Abstract
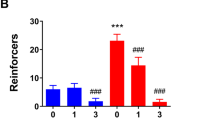
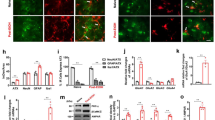
It is well documented that ethanol exposure alters GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)-releasing synapses, and ethanol addiction is associated with endogenous opioid system. Emerging evidence indicates that opioids block long-term potentiation in the fast inhibitory GABAA receptor synapses (LTPGABA) onto dopamine-containing neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a brain region essential for reward-seeking behavior. However, how ethanol affects LTPGABA is not known. We report here that in acute midbrain slices from rats, clinically relevant concentrations of ethanol applied both in vitro and in vivo prevents LTPGABA, which is reversed, respectively, by in vitro and in vivo administration of naloxone, a μ-opioid receptor (MOR) antagonist. Furthermore, the blockade of LTPGABA induced by a brief in vitro ethanol treatment is mimicked by DAMGO ([D-Ala2, N-MePhe4, Gly-ol]-enkephalin), a MOR agonist. Paired-pulse ratios are similar in slices, 24 h after in vivo injection with either saline or ethanol. Sp-cAMPS, a stable cAMP analog, and pCPT-cGMP, a cGMP analog, potentiates GABAA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic currents in slices from ethanol-treated rats, indicating that a single in vivo ethanol exposure does not maximally increase GABA release, instead, ethanol produces a long-lasting inability to generate LTPGABA. These neuroadaptations to ethanol might contribute to early stage of addiction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Bergevin A, Girardot D, Bourque MJ, Trudeau LE (2002). Presynaptic mu-opioid receptors regulate a late step of the secretory process in rat ventral tegmental area GABAergic neurons. Neuropharmacology 42: 1065–1078.
Bonci A, Williams JT (1997). Increased probability of GABA release during withdrawal from morphine. J Neurosci 17: 796–803.
Chefer VI, Denoroy L, Zapata A, Shippenberg TS (2009). Mu opioid receptor modulation of somatodendritic dopamine overflow: GABAergic and glutamatergic mechanisms. Eur J Neurosci 30: 272–278.
Chen BT, Bowers MS, Martin M, Hopf FW, Guillory AM, Carelli RM et al (2008). Cocaine but not natural reward self-administration nor passive cocaine infusion produces persistent LTP in the VTA. Neuron 59: 288–297.
Deng C, Li KY, Zhou C, Ye JH (2009). Ethanol enhances glutamate transmission by retrograde dopamine signaling in a postsynaptic neuron/synaptic bouton preparation from the ventral tegmental area. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 1233–1244.
Di Chiara G, North RA (1992). Neurobiology of opiate abuse. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13: 185–193.
Gallegos RA, Lee RS, Criado JR, Henriksen SJ, Steffensen SC (1999). Adaptive responses of gamma-aminobutyric acid neurons in the ventral tegmental area to chronic ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291: 1045–1053.
Garzon M, Pickel VM (2001). Plasmalemmal mu-opioid receptor distribution mainly in nondopaminergic neurons in the rat ventral tegmental area. Synapse 41: 311–328.
Herz A (1997). Endogenous opioid systems and alcohol addiction. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 129: 99–111.
Hyman SE, Malenka RC (2001). Addiction and the brain: the neurobiology of compulsion and its persistence. Nat Rev Neurosci 2: 695–703.
Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (2006). Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Ann Rev Neurosci 29: 565–598.
Hyytia P, Kiianmaa K (2001). Suppression of ethanol responding by centrally administered CTOP and naltrindole in AA and Wistar rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25: 25–33.
Jarjour S, Bai L, Gianoulakis C (2009). Effect of acute ethanol administration on the release of opioid peptides from the midbrain including the ventral tegmental area. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33: 1033–1043.
Johnson SW, North RA (1992a). Opioids excite dopamine neurons by hyperpolarization of local interneurons. J Neurosci 12: 483–488.
Johnson SW, North RA (1992b). Two types of neurone in the rat ventral tegmental area and their synaptic inputs. J Physiol 450: 455–468.
Kauer JA, Malenka RC (2007). Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 8: 844–858.
Kim SG, Stromberg MF, Kim MJ, Volpicelli JR, Park JM (2000). The effect of antagonists selective for mu- and delta-opioid receptor subtypes on alcohol consumption in C57BL/6 mice. Alcohol 22: 85–90.
Krishnan-Sarin S, Wand GS, Li XW, Portoghese PS, Froehlich JC (1998). Effect of mu opioid receptor blockade on alcohol intake in rats bred for high alcohol drinking. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59: 627–635.
Lam MP, Marinelli PW, Bai L, Gianoulakis C (2008). Effects of acute ethanol on opioid peptide release in the central amygdala: an in vivo microdialysis study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 201: 261–271.
Livy DJ, Parnell SE, West JR (2003). Blood ethanol concentration profiles: a comparison between rats and mice. Alcohol 29: 165–171.
Mansour A, Fox CA, Akil H, Watson SJ (1995). Opioid-receptor mRNA expression in the rat CNS: anatomical and functional implications. Trends Neurosci 18: 22–29.
Margolis EB, Fields HL, Hjelmstad GO, Mitchell JM (2008). Delta-opioid receptor expression in the ventral tegmental area protects against elevated alcohol consumption. J Neurosci 28: 12672–12681.
Margolis EB, Hjelmstad GO, Bonci A, Fields HL (2003). Kappa-opioid agonists directly inhibit midbrain dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 23: 9981–9986.
Margolis EB, Lock H, Chefer VI, Shippenberg TS, Hjelmstad GO, Fields HL (2006). Kappa opioids selectively control dopaminergic neurons projecting to the prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 2938–2942.
Marinelli PW, Quirion R, Gianoulakis C (2004). An in vivo profile of beta-endorphin release in the arcuate nucleus and nucleus accumbens following exposure to stress or alcohol. Neuroscience 127: 777–784.
Melis M, Camarini R, Ungless MA, Bonci A (2002). Long-lasting potentiation of GABAergic synapses in dopamine neurons after a single in vivo ethanol exposure. J Neurosci 22: 2074–2082.
Mendez M, Leriche M, Carlos Calva J (2003). Acute ethanol administration transiently decreases [3H]-DAMGO binding to mu opioid receptors in the rat substantia nigra pars reticulata but not in the caudate-putamen. Neurosci Res 47: 153–160.
Mendez M, Morales-Mulia M (2008). Role of mu and delta opioid receptors in alcohol drinking behaviour. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 1: 239–252.
Mihic SJ (1999). Acute effects of ethanol on GABAA and glycine receptor function. Neurochem Int 35: 115–123.
Nugent FS, Kauer JA (2008). LTP of GABAergic synapses in the ventral tegmental area and beyond. J Physiol 586: 1487–1493.
Nugent FS, Niehaus JL, Kauer JA (2009). PKG and PKA signaling in LTP at GABAergic synapses. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 1829–1842.
Nugent FS, Penick EC, Kauer JA (2007). Opioids block long-term potentiation of inhibitory synapses. Nature 446: 1086–1090.
Olive MF, Koenig HN, Nannini MA, Hodge CW (2001). Stimulation of endorphin neurotransmission in the nucleus accumbens by ethanol, cocaine, and amphetamine. J Neurosci 21: RC184.
Oswald LM, Wand GS (2004). Opioids and alcoholism. Physiol Behav 81: 339–358.
Siggins GR, Roberto M, Nie Z (2005). The tipsy terminal: presynaptic effects of ethanol. Pharmacol Ther 107: 80–98.
Steffensen SC, Svingos AL, Pickel VM, Henriksen SJ (1998). Electrophysiological characterization of GABAergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 18: 8003–8015.
Stein EA (1993). Ventral tegmental self-stimulation selectively induces opioid peptide release in rat CNS. Synapse 13: 63–73.
Stobbs SH, Ohran AJ, Lassen MB, Allison DW, Brown JE, Steffensen SC (2004). Ethanol suppression of ventral tegmental area GABA neuron electrical transmission involves N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 311: 282–289.
Suzdak PD, Schwartz RD, Skolnick P, Paul SM (1986). Ethanol stimulates gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-mediated chloride transport in rat brain synaptoneurosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 4071–4075.
Svingos AL, Garzón M, Colago EE, Pickel VM (2001). Mu-opioid receptors in the ventral tegmental area are targeted to presynaptically and directly modulate mesocortical projection neurons. Synapse 41: 221–229.
Theile JW, Morikawa H, Gonzales RA, Morrisett RA (2008). Ethanol enhances GABAergic transmission onto dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area of the rat. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32: 1040–1048.
Theile JW, Morikawa H, Gonzales RA, Morrisett RA (2009). Role of 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors in Ca2+-dependent ethanol potentiation of GABA release onto ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329: 625–633.
Weiner JL, Valenzuela CF (2006). Ethanol modulation of GABAergic transmission: the view from the slice. Pharmacol Ther 111: 533–554.
Xiao C, Shao XM, Olive MF, Griffin III WC, Li KY, Krnjevic K et al (2009). Ethanol facilitates glutamatergic transmission to dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 307–318.
Xiao C, Ye JH (2008). Ethanol dually modulates GABAergic synaptic transmission onto dopaminergic neurons in ventral tegmental area: role of mu-opioid receptors. Neuroscience 153: 240–248.
Xiao C, Zhou C, Li K, Ye JH (2007a). Presynaptic GABAA receptors facilitate GABAergic transmission to dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area of young rats. J Physiol 580: 731–743.
Xiao C, Zhang J, Krnjevic K, Ye JH (2007b). Effects of ethanol on midbrain neurons: role of opioid receptors. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31: 1106–1113.
Ye JH, Wang F, Krnjevic K, Wang W, Xiong ZG, Zhang J (2004). Presynaptic glycine receptors on GABAergic terminals facilitate discharge of dopaminergic neurons in ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 24: 8961–8974.
Ye JH, Zhang J, Xiao C, Kong JQ (2006). Patch-clamp studies in the CNS illustrate a simple new method for obtaining viable neurons in rat brain slices: glycerol replacement of NaCl protects CNS neurons. J Neurosci Methods 158: 251–259.
Zucker RS, Regehr WG (2002). Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu Rev Physiol 64: 355–405.
Acknowledgements
This work was made possible by the support of NIH grants to JHY (R01AA016964; R21AA015925 and R21AA016618). We are grateful to Dr K Krnjevic’ for his helpful comments on this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Yz., Ye, JH. Ethanol Blocks Long-Term Potentiation of GABAergic Synapses in the Ventral Tegmental Area Involving μ-Opioid Receptors. Neuropsychopharmacol 35, 1841–1849 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.51
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2010.51
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Role of KCC2 in the Regulation of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on Ethanol Consumption in Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Nitric Oxide Signaling Pathway in Ventral Tegmental Area is Involved in Regulation of 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone on Alcohol Consumption in Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
7,8-Dihydroxyflavone Alleviates Anxiety-Like Behavior Induced by Chronic Alcohol Exposure in Mice Involving Tropomyosin-Related Kinase B in the Amygdala
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Dopamine and addiction: what have we learned from 40 years of research
Journal of Neural Transmission (2019)
-
Ethanol actions on the ventral tegmental area: novel potential targets on reward pathway neurons
Psychopharmacology (2018)