Abstract
Background:
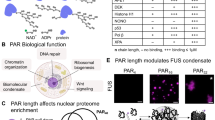
Poly-ADP-ribosylation (PAR), a reversible post-translational modification of cellular proteins, is involved in various cellular and molecular processes including carcinogenesis (Althaus & Richter, 1987; Jacobson & Jacobson, 1989; Poirier & Moreau, 1992; Boulikas, 1993; Sharan, 2009). ADP-ribose polymer adducts are added onto target cellular proteins by this metabolic process. We hypothesize that a decrease in the concentration of total poly-ADP-ribose adducts of peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL) proteins strongly correlates with incidence of human cancer. Methods: A novel, sensitive and convenient immunoprobe assay of poly-ADP-ribose adducts of cellular proteins has been employed using slot blots of total PBL lysate (Sharan et al, 1998; 2005; Sharan, 2009). This assay quantifies the metabolic concentration of poly-ADP-ribose adducts of cellular proteins.
Results:
Using the immunoprobe assay, we show a statistically significant (P ≤ 0.001) reduction (~ 42 to 49%) in the level of poly-ADP-ribose adducts of PBL proteins of patients with advanced cancers of head & neck (H & N) region (comprising fourteen distinct types of cancers at different sites), breast and cervix in comparison to healthy controls. Conclusion: These preliminary findings may imply potential utility of the poly-ADP-ribose adducts of PBL proteins as a novel and general biomarker of human cancers with potentials of clinical and epidemiological applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakadong, R., Kataki, A. & Sharan, R. ADP-ribose polymer - a novel and general biomarker of human cancers of head & neck, breast, and cervix. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4650.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.4650.1