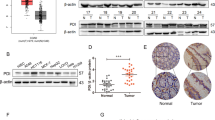
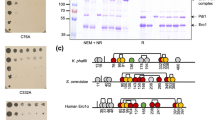
Abstract
B3(Fv)–PE38KDEL, a recombinant immunotoxin, forms inclusion bodies when produced in Escherichia coli. In renaturation experiments, nonspecific aggregation of non–native polypeptide chains, and the formation of incorrect disulfide linkages lead to inactive molecules. To prevent these side reactions, we added molecular chaperones and protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) to the refolding buffer. Both DnaK and GroEL/S influenced the reactivation process. GroEL alone inhibited reactivation, but in the presence of ATP, GroEL and GroES significantly increased the yield of active protein. DnaK also increased the yield of properly folded protein and the stimulating effect of DnaK was also observed using immobilized DnaK, which can be used repeatedly without significant loss of activity. PDI, which catalyzes disulfide bridging of proteins, also stimulated reactivation of the immunotoxin. Under optimum conditions, reactivation yields in the presence of PDI were about twice that obtained with nonenzymatic disulfide bond formation. Furthermore, DnaK and PDI were additive when renaturation was performed in the presence of both proteins.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jaenicke, R. 1987. Folding and association of proteins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 49: 117–237.
Jaenicke, R. 1991. Protein folding: local structures, domains, subunits and assemblies. Biochemistry 30: 3147–3161.
Rudolph, R. 1990. Renaturation of recombinant, disulfide-bonded proteins from inclusion bodies. p. 149–171. In: Modern Methods in Protein and Nucleic Acid Research. H. Tschesche (Ed.). Walter DeGruyter, Berlin.
Buchner, J. and Rudolph, R. 1991. Renaturation, purification and characterization of recombinant Fab-fragments produced in Escherichia coli. Bio/Technology 9: 157–162.
Ellis, J.R. and van der Vies, S.M. 1991. Molecular chaperones. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 60: 321–348.
Skowyra, D., Georgopoulos, C. and Zylicz, M. 1990. The E. coli DnaK gene product, the hsp70 homolog can reactivate heat-inactivated RNA polymerase in an ATP hydrolysis-dependent manner. Cell 62: 939–944.
Goloubinoff, P., Christelle, S.T., Gatenby, A.A. and Lorimer, G.J. 1989. Reconstitution of active dimeric ribulose biphosphate carboxylase from an unfolded state depends on two chaperonine proteins and Mg-ATP. Nature 342: 884–885.
Buchner, J., Schmidt, M., Fuchs, M., Jaenicke, R., Rudolph, R., Schmid, F.X. and Kiefhaber, T. 1991. GroE facilitates refolding of citrate synthase by suppressing aggregation. Biochemistry 30: 1587–1591.
Martin, J., Mendoza, J.A., Rogers, E., Lorimer, G.H. and Horowitz, P. 1991. Chaperonines facilitate the in vitro folding of monomeric mitochondrial rhodanese. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 13044–13049.
Laminet, A.A., Ziegelhofer, T., Georgopoulos, C. and Pluckthun, A. 1990. The Escherichia coli heat shock proteins GroEL and GroES modulate the folding of the β-lactamase precursor. EMBO J. 9: 2315–2319.
Holl-Neugebauer, B., Rudolph, R., Schmidt, M. and Buchner, J. 1992. Reconstitution of a heat shock effect in vitro: influence of GroE on the thermal aggregation of α-glucosidase from yeast. Biochemistry In press.
Mendoza, S.A., Rogers, E., Lorimer, G.H. and Horowitz, P.M. 1991. Chaperonine facilitate the in vitro folding of monomeric mitochondrial rhodanese. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 13044–13049.
Gatenby, A.A., Viitanen, P.V. and Lorimer, G.H. 1990. Chaperonine assisted polypeptide folding and assembly: implications for the production of functional proteins in bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 8: 354–358.
Buchner, J. and Rudolph, R. 1991. Routes to active proteins from transformed microorganisms. Current Opinion in Biotechnolo. 2: 532–538.
Bulleid, N.J. and Freedman, R.B. 1990. Defective co-translational formation of disulfide bonds in protein disulfide-isomerase-deficient microsomes. Nature 335: 649–657.
Freedman, R.B., Bulleid, N.J., Hawkins, H.C. and Paver, J.L. 1989. Role of protein disulfide isomerase in the expression of native proteins. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 55: 167–192.
Buchner, J., Pastan, I. and Brinkmann, U. 1992. Refolding of a single-chain immunotoxin from bacterial inclusion bodies. Anal. Biochem. In press.
Brinkmann, U., Pai, L.H., FitzGerald, D.J., Willingham, M. and Pastan, I. 1991. B3(Fv)-PE38KDEL, a single-chain immunotoxins that causes complete regression of a human carcinoma in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 8616–8620.
Pastan, I., Lovelace, E.T., Gallo, M.G., Rutherford, A.V., Magnani, J.I. and Willingham, M.C. 1991. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies B1 and B3 that react with mucinous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 51: 3781–3787.
Pai, L.H., FitzGerald, D.J., Willingham, M.C. and Pastan, I. 1991. Anti-tumor activities of immunotoxins made of monoclonal antibody B3 and various forms of Pseudomonas exotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 3358–3362.
Brinkmann, U., Buchner, J. and Pastan, I. 1992. Independent domain folding of Pseudomonas exotoxin and single-chain immunotoxins: Influence of interdomain connectors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 3075–3079.
Bradford, M.M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 241–245.
Studier, F.W. and Moffatt, B.A. 1986. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 189: 113–130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchner, J., Brinkmann, U. & Pastan, I. Renaturation of a Single–Chain Immunotoxin Facilitated by Chaperones and Protein Disulfide Isomerase. Nat Biotechnol 10, 682–685 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0692-682
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0692-682
This article is cited by
-
Folding machineries displayed on a cation-exchanger for the concerted refolding of cysteine- or proline-rich proteins
BMC Biotechnology (2009)
-
Antigen recognition and targeted delivery by the single-chain Fv
Cell Biophysics (1993)