Abstract
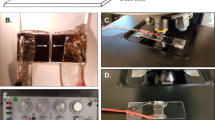
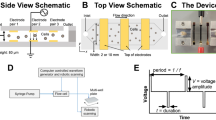
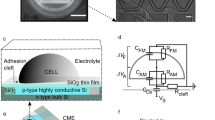
We present a high-throughput method that enables efficient delivery of biomolecules into cells. The device consists of an array of 96 suspended electrode pairs, where small sample volumes are top-loaded, electroporated and bottom-ejected into 96-well plates. We demonstrate the use of this suspended-drop electroporation (SDE) device to effectively introduce fluorescent dextran, small interfering RNA (siRNA) or cDNA into primary neurons, differentiated neutrophils and other cell types with conventionally low transfection rates.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Felgner, P.L. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 7413–7417 (1987).
Jordan, M., Schallhorn, A. & Wurm, F.M. Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 596–601 (1996).
Kaang, B.K., Kandel, E.R. & Grant, S.G. Neuron 10, 427–435 (1993).
Lo, D.C., McAllister, A.K. & Katz, L.C. Neuron 13, 1263–1268 (1994).
Moriyoshi, K., Richards, L.J., Akazawa, C., O'Leary, D.D. & Nakanishi, S. Neuron 16, 255–260 (1996).
Pettit, D.L., Koothan, T., Liao, D. & Malinow, R. Neuron 14, 685–688 (1995).
Kinosita, K., Jr & Tsong, T.Y. Nature 268, 438–441 (1977).
Teruel, M.N. & Meyer, T. Biophys. J. 73, 1785–1796 (1997).
Niggli, V. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 35, 1619–1638 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Merkle for machining the SDE device, D. Profitt for building the power supply, A. Hahn and P. Vitorino for careful reading of the manuscript, all the members of the Meyer lab for valuable discussions and advice. This work was financially supported by the Swiss Science Foundation and the US National Institute of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–4, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods (PDF 1782 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guignet, E., Meyer, T. Suspended-drop electroporation for high-throughput delivery of biomolecules into cells. Nat Methods 5, 393–395 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1201
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1201
This article is cited by
-
Optogenetic control of receptors reveals distinct roles for actin- and Cdc42-dependent negative signals in chemotactic signal processing
Nature Communications (2021)
-
High-throughput in situ cell electroporation microsystem for parallel delivery of single guide RNAs into mammalian cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Locally excitable Cdc42 signals steer cells during chemotaxis
Nature Cell Biology (2016)
-
Size Specific Transfection to Mammalian Cells by Micropillar Array Electroporation
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Massively parallel delivery of large cargo into mammalian cells with light pulses
Nature Methods (2015)