Abstract
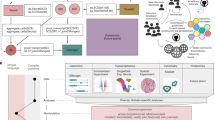
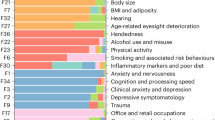
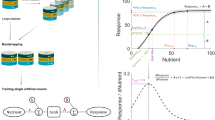
Biology is rapidly developing into a data-driven science and faces not only the challenge of coping with an ever growing amount of data but also that of interpreting its complex diversity. The requirement of systems biology to connect different levels of biological research leads directly to a need for large scale data integration. The nutritional phenotype database (dbNP) addresses this challenge for nutrigenomics. A particularly urgent objective in coping with the data avalanche is making biologically meaningful information accessible to the researcher. In this presentation we will describe how we intend to meet this objective with the nutritional phenotype database. We will outline relevant parts of the system architecture, describe the kinds of data to be managed, and show how the system can support retrieval of biological meaningful information by means of biological profiles, pathways and ontologies in full-text and structured queries. Our presentation will point out critical points and will describe several technical hurdles and demonstrate how pathway analysis in the omics modules of the nutritional phenotype database can improve the functionality of queries and comparisons of nutrition studies. Directions for future research will be given. Through development of a ranking system for the results of free text queries we will aim to improve the user interaction with dbNP. Profiles describing the relevant changes in biological pathways and GO levels will be used in a mathematical way to calculate distances between the biological outcomes of experiments and will allow the user to ask intuitive questions like “what experiments showed an effect on apoptosis?” or “which other studies showed an effect that looked like mine?”.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evelo, C. The nutritional phenotype database*. A real data structure for systems biology. Nat Prec (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.5141.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2010.5141.1