Abstract
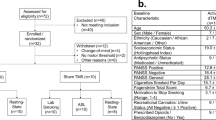
3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzylidene)-anabaseine (DMXB-A) is a partial agonist at α7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and is now in early clinical development for treatment of deficits in neurocognition and sensory gating in schizophrenia. During its initial phase 2 test, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies were conducted to determine whether the drug had its intended effect on hippocampal inhibitory interneurons. Increased hemodynamic activity in the hippocampus in schizophrenia is found during many tasks, including smooth pursuit eye movements, and may reflect inhibitory dysfunction. Placebo and two doses of drug were administered in a random, double-blind crossover design. After the morning drug/placebo ingestion, subjects underwent fMRI while performing a smooth pursuit eye movement task. Data were analyzed from 16 nonsmoking patients, including 7 women and 9 men. The 150-mg dose of DMXB-A, compared with placebo, diminished the activity of the hippocampus during pursuit eye movements, but the 75-mg dose was ineffective. The effect at the 150-mg dose was negatively correlated with plasma drug levels. The findings are consistent with the previously established function of α7-nicotinic receptors on inhibitory interneurons in the hippocampus and with genetic evidence for deficits in these receptors in schizophrenia. Imaging of drug response is useful in planning future clinical tests of this compound and other nicotinic agonists for schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Andreasen NC (1982). Negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Definition and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39: 784–788.
Breese CR, Adams C, Logel J, Drebing C, Rollins Y, Barnhart M et al (1997). Comparison of the regional expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor α7 mRNA and [125I]-α-bungarotoxin binding in human postmortem brain. J Comp Neurol 387: 385–398.
Briggs CA, McKenna DG, Piattoni-Kaplan M (1995). Human alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor responses to novel ligands. Neuropharmacology 34: 583–590.
De Fiebre CM, Meyer EM, Henry JC, Muraskin SI, Kem WR, Papke RL (1995). Characterization of a series of anabaseine-derived compounds reveals that the 3-(4)-dimethylaminocinnamylidine derivative is a selective agonist at neuronal nicotinic alpha-7/125 I-alpha-bungarotoxin receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol 47: 164–171.
Frazier CJ, Rollins YD, Breese CR, Leonard S, Freedman R, Dunwiddie TV (1998). Acetylcholine activates an alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic current in rat hippocampal interneurons, but not pyramidal cells. J Neurosci 18: 1187–1195.
Freedman R, Coon H, Myles-Worsley M, Orr-Urtreger A, Olincy A, Davis A et al (1997). Linkage of a neurophysiological deficit in schizophrenia to a chromosome 15 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94: 587–592.
Freedman R, Olincy A, Buchanan RW, Harris JG, Gold JM, Johnson L et al (2008). Initial phase 2 trial of a nicotinic agonist in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 165: 1040–1047.
Kem WR, Mahnir VM, Prokai L, Papke RL, Cao X, LeFrancois S et al (2004). Hydroxy metabolites of the Alzheimer's drug candidate 3-[(2,4-dimethoxy)benzylidene]-anabaseine dihydrochloride (GTS-21): their molecular properties, interactions with brain nicotinic receptors, and brain penetration. Mol Pharmacol 65: 56–67.
Mahnir V, Lin B, Prokai-Tatrai K, Kem WR (1998). Pharmacokinetics and urinary excretion of DMXB-A (GTS-21), a compound enhancing cognition. Biopharm Drug Dispos 19: 147–151.
Malaspina D, Storer S, Furman V, Esser P, Printz D, Berman A et al (1999). SPECT study of visual fixation in schizophrenia and comparison subjects. Biol Psychiatry 46: 89–93.
Martin LF, Kem WR, Freedman R (2004). Alpha-7 nicotinic receptor agonists: potential new candidates for the treatment of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 174: 54–64.
Olincy A, Harris JG, Johnson LL, Pender V, Kongs S, Allensworth D et al (2006). Proof-of-concept trial of an a7 nicotinic agonist in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63: 630–638.
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962). The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychol Rep 10: 799–812.
Papke RL, Porter-Papke JK (2002). Comparative pharmacology of rat and human α7 nAChR conducted with net charge analysis. Br J Pharmacol 137: 49–61.
Papke RL, Thinschmidt JS (1998). The correction of alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor concentration-response relationships in Xenopus oocytes. Neurosci Lett 256: 163–166.
Simpson GM, Angus JWS (1970). A rating scale for extrapyramidal side effects. Acta Psychiatr Scand 45: 11–19.
Sobotka S, Nowicka A, Ringo JL (1997). Activity linked to externally cued saccades in single units recorded from hippocampal, parahippocampal, and inferotemporal areas of macaques. J Neurophysiol 78: 2156–2163.
Stevens KE, Kem WR, Mahnir VM, Freedman R (1998). Selective α7-nicotinic agonists normalize inhibition of auditory response in DBA mice. Psychopharmacology 126: 320–327.
Tanabe J, Tregellas J, Miller D, Ross RG, Freedman R (2002). Brain activation during smooth-pursuit eye movements. Neuroimage 17: 1315–1324.
Tregellas J, Tanabe JL, Martin LF, Freedman R (2005). fMRI of response to nicotine during a smooth pursuit eye movement task in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 162: 391–393.
Tregellas JR, Tanabe JL, Miller DE, Ross RG, Olincy A, Freedman R (2004). Neurobiology of smooth pursuit eye movement deficits in schizophrenia: an fMRI study. Am J Psychiatry 161: 315–321.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the VA Biomedical Laboratory and Clinical Science Research and Development Service; the Mental Illness Research, Education, and Clinical Centers of Veterans Integrated Service Networks 5 and 19; NIMH Grants MH-061412 and MH-086383; the National Association for Research in Schizophrenia and Affective Disorders; the Dana Foundation; and by the Institute for Children's Mental Disorders.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
DISCLOSURE
Dr Freedman has a patent through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) on the CHRNA7 gene sequence. Drs Kem and Soti have patents through the University of Florida on the manufacture and use of DMXB-A and have a research grant from CoMentis; Drs Olincy and Johnson receive research support from Lundbeck. The other authors have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tregellas, J., Olincy, A., Johnson, L. et al. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Effects of a Nicotinic Agonist in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacol 35, 938–942 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.196
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.196
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Effects of nicotine on smooth pursuit eye movements in healthy non-smokers
Psychopharmacology (2019)
-
Bidirectional Regulation of Aggression in Mice by Hippocampal Alpha-7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors
Neuropsychopharmacology (2018)
-
Modulatory effects of α7 nAChRs on the immune system and its relevance for CNS disorders
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2016)
-
Translating Neurobiology to the Treatment of Dual Diagnosis: The Example of Nicotinic Receptors and Neurocognitive Endophenotypes in Schizophrenia
Current Addiction Reports (2014)
-
Pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia: a critical review of the pharmacology and clinical effects of current and future therapeutic agents
Molecular Psychiatry (2012)