Abstract
Background & Aim:
The immunopathogenesis of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a matter of great controversy. The imbalance of T-helper lymphocyte cell cytokine production was believed to play an important pathogenic role in chronic viral hepatitis. Occult hepatitis C infection is regarded as a new entity that should be considered when diagnosing patients with a liver disease of unknown origin. The aim of this study was to determine serum T-helper 1 and T-helper 2 cytokine production in patients with occult HCV infection and its role in pathogenesis versus chronic viral hepatitis C infection.
Methods:
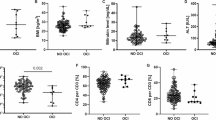
Serum levels of cytokines of T-helper 1 (IL-2, IFN-[gamma]) and T-helper 2 (IL-4) were measured in 27 patients with occult HCV infection and 50 patients with chronic hepatitis C infection.
Results:
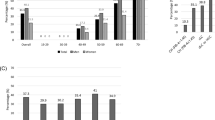
The levels of the T-helper 1 cytokines, IL-2 and IFN-[gamma], were highly and significantly increased in patients with chronic HCV infection as compared with occult HCV infection (p<0.001). The T-helper 2 cytokine IL-4 was highly and significantly increased in occult HCV infection as compared with chronic HCV infection (p<0.001). Necroinflammation (P<0.001) fibrosis (P<0.001) and cirrhosis (P =0.03) were significantly increased in chronic HCV than occult HCV.
Conclusion:
Patients with occult HCV infection exhibited distinct immunoregulatory cytokine patterns, favoring viral persistence in the liver in spite of its absence from peripheral blood and explaining the less aggressive course of this disease entity than chronic hepatitis C virus infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mousa, N., Abousamra, N., Azza Abdel-Aziz, A. et al. Distinct cytokine patterns in Occult Hepatitis C and Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Nat Prec (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2011.6654.1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/npre.2011.6654.1