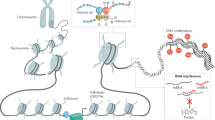
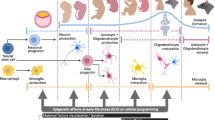
Abstract
Development is a dynamic process that involves interplay between genes and the environment. In mammals, the quality of the postnatal environment is shaped by parent–offspring interactions that promote growth and survival and can lead to divergent developmental trajectories with implications for later-life neurobiological and behavioral characteristics. Emerging evidence suggests that epigenetic factors (ie, DNA methylation, posttranslational histone modifications, and small non-coding RNAs) may have a critical role in these parental care effects. Although this evidence is drawn primarily from rodent studies, there is increasing support for these effects in humans. Through these molecular mechanisms, variation in risk of psychopathology may emerge, particularly as a consequence of early-life neglect and abuse. Here we will highlight evidence of dynamic epigenetic changes in the developing brain in response to variation in the quality of postnatal parent–offspring interactions. The recruitment of epigenetic pathways for the biological embedding of early-life experience may also have transgenerational consequences and we will describe and contrast two routes through which this transmission can occur: experience dependent vs germline inheritance. Finally, we will speculate regarding the future directions of epigenetic research and how it can help us gain a better understanding of the developmental origins of psychiatric dysfunction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
References
Adegbola A, Gao H, Sommer S, Browning M (2008). A novel mutation in JARID1C/SMCX in a patient with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Am J Med Genet A 146A: 505–511.
Ader R (1970). The effects of early experience on the adrenocortical response to different magnitudes of stimulation. Physiol Behav 5: 837–839.
Andersen SL, Lyss PJ, Dumont NL, Teicher MH (1999). Enduring neurochemical effects of early maternal separation on limbic structures. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877: 756–759.
Anway MD, Skinner MK (2006). Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors. Endocrinology 147: S43–S49.
Bagot RC, van Hasselt FN, Champagne DL, Meaney MJ, Krugers HJ, Joels M (2009). Maternal care determines rapid effects of stress mediators on synaptic plasticity in adult rat hippocampal dentate gyrus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92: 292–300.
Bagot RC, Zhang TY, Wen X, Nguyen TT, Nguyen HB, Diorio J et al (2012). Variations in postnatal maternal care and the epigenetic regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 expression and hippocampal function in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109 (Suppl 2): 17200–17207.
Baram TZ, Davis EP, Obenaus A, Sandman CA, Small SL, Solodkin A et al (2012). Fragmentation and unpredictability of early-life experience in mental disorders. Am J Psychiatry 169: 907–915.
Barres R, Yan J, Egan B, Treebak JT, Rasmussen M, Fritz T et al (2012). Acute exercise remodels promoter methylation in human skeletal muscle. Cell Metab 15: 405–411.
Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z et al (2007). High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129: 823–837.
Bernard K, Dozier M (2010). Examining infants’ cortisol responses to laboratory tasks among children varying in attachment disorganization: stress reactivity or return to baseline? Dev Psychol 46: 1771–1778.
Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, Murchison EP, Alcorn H, Li MZ et al (2003). Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet 35: 215–217.
Bester-Meredith JK, Marler CA (2003). Vasopressin and the transmission of paternal behavior across generations in mated, cross-fostered Peromyscus mice. Behav Neurosci 117: 455–463.
Birnie AK, Taylor JH, Cavanaugh J, French JA (2013). Quality of maternal and paternal care predicts later stress reactivity in the cooperatively-breeding marmoset (Callithrix geoffroyi). Psychoneuroendocrinology 38: 3003–3014.
Blaze J, Roth TL (2013). Exposure to caregiver maltreatment alters expression levels of epigenetic regulators in the medial prefrontal cortex. Int J Dev Neurosci 31: 804–810.
Branchi I, Curley JP, D’Andrea I, Cirulli F, Champagne FA, Alleva E (2013). Early interactions with mother and peers independently build adult social skills and shape BDNF and oxytocin receptor brain levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38: 522–532.
Branchi I, D’Andrea I, Fiore M, Di Fausto V, Aloe L, Alleva E (2006a). Early social enrichment shapes social behavior and nerve growth factor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in the adult mouse brain. Biol Psychiatry 60: 690–696.
Branchi I, D’Andrea I, Sietzema J, Fiore M, Di Fausto V, Aloe L et al (2006b). Early social enrichment augments adult hippocampal BDNF levels and survival of BrdU-positive cells while increasing anxiety- and ‘depression’-like behavior. J Neurosci Res 83: 965–973.
Branchi I, Karpova NN, D’Andrea I, Castren E, Alleva E (2011). Epigenetic modifications induced by early enrichment are associated with changes in timing of induction of BDNF expression. Neurosci Lett 495: 168–172.
Braun K, Seidel K, Holetschka R, Groeger N, Poeggel G (2013). Paternal deprivation alters the development of catecholaminergic innervation in the prefrontal cortex and related limbic brain regions. Brain Struct Funct 218: 859–872.
Bredy TW, Brown RE, Meaney MJ (2007). Effect of resource availability on biparental care, and offspring neural and behavioral development in the California mouse (Peromyscus californicus). Eur J Neurosci 25: 567–575.
Cameron N, Del Corpo A, Diorio J, McAllister K, Sharma S, Meaney MJ (2008). Maternal programming of sexual behavior and hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal function in the female rat. PLoS One 3: e2210.
Cameron NM, Champagne FA, Parent C, Fish EW, Ozaki-Kuroda K, Meaney MJ (2005). The programming of individual differences in defensive responses and reproductive strategies in the rat through variations in maternal care. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29: 843–865.
Cao Y, Wu R, Tai F, Zhang X, Yu P, An X et al (2014). Neonatal paternal deprivation impairs social recognition and alters levels of oxytocin and estrogen receptor alpha mRNA expression in the MeA and NAcc, and serum oxytocin in mandarin voles. Horm Behav 65: 57–65.
Carlson EA (1998). A prospective longitudinal study of attachment disorganization/disorientation. Child Dev 69: 1107–1128.
Carlson EA, Egeland B, Sroufe LA (2009). A prospective investigation of the development of borderline personality symptoms. Dev Psychopathol 21: 1311–1334.
Carpenter LL, Shattuck TT, Tyrka AR, Geracioti TD, Price LH (2011). Effect of childhood physical abuse on cortisol stress response. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 214: 367–375.
Caspi A, Sugden K, Moffitt TE, Taylor A, Craig IW, Harrington H et al (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science 301: 386–389.
Champagne DL, Bagot RC, van Hasselt F, Ramakers G, Meaney MJ, de Kloet ER et al (2008). Maternal care and hippocampal plasticity: evidence for experience-dependent structural plasticity, altered synaptic functioning, and differential responsiveness to glucocorticoids and stress. J Neurosci 28: 6037–6045.
Champagne F, Diorio J, Sharma S, Meaney MJ (2001). Naturally occurring variations in maternal behavior in the rat are associated with differences in estrogen-inducible central oxytocin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 12736–12741.
Champagne FA (2008). Epigenetic mechanisms and the transgenerational effects of maternal care. Front Neuroendocrinol 29: 386–397.
Champagne FA (2013). Early environments, glucocorticoid receptors, and behavioral epigenetics. Behav Neurosci 127: 628–636.
Champagne FA, Francis DD, Mar A, Meaney MJ (2003a). Variations in maternal care in the rat as a mediating influence for the effects of environment on development. Physiol Behav 79: 359–371.
Champagne FA, Meaney MJ (2006a). Stress during gestation alters postpartum maternal care and the development of the offspring in a rodent model. Biol Psychiatry 59: 1227–1235.
Champagne FA, Meaney MJ (2007). Transgenerational effects of social environment on variations in maternal care and behavioral response to novelty. Behav Neurosci 121: 1353–1363.
Champagne FA, Weaver IC, Diorio J, Dymov S, Szyf M, Meaney MJ (2006b). Maternal care associated with methylation of the estrogen receptor-alpha1b promoter and estrogen receptor-alpha expression in the medial preoptic area of female offspring. Endocrinology 147: 2909–2915.
Champagne FA, Weaver IC, Diorio J, Sharma S, Meaney MJ (2003b). Natural variations in maternal care are associated with estrogen receptor alpha expression and estrogen sensitivity in the medial preoptic area. Endocrinology 144: 4720–4724.
Chatterjee D, Chatterjee-Chakraborty M, Rees S, Cauchi J, de Medeiros CB, Fleming AS (2007). Maternal isolation alters the expression of neural proteins during development: ‘stroking’ stimulation reverses these effects. Brain Res 1158: 11–27.
Coplan JD, Altemus M, Mathew SJ, Smith EL, Sharf B, Coplan PM et al (2005). Synchronized maternal-infant elevations of primate CSF CRF concentrations in response to variable foraging demand. CNS Spectr 10: 530–536.
Coplan JD, Smith EL, Altemus M, Mathew SJ, Perera T, Kral JG et al (2006). Maternal-infant response to variable foraging demand in nonhuman primates: effects of timing of stressor on cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin-releasing factor and circulating glucocorticoid concentrations. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1071: 525–533.
Curley JP, Davidson S, Bateson P, Champagne FA (2009). Social enrichment during postnatal development induces transgenerational effects on emotional and reproductive behavior in mice. Front Behav Neurosci 3: 25.
Curley JP, Mashoodh R, Champagne FA (2011). Epigenetics and the origins of paternal effects. Horm Behav 59: 306–314.
D’Addario C, Dell’Osso B, Palazzo MC, Benatti B, Lietti L, Cattaneo E et al (2012). Selective DNA methylation of BDNF promoter in bipolar disorder: differences among patients with BDI and BDII. Neuropsychopharmacology 37: 1647–1655.
Davies MN, Volta M, Pidsley R, Lunnon K, Dixit A, Lovestone S et al (2012). Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. Genome Biol 13: R43.
Davis TH, Cuellar TL, Koch SM, Barker AJ, Harfe BD, McManus MT et al (2008). Conditional loss of Dicer disrupts cellular and tissue morphogenesis in the cortex and hippocampus. J Neurosci 28: 4322–4330.
Daxinger L, Whitelaw E (2012). Understanding transgenerational epigenetic inheritance via the gametes in mammals. Nat Rev Genet 13: 153–162.
Day JJ, Sweatt JD (2010). DNA methylation and memory formation. Nat Neurosci 13: 1319–1323.
De Bellis MD (2005). The psychobiology of neglect. Child Maltreat 10: 150–172.
De Wolff MS, van Ijzendoorn MH (1997). Sensitivity and attachment: a meta-analysis on parental antecedents of infant attachment. Child Dev 68: 571–591.
Dettmer AM, Novak MA, Suomi SJ, Meyer JS (2012). Physiological and behavioral adaptation to relocation stress in differentially reared rhesus monkeys: hair cortisol as a biomarker for anxiety-related responses. Psychoneuroendocrinology 37: 191–199.
El-Maarri O, Kareta MS, Mikeska T, Becker T, Diaz-Lacava A, Junen J et al (2009). A systematic search for DNA methyltransferase polymorphisms reveals a rare DNMT3L variant associated with subtelomeric hypomethylation. Hum Mol Genet 18: 1755–1768.
Engert V, Efanov SI, Dedovic K, Duchesne A, Dagher A, Pruessner JC (2010). Perceived early-life maternal care and the cortisol response to repeated psychosocial stress. J Psychiatry Neurosci 35: 370–377.
Fairbanks LA, McGuire MT (1988). Long-term effects of early mothering behavior on responsiveness to the environment in vervet monkeys. Dev Psychobiol 21: 711–724.
Fan G, Hutnick L (2005). Methyl-CpG binding proteins in the nervous system. Cell Res 15: 255–261.
Francis D, Diorio J, Liu D, Meaney MJ (1999). Nongenomic transmission across generations of maternal behavior and stress responses in the rat. Science 286: 1155–1158.
Franklin TB, Linder N, Russig H, Thony B, Mansuy IM (2011). Influence of early stress on social abilities and serotonergic functions across generations in mice. PLoS One 6: e21842.
Franklin TB, Russig H, Weiss IC, Graff J, Linder N, Michalon A et al (2010). Epigenetic transmission of the impact of early stress across generations. Biol Psychiatry 68: 408–415.
Frazier CR, Trainor BC, Cravens CJ, Whitney TK, Marler CA (2006). Paternal behavior influences development of aggression and vasopressin expression in male California mouse offspring. Horm Behav 50: 699–707.
Fuchikami M, Morinobu S, Segawa M, Okamoto Y, Yamawaki S, Ozaki N et al (2011). DNA methylation profiles of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene as a potent diagnostic biomarker in major depression. PLoS One 6: e23881.
Gapp K, Jawaid A, Sarkies P, Bohacek J, Pelczar P, Prados J et al (2014). Implication of sperm RNAs in transgenerational inheritance of the effects of early trauma in mice. Nat Neurosci 17: 667–669.
Gleason ED, Marler CA (2013). Non-genomic transmission of paternal behaviour between fathers and sons in the monogamous and biparental California mouse. Proc Biol Sci 280: 20130824.
Gorman JM, Mathew S, Coplan J (2002). Neurobiology of early life stress: nonhuman primate models. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry 7: 96–103.
Gunnar MR, Morison SJ, Chisholm K, Schuder M (2001). Salivary cortisol levels in children adopted from romanian orphanages. Dev Psychopathol 13: 611–628.
Hane AA, Fox NA (2006). Ordinary variations in maternal caregiving influence human infants’ stress reactivity. Psychol Sci 17: 550–556.
Hane AA, Henderson HA, Reeb-Sutherland BC, Fox NA (2010). Ordinary variations in human maternal caregiving in infancy and biobehavioral development in early childhood: A follow-up study. Dev Psychobiol 52: 558–567.
Harlow HF, Dodsworth RO, Harlow MK (1965). Total social isolation in monkeys. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54: 90–97.
Heim C, Shugart M, Craighead WE, Nemeroff CB (2010). Neurobiological and psychiatric consequences of child abuse and neglect. Dev Psychobiol 52: 671–690.
Hostinar CE, Stellern SA, Schaefer C, Carlson SM, Gunnar MR (2012). Associations between early life adversity and executive function in children adopted internationally from orphanages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109 (Suppl 2): 17208–17212.
Howell BR, McCormack KM, Grand AP, Sawyer NT, Zhang X, Maestripieri D et al (2013). Brain white matter microstructure alterations in adolescent rhesus monkeys exposed to early life stress: associations with high cortisol during infancy. Biol Mood Anxiety Disord 3: 21.
Jackowski A, Perera TD, Abdallah CG, Garrido G, Tang CY, Martinez J et al (2011). Early-life stress, corpus callosum development, hippocampal volumetrics, and anxious behavior in male nonhuman primates. Psychiatry Res 192: 37–44.
Jackson-Grusby L, Beard C, Possemato R, Tudor M, Fambrough D, Csankovszki G et al (2001). Loss of genomic methylation causes p53-dependent apoptosis and epigenetic deregulation. Nat Genet 27: 31–39.
Jenuwein T, Allis CD (2001). Translating the histone code. Science 293: 1074–1080.
Jia R, Tai F, An S, Zhang X, Broders H (2009). Effects of neonatal paternal deprivation or early deprivation on anxiety and social behaviors of the adults in mandarin voles. Behav Processes 82: 271–278.
Johnson JG, Cohen P, Brown J, Smailes EM, Bernstein DP (1999). Childhood maltreatment increases risk for personality disorders during early adulthood. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56: 600–606.
Kember RL, Dempster EL, Lee TH, Schalkwyk LC, Mill J, Fernandes C (2012). Maternal separation is associated with strain-specific responses to stress and epigenetic alterations to Nr3c1, Avp, and Nr4a1 in mouse. Brain Behav 2: 455–467.
Kinnally EL, Capitanio JP, Leibel R, Deng L, LeDuc C, Haghighi F et al (2010). Epigenetic regulation of serotonin transporter expression and behavior in infant rhesus macaques. Genes, Brain and Behavior 9: 575–582.
Koch CM, Andrews RM, Flicek P, Dillon SC, Karaoz U, Clelland GK et al (2007). The landscape of histone modifications across 1% of the human genome in five human cell lines. Genome Res 17: 691–707.
Koch H, McCormack K, Sanchez MM, Maestripieri D (2014). The development of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in rhesus monkeys: Effects of age, sex, and early experience. Dev Psychobiol 56: 86–95.
Kundakovic M, Lim S, Gudsnuk K, Champagne FA (2013). Sex-specific and strain-dependent effects of early life adversity on behavioral and epigenetic outcomes. Front Psychiatry 4: 78.
Kurian JR, Olesen KM, Auger AP (2010). Sex differences in epigenetic regulation of the estrogen receptor-alpha promoter within the developing preoptic area. Endocrinology 151: 2297–2305.
Labonte B, Suderman M, Maussion G, Navaro L, Yerko V, Mahar I et al (2012). Genome-wide epigenetic regulation by early-life trauma. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69: 722–731.
Lee MHS, Williams DI (1974). Changes in licking behaviour of rat mother following handling of young. Anim Behav 22: 679–681.
Lehmann J, Pryce CR, Bettschen D, Feldon J (1999). The maternal separation paradigm and adult emotionality and cognition in male and female Wistar rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 64: 705–715.
Levy F, Melo AI, Galef BG Jr., Madden M, Fleming AS (2003). Complete maternal deprivation affects social, but not spatial, learning in adult rats. Dev Psychobiol 43: 177–191.
Liu D, Diorio J, Day JC, Francis DD, Meaney MJ (2000). Maternal care, hippocampal synaptogenesis and cognitive development in rats. Nat Neurosci 3: 799–806.
Liu D, Diorio J, Tannenbaum B, Caldji C, Francis D, Freedman A et al (1997). Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress. Science 277: 1659–1662.
Lovic V, Fleming AS (2004). Artificially-reared female rats show reduced prepulse inhibition and deficits in the attentional set shifting task—reversal of effects with maternal-like licking stimulation. Behav Brain Res 148: 209–219.
Lovic V, Keen D, Fletcher PJ, Fleming AS (2011). Early-life maternal separation and social isolation produce an increase in impulsive action but not impulsive choice. Behav Neurosci 125: 481–491.
Maestripieri D, Higley JD, Lindell SG, Newman TK, McCormack KM, Sanchez MM (2006). Early maternal rejection affects the development of monoaminergic systems and adult abusive parenting in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Behav Neurosci 120: 1017–1024.
Maheu FS, Dozier M, Guyer AE, Mandell D, Peloso E, Poeth K et al (2010). A preliminary study of medial temporal lobe function in youths with a history of caregiver deprivation and emotional neglect. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 10: 34–49.
McCormack K, Sanchez MM, Bardi M, Maestripieri D (2006). Maternal care patterns and behavioral development of rhesus macaque abused infants in the first 6 months of life. Dev Psychobiol 48: 537–550.
McGoron L, Gleason MM, Smyke AT, Drury SS, Nelson CA 3rd, Gregas MC et al (2012). Recovering from early deprivation: attachment mediates effects of caregiving on psychopathology. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51: 683–693.
McGowan PO, Sasaki A, D’Alessio AC, Dymov S, Labonte B, Szyf M et al (2009). Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nat Neurosci 12: 342–348.
McGowan PO, Suderman M, Sasaki A, Huang TC, Hallett M, Meaney MJ et al (2011). Broad epigenetic signature of maternal care in the brain of adult rats. PLoS One 6: e14739.
Meaney MJ, Aitken DH, Bodnoff SR, Iny LJ, Tatarewicz JE, Sapolsky RM (1985). Early postnatal handling alters glucocorticoid receptor concentrations in selected brain regions. Behav Neurosci 99: 765–770.
Morgan CP, Bale TL (2011). Early prenatal stress epigenetically programs dysmasculinization in second-generation offspring via the paternal lineage. J Neurosci 31: 11748–11755.
Murgatroyd C, Patchev AV, Wu Y, Micale V, Bockmuhl Y, Fischer D et al (2009). Dynamic DNA methylation programs persistent adverse effects of early-life stress. Nat Neurosci 12: 1559–1566.
Narita K, Fujihara K, Takei Y, Suda M, Aoyama Y, Uehara T et al (2012). Associations among parenting experiences during childhood and adolescence, hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis hypoactivity, and hippocampal gray matter volume reduction in young adults. Hum Brain Mapp 33: 2211–2223.
Narita K, Takei Y, Suda M, Aoyama Y, Uehara T, Kosaka H et al (2010). Relationship of parental bonding styles with gray matter volume of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in young adults. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry.
Naumova OY, Lee M, Koposov R, Szyf M, Dozier M, Grigorenko EL (2012). Differential patterns of whole-genome DNA methylation in institutionalized children and children raised by their biological parents. Dev Psychopathol 24: 143–155.
O’Connor TG, Rutter M, Beckett C, Keaveney L, Kreppner JM (2000). The effects of global severe privation on cognitive competence: extension and longitudinal follow-up. English and Romanian Adoptees Study Team. Child Dev 71: 376–390.
Okano M, Bell DW, Haber DA, Li E (1999). DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell 99: 247–257.
Parker G (1990). The parental bonding instrument: a decade of research. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 25: 281–282.
Pauli A, Rinn JL, Schier AF (2011). Non-coding RNAs as regulators of embryogenesis. Nat Rev Genet 12: 136–149.
Pena CJ, Neugut YD, Champagne FA (2013). Developmental timing of the effects of maternal care on gene expression and epigenetic regulation of hormone receptor levels in female rats. Endocrinology 154: 4340–4351.
Perroud N, Dayer A, Piguet C, Nallet A, Favre S, Malafosse A et al (2014). Childhood maltreatment and methylation of the glucocorticoid receptor gene NR3C1 in bipolar disorder. Br J Psychiatry 204: 30–35.
Peterson CL, Laniel MA (2004). Histones and histone modifications. Curr Biol 14: R546–R551.
Pinkernelle J, Abraham A, Seidel K, Braun K (2009). Paternal deprivation induces dendritic and synaptic changes and hemispheric asymmetry of pyramidal neurons in the somatosensory cortex. Dev Neurobiol 69: 663–673.
Provencal N, Suderman MJ, Guillemin C, Massart R, Ruggiero A, Wang D et al (2012). The signature of maternal rearing in the methylome in rhesus macaque prefrontal cortex and T cells. J Neurosci 32: 15626–15642.
Pruessner JC, Champagne F, Meaney MJ, Dagher A (2004). Dopamine release in response to a psychological stress in humans and its relationship to early life maternal care: a positron emission tomography study using [11C]raclopride. J Neurosci 24: 2825–2831.
Razin A (1998). CpG methylation, chromatin structure and gene silencing-a three-way connection. EMBO J 17: 4905–4908.
Rice CJ, Sandman CA, Lenjavi MR, Baram TZ (2008). A novel mouse model for acute and long-lasting consequences of early life stress. Endocrinology 149: 4892–4900.
Rodenas-Ruano A, Chavez AE, Cossio MJ, Castillo PE, Zukin RS (2012). REST-dependent epigenetic remodeling promotes the developmental switch in synaptic NMDA receptors. Nat Neurosci 15: 1382–1390.
Roth TL, Lubin FD, Funk AJ, Sweatt JD (2009). Lasting epigenetic influence of early-life adversity on the BDNF gene. Biol Psychiatry 65: 760–769.
Rutter M, O’Connor TG (2004). Are there biological programming effects for psychological development? Findings from a study of Romanian adoptees. Dev Psychol 40: 81–94.
Saavedra-Rodriguez L, Feig LA (2013). Chronic social instability induces anxiety and defective social interactions across generations. Biol Psychiatry 73: 44–53.
Sanchez MM, McCormack K, Grand AP, Fulks R, Graff A, Maestripieri D (2010). Effects of sex and early maternal abuse on adrenocorticotropin hormone and cortisol responses to the corticotropin-releasing hormone challenge during the first 3 years of life in group-living rhesus monkeys. Dev Psychopathol 22: 45–53.
Sapolsky RM, Meaney MJ, McEwen BS (1985). The development of the glucocorticoid receptor system in the rat limbic brain. III. Negative-feedback regulation. Brain Res 350: 169–173.
Sato F, Tsuchiya S, Meltzer SJ, Shimizu K (2011). MicroRNAs and epigenetics. FEBS J 278: 1598–1609.
Schmidt MV (2011). Animal models for depression and the mismatch hypothesis of disease. Psychoneuroendocrinology 36: 330–338.
Seidel K, Poeggel G, Holetschka R, Helmeke C, Braun K (2011). Paternal deprivation affects the development of corticotrophin-releasing factor-expressing neurones in prefrontal cortex, amygdala and hippocampus of the biparental Octodon degus. J Neuroendocrinol 23: 1166–1176.
Smyke AT, Dumitrescu A, Zeanah CH (2002). Attachment disturbances in young children. I: the continuum of caretaking casualty. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 41: 972–982.
Spinelli S, Chefer S, Carson RE, Jagoda E, Lang L, Heilig M et al (2010). Effects of early-life stress on serotonin(1A) receptors in juvenile Rhesus monkeys measured by positron emission tomography. Biol Psychiatry 67: 1146–1153.
Spinelli S, Chefer S, Suomi SJ, Higley JD, Barr CS, Stein E (2009). Early-life stress induces long-term morphologic changes in primate brain. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66: 658–665.
Sroufe LA (2005). Attachment and development: a prospective, longitudinal study from birth to adulthood. Attach Hum Dev 7: 349–367.
Stanton ME, Gutierrez YR, Levine S (1988). Maternal deprivation potentiates pituitary-adrenal stress responses in infant rats. Behav Neurosci 102: 692–700.
Suderman M, Borghol N, Pappas JJ, Pinto Pereira SM, Pembrey M, Hertzman C et al (2014). Childhood abuse is associated with methylation of multiple loci in adult DNA. BMC Med Genomics 7: 13.
Suomi SJ (1991). Early stress and adult emotional reactivity in rhesus monkeys. Ciba Found Symp 156: 171–183.
Suomi SJ, Harlow HF, Kimball SD (1971). Behavioral effects of prolonged partial social isolation in the rhesus monkey. Psychol Rep 29: 1171–1177.
Suri D, Veenit V, Sarkar A, Thiagarajan D, Kumar A, Nestler EJ et al (2013). Early stress evokes age-dependent biphasic changes in hippocampal neurogenesis, BDNF expression, and cognition. Biol Psychiatry 73: 658–666.
Tahiliani M, Mei P, Fang R, Leonor T, Rutenberg M, Shimizu F et al (2007). The histone H3K4 demethylase SMCX links REST target genes to X-linked mental retardation. Nature 447: 601–605.
Tang AC (2001). Neonatal exposure to novel environment enhances hippocampal-dependent memory function during infancy and adulthood. Learn Mem 8: 257–264.
Tang AC, Akers KG, Reeb BC, Romeo RD, McEwen BS (2006). Programming social, cognitive, and neuroendocrine development by early exposure to novelty. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 15716–15721.
Taylor SM, Jones PA (1985). Cellular differentiation. Int J Obes 9 (Suppl 1): 15–21.
Toda H, Boku S, Nakagawa S, Inoue T, Kato A, Takamura N et al (2014). Maternal separation enhances conditioned fear and decreases the mRNA levels of the neurotensin receptor 1 gene with hypermethylation of this gene in the rat amygdala. PLoS One 9: e97421.
Tottenham N, Hare TA, Millner A, Gilhooly T, Zevin JD, Casey BJ (2011). Elevated amygdala response to faces following early deprivation. Dev Sci 14: 190–204.
Trickett P, McBride-Chang C (1995). The developmental impact of different forms of child abuse and neglect. Devel Rev 15: 11–37.
Tyrka AR, Price LH, Marsit C, Walters OC, Carpenter LL (2012). Childhood adversity and epigenetic modulation of the leukocyte glucocorticoid receptor: preliminary findings in healthy adults. PLoS One 7: e30148.
Uher R, Weaver IC (2014). Epigenetic traces of childhood maltreatment in peripheral blood: a new strategy to explore gene-environment interactions. Br J Psychiatry 204: 3–5.
van Harmelen AL, van Tol MJ, van der Wee NJ, Veltman DJ, Aleman A, Spinhoven P et al (2010). Reduced medial prefrontal cortex volume in adults reporting childhood emotional maltreatment. Biol Psychiatry 68: 832–838.
van Ijzendoorn MH, Schuengel C, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ (1999). Disorganized attachment in early childhood: meta-analysis of precursors, concomitants, and sequelae. Dev Psychopathol 11: 225–249.
Wang A, Nie W, Li H, Hou Y, Yu Z, Fan Q et al (2014). Epigenetic upregulation of corticotrophin-releasing hormone mediates postnatal maternal separation-induced memory deficiency. PLoS One 9: e94394.
Wang J, Tai F, Yan X, Yu P (2012). Paternal deprivation alters play-fighting, serum corticosterone and the expression of hypothalamic vasopressin and oxytocin in juvenile male mandarin voles. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 198: 787–796.
Wang XD, Rammes G, Kraev I, Wolf M, Liebl C, Scharf SH et al (2011). Forebrain CRF(1) modulates early-life stress-programmed cognitive deficits. J Neurosci 31: 13625–13634.
Weaver IC, Cervoni N, Champagne FA, D’Alessio AC, Sharma S, Seckl JR et al (2004). Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior. Nat Neurosci 7: 847–854.
Weaver IC, Meaney MJ, Szyf M (2006). Maternal care effects on the hippocampal transcriptome and anxiety-mediated behaviors in the offspring that are reversible in adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 3480–3485.
Wu Y, Patchev AV, Daniel G, Almeida OF, Spengler D (2014). Early-life stress reduces DNA methylation of the pomc gene in male mice. Endocrinology 155: 1751–1762.
Yu P, An S, Tai F, Zhang X, He F, Wang J et al (2012). The effects of neonatal paternal deprivation on pair bonding, NAcc dopamine receptor mRNA expression and serum corticosterone in mandarin voles. Horm Behav 61: 669–677.
Zhang TY, Hellstrom IC, Bagot RC, Wen X, Diorio J, Meaney MJ (2010). Maternal care and DNA methylation of a glutamic acid decarboxylase 1 promoter in rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 30: 13130–13137.
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by NIMH funding 1P50MH090964-01A1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kundakovic, M., Champagne, F. Early-Life Experience, Epigenetics, and the Developing Brain. Neuropsychopharmacol 40, 141–153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2014.140
This article is cited by
-
Early life adversity as a risk factor for cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease
Translational Neurodegeneration (2023)
-
Interaction of the pre- and postnatal environment in the maternal immune activation model
Discover Mental Health (2023)
-
Maternal attachment insecurity, maltreatment history, and depressive symptoms are associated with broad DNA methylation signatures in infants
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Cell-type-specific epigenetic effects of early life stress on the brain
Translational Psychiatry (2022)
-
Family Context and ADHD Symptoms in Middle Childhood: an Explanatory Model
Journal of Child and Family Studies (2022)