.W. Mucosal immunization with a bacterial protein antigen genetically coupled to cholera toxin A2/B subunits. J. Immunol. 154, 4322–4332 (1995).
Dertzbaugh, M.T., Peterson, D.L. & Macrina, F.L. Cholera toxin B–subunit gene fusion: structural and functional analysis of the chimeric protein. Infect. Immun. 58, 70–79 (1990).
Angel, J., Tang, B., Feng, N., Greenberg, H.B. & Bass, D. Studies of the role for NSP4 in the pathogenesis of homologous murine rotavirus diarrhea. J. Infect. Dis. 177, 455–458 (1998).
Ishida, S.I., Feng, N., Gibert, J.M., Tang, B. & Greenberg, H.B. Immune responses to individual rotavirus proteins following heterologous and homologous rotavirus infection in mice. J. Infect. Dis. 175, 1317–1323 (1997).
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. John Mekalanos (Harvard University School of Medicine) for the gift of the CTX gene, Dr. Mary Estes and Dr. Carl Zeng (Baylor School of Medicine) for providing rotavirus antiserum specific for the NSP4 22–amino acid epitope and rotavirus SA-11 for rotavirus challenge experiments, and for many helpful discussions. Further, we would like to thank Dr. Myron Levine (Center for Vaccine Development, University of Maryland School of Medicine) for providing us with the E. coli CFA/I gene and the CFA/I fimbrial protein. This work was supported in part by a subcontract to W.H.R.L. by the US Army and the National Medical Technology Testbed Inc. and by an intramural grant awarded to W.H.R.L. by Loma Linda University. The views, opinions, and/or findings contained in this report are strictly those of the authors and should not be construed as a position policy, decision, or endorsement of the federal government or of the National Medical Technology Testbed, Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Langridge, W. A plant-based multicomponent vaccine protects mice from enteric diseases. Nat Biotechnol 19, 548–552 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/89297
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/89297
This article is cited by
-
Combined use of lactic-acid-producing bacteria as probiotics and rotavirus vaccine candidates expressing virus-specific proteins
Archives of Virology (2021)
-
Plant Platforms for Efficient Heterologous Protein Production
Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering (2021)
-
Antibodies induced by oral immunization of mice with a recombinant protein produced in tobacco plants harboring Bordetella pertussis epitopes
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) (2021)
-
A milk-based self-assemble rotavirus VP6–ferritin nanoparticle vaccine elicited protection against the viral infection
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2019)
-
Improved expression of porcine epidemic diarrhea antigen by fusion with cholera toxin B subunit and chloroplast transformation in Nicotiana tabacum
Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) (2019)