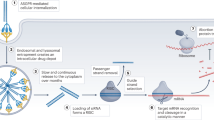
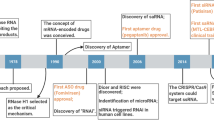
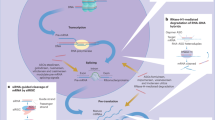
Abstract
RNA interference (RNAi) quietly crept into biological research in the 1990s when unexpected gene-silencing phenomena in plants and flatworms first perplexed scientists. Following the demonstration of RNAi in mammalian cells in 2001, it was quickly realized that this highly specific mechanism of sequence-specific gene silencing might be harnessed to develop a new class of drugs that interfere with disease-causing or disease-promoting genes. Here we discuss the considerations that go into developing RNAi-based therapeutics starting from in vitro lead design and identification, to in vivo pre-clinical drug delivery and testing. We conclude by reviewing the latest clinical experience with RNAi therapeutics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fire, A. et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 391, 806–811 (1998).
Elbashir, S. M. et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411, 494–498 (2001).
Song, E. et al. RNA interference targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nature Med. 9, 347–351 (2003).
Meister, G. & Tuschl, T. Mechanisms of gene silencing by double-stranded RNA. Nature 431, 343–349 (2004).
Kim, D. H. & Rossi, J. J. Strategies for silencing human disease using RNA interference. Nature Rev. Genet. 8, 173–184 (2007).
He, L. & Hannon, G. J. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nature Rev. Genet. 5, 522–531 (2004).
Matranga, C. et al. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of siRNA into Ago2-containing RNAi enzyme complexes. Cell 123, 607–620 (2005).
Liu, J. et al. MicroRNA-dependent localization of targeted mRNAs to mammalian P-bodies. Nature Cell Biol. 7, 719–723 (2005).
Hutvagner, G. & Zamore, P. D. A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science 297, 2056–2060 (2002).
Grimm, D. et al. Fatality in mice due to oversaturation of cellular microRNA/short hairpin RNA pathways. Nature 441, 537–541 (2006).
Pei, Y. & Tuschl, T. On the art of identifying effective and specific siRNAs. Nature Methods 3, 670–676 (2006).
Reynolds, A. et al. Rational siRNA design for RNA interference. Nature Biotechnol. 22, 326–330 (2004).
Kim, D. H. et al. Synthetic dsRNA Dicer substrates enhance RNAi potency and efficacy. Nature Biotechnol. 23, 222–226 (2005).
Reynolds, A. et al. Induction of the interferon response by siRNA is cell type- and duplex length-dependent. RNA 6, 988–993 (2006).
Schwarz, D. S. et al. Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex. Cell 115, 199–208 (2003).
Khvorova, A., Reynolds, A. & Jayasena, S. D. Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell 115, 209–216 (2003).
Aza-Blanc, P. et al. Identification of modulators of TRAIL-induced apoptosis via RNAi-based phenotypic screening. Mol. Cell 12, 627–637 (2003).
Schwarz, D. S. et al. Designing siRNA that distinguish between genes that differ by a single nucleotide. PLoS Genetics 2, 1307–1318 (2006).
Jackson, A. L. et al. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nature Biotech. 21, 635–637 (2003).
Lin, X. et al. siRNA-mediated off-target gene silencing triggered by a 7 nt complementation. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 4527–4535 (2005).
Qiu, S., Adema, C. M. & Lane, T. A computational study of off-target effects of RNA interference. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 1834–1847 (2005).
Jackson, A. L. et al. Widespread siRNA off-target transcript silencing mediated by seed region sequence complementarity. RNA 12, 1179–1187 (2006).
Birmingham, A. et al. 3′ UTR seed matches, but not overall identity, are associated with RNAi off-targets. Nature Methods 3, 199–204 (2006).
Jackson, A. L. et al. Position-specific chemical modification of siRNAs reduces off-target transcript silencing. RNA 12, 1197–1205 (2006).
Fedorov, Y. et al. Off-target effects by siRNA can induce toxic phenotype. RNA 12, 1188–1196 (2006).
Schlee, M. et al. SiRNA and isRNA: two edges of one sword. Mol. Ther. 14, 463–470 (2006).
Hornung, V. et al. Sequence-specific potent induction of IFN-α by short interfering RNA in plasmacytoid dendritic cells through TLR7. Nature Med. 11, 263–270 (2005).
Judge, A. D. et al. Sequence-dependent stimulation of the mammalian innate immune response by synthetic siRNA. Nature Biotechnol. 23, 457–462 (2005).
Judge, A. D. et al. Design of non-inflammatory synthetic siRNA mediating potent gene silencing in vivo. Mol. Ther. 13, 494–505 (2006).
Layzer, J. M. et al. In vivo activity of nuclease-resistant siRNAs. RNA 10, 766–771 (2004).
Choung, S. et al. Chemical modification of siRNAs to improve serum stability without loss of efficacy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 342, 919–927 (2006).
Allerson, C. R. et al. Fully 2′-modified oligonucleotide duplexes with improved in vitro potency and stability compared to unmodified small interfering RNA. J. Med. Chem. 48, 901–904 (2005).
de Fougerolles, A. R. et al. RNA interference in vivo: toward synthetic small inhibitory RNA-based therapeutics. Methods Enzymol. 392, 278–296 (2005).
Morrissey, D. V. et al. Activity of stabilized short interfering RNA in a mouse model of hepatitis B virus replication. Hepatology 41, 1349–1356 (2005).
Bartlett, D. W. & Davis, M. E. Insights into the kinetics of siRNA-mediated gene silencing from live-cell and live-animal bioluminescent imaging. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, 322–333 (2006).
Raemdonck, K. et al. In situ analysis of single-stranded and duplex siRNA integrity in living cells. Biochemistry 45, 10614–10623 (2006).
Fedorov, Y. et al. Different delivery methods-different expression profiles. Nature Methods 2, 241 (2005).
Aigner, A. Gene silencing through RNA interference (RNAi) in vivo: strategies based on the direct application of siRNAs. J. Biotechnology 124, 12–25 (2006).
Bumcrot, D. et al. RNAi therapeutics: a potential new class of pharmaceutical drugs. Nature Chem. Biol. 2, 711–719 (2006).
Reich, S. J. et al. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting VEGF effectively inhibits ocular neovascularization in a mouse model. Mol. Vision 9, 210–216 (2003).
Tolentino, M. J. et al. Intravitreal injection of vascular endothelial growth factor small interfering RNA inhibits growth and leakage in a nonhuman primate, laser-induced model of choroidal neovascularization. Retina 24, 132–138 & 660–661 (2004).
Shen, J. et al. Suppression of ocular neovascularization with siRNA targeting VEGF receptor 1. Gene Ther. 13, 225–234 (2006).
Nakamura, H. et al. RNA interference targeting transforming growth factor-β type II receptor suppresses ocular inflammation and fibrosis. Mol. Vision 10, 703–711 (2004).
Bitko, V. et al. Inhibition of respiratory viruses by nasally administered siRNA. Nature Med. 11, 50–55 (2005).
Li, B. J. et al. Using siRNA in prophylactic and therapeutic regimens against SARS coronavirus in Rhesus macaque. Nature Med. 11, 944–951 (2005).
Zhang, X. et al. Small interfering RNA targeting heme oxygenase-1 enhances ischemia-reperfusion-induced lung apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 10677–10684 (2004).
Lomas-Neira, J. L. et al.. In vivo gene silencing (with siRNA) of pulmonary expression of MIP-2 versus KC results in divergent effects on hemorrhage-induced, neutrophil-mediated septic acute lung injury. J. Leukoc. Biol. 77, 846–853 (2005).
Perl, M. et al. Silencing of Fas, but not caspase-8, in lung epithelial cells ameliorates pulmonary apoptosis, inflammation and neutrophil influx after hemorrhagic shock and sepsis. Am. J. Pathol. 167, 1545–1559 (2005).
Bhandari, V. et al. Hypoxia causes angiopoietin-2-mediated acute lung injury and necrotic cell death. Nature Med. 12, 1286–1292 (2006).
Matsuyama, W. et al. Suppression of discoidin domain receptor 1 by RNA interference attenuates lung inflammation. J. Immunol. 176, 1928–1936 (2006).
Makimura, H. et al. Reducing hypothalamic AGRP by RNA interference increases metabolic rate and decreases body weight without influencing food intake. BMC Neurosci. 3, 18 (2002).
Thakker, D. R. et al. Neurochemical and behavioral consequences of widespread gene knockdown in the adult mouse brain by using nonviral RNA interference. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 17270–17275 (2004).
Thakker, D. R. et al. siRNA-mediated knockdown of the serotonin transporter in the adult mouse brain. Mol. Psychiatry 10, 782–789 (2005).
Dorn, G. et al. SiRNA relieves chronic neuropathic pain. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, e49 (2004).
Luo, M. C. et al. An efficient intrathecal delivery of small interfering RNA to the spinal cord and peripheral neurons. Mol. Pain 1, 29 (2005).
Tan, P. H. et al. Gene knockdown with intrathecal siRNA of NMDA receptor NR2B subunit reduces formalin-induced nociception in the rat. Gene Ther. 12, 59–66 (2005).
Kumar, P. et al. A single siRNA suppresses fatal encephalitis induced by two different flaviviruses. PLoS Med. 3, 505–514 (2006).
Biessen, E. A. et al. Targeted delivery of oligodeoxynucleotides to parenchymal liver cells in vivo. Biochem. J. 340, 783–792 (1999).
Soutschek, J. et al. Therapeutic silencing of an endogenous gene by systemic administration of modified siRNAs. Nature 432, 173–178 (2004).
Muratovska, A. & Eccles, M. R. Conjugate for efficient delivery of short interfering RNA (siRNA) into mammalian cells. FEBS Letters 558, 63–68 (2004).
Hu-Lieskovan, S. et al. Sequence-specific knockdown of EWS-FLI1 by targeted, nonviral delivery of small interfering RNA inhibits tumor growth in a murine model of metastatic Ewing's sarcoma. Cancer Res. 65, 8984–8992 (2005).
Kim, S. H. et al. Target-specific gene silencing by siRNA plasmid DNA complexed with folate-modified poly(ethylenimine). J. Controlled Release 104, 223–232 (2005).
Schiffelers, R. M. et al. Cancer siRNA therapy by tumor selective delivery with ligand-targeted sterically stabilized nanoparticle. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, e149 (2004).
McNamara, J. O. et al. Cell type-specific delivery of siRNAs with aptamer-siRNA chimeras. Nature Biotechnol. 24, 1005–1015 (2006).
Chu, T. C. et al. Aptamer mediated siRNA delivery. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e73 (2006).
Nimjee, S. M., Rusconi, C. P. & Sullenger B.A. Aptamers: an emerging class of therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Med. 56, 555–583 (2005).
Torchilin, V. P. Recent approaches to intracellular delivery of drugs and DNA and organelle targeting. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 8, 343–375 (2006).
Li, W. Szoka F. C. Lipid-based nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery. Pharm. Res. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 24, 438–449 (2007).
Zimmermann, T. S. et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing in non-human primates. Nature 441, 111–114 (2006).
Morrissey, D. V. et al. Potent and persistent in vivo anti-HBV activity of chemically modified siRNAs. Nature Biotechnol. 23, 1002–1007 (2005).
Geisbert, T. W. et al. Postexposure protection of guinea pigs against lethal ebola virus challenge is conferred by RNA interference. J. Infect. Dis. 193, 1650–1657 (2006).
Khoury, M. et al. Efficient new cationic liposome formulation for systemic delivery of small interfering RNA silencing tumor necrosis factor-α in experimental arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatism 54, 1867–1877 (2006).
Miyawaki-Shimizu, K. et al. SiRNA-induced caveolin-1 knockdown in mice increases lung vascular permeability via the junctional pathway Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 290, L405–L413 (2006).
Niu, X. Y. et al. Inhibition of HPV 16 E6 oncogene expression by RNA interference in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 16, 743–751 (2006).
Palliser, D. et al. An siRNA-based microbicide protects mice from lethal herpes simplex virus 2 infection. Nature 439, 89–94 (2006).
Zhang, Y. et al. Engineering mucosal RNA interference in vivo. Mol. Ther. 4, 336–342 (2006).
Juliano, R. L. Peptide-oligonucleotide conjugates for the delivery of antisense and siRNA. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 7, 132–136 (2005).
Merdan, T. et al. Prospects for cationic polymers in gene and oligonucleotide therapy against cancer. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 54, 715–758 (2002).
Li, W, Nicol, F. & Szoka F. C. GALA: a designed synthetic pH-responsive amphipathic peptide with applications in drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56, 967–985 (2004).
Oliveira, S. et al. Fusogenic peptides enhance endosomal escape improving siRNA-induced silencing of oncogenes. Int. J. Pharm. 2007 331, 211–214 (2007).
Boussif, O. et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7297–7301 (1995).
Ge, Q. et al. Inhibition of influenza virus production in virus-infected mice by RNA interference. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 8676–8681 (2004).
Grzelinski, M. et al. RNA interference-mediated gene silencing of pleiotrophin through polyethylenimine-complexed small interfering RNAs in vivo exerts antitumoral effects in glioblastoma xenografts. Hum. Gene Ther. 17, 751–766 (2006).
Urban-Klein, B. et al. RNAi-mediated gene-targeting through systemic application of polyethylenimine (PEI)-complexed siRNA in vivo. Gene Ther. 12, 461–466 (2005).
Thomas, M. et al. Full deacylation of polyethylenimine dramatically boosts its gene delivery efficiency and specificity to mouse lung. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 5679–5684 (2005).
Grayson, A. C. et al. Biophysical and structural characterization of polyethylenimine-mediated siRNA delivery in vitro. Pharm. Res. 23, 1868–1876 (2006).
Werth, S. et al. A low molecular weight fraction of polyethylenimine (PEI) displays increased transfection efficiency of DNA and siRNA in fresh or lyophilized complexes. J. Controlled Release 112, 257–270 (2006).
Read, M. L. et al. A versatile reducible polycation-based system for efficient delivery of a broad range of nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, e86 (2005).
Howard, K. A. et al. RNA interference in vitro and in vivo using a novel chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle system. Mol. Ther. 14, 476–484 (2006).
Pille, J. Y. et al. Intravenous delivery of anti-rhoA small interfering RNA loaded in nanoparticles of chitosan in mice: safety and efficacy in xenografted aggressive breast cancer. Human Gene Ther. 17, 1019–1026 (2006).
Heidel, J. D. et al. Administration in non-human primates of escalating intravenous doses of targeted nanoparticles containing ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 siRNA. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 5715–5721 (2007).
Takei, Y. et al. A small interfering RNA targeting vascular endothelial growth factor as cancer therapeutics. Cancer Res. 64, 3365–3370 (2004).
Takeshita, F. & Ochiya, T. Therapeutic potential of RNA interference against cancer. Cancer Sci. 97, 689–696 (2006).
Khan, A. et al. Sustained polymeric delivery of gene silencing antisense ODNs, siRNA, DNAzymes and ribozymes: in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Drug Target 12, 393–404 (2004).
Kang, H. et al. Tat-conjugated PAMAM dendrimers as delivery agents for antisense and siRNA oligonucleotides. Pharm. Res. 22, 2099–2106 (2005).
Zatsepin, T. S. et al. Conjugates of oligonucleotides and analogues with cell penetrating peptides as gene silencing agents. Curr. Pharm. Des. 11, 3639–3654 (2005).
Simeoni, F. et al. Insight into the mechanism of the peptide-based gene delivery system MPG: implications for delivery of siRNA into mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 2717–2724 (2003).
Davidson, T. J. et al. Highly efficient small interfering RNA delivery to primary mammalian neurons induces micro-RNA-like effects before mRNA degragation. J. Neurosci. 24, 10040–10046 (2004).
Kim, W. J. et al. Cholesteryl oligoarginine delivering vascular endothelial growth factor siRNA effectively inhibits tumor growth in colon adenocarcinoma. Mol. Ther. 14, 343–350 (2006).
Longmuir, K. J. et al. Effective targeting of liposomes to liver and hepatocytes in vivo by incorporation of a Plasmodium amino acid sequence. Pharm. Res. 23, 759–769 (2006).
Song, E. et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nature Biotechnol. 23, 709–717 (2005).
Peer, D. et al. Selective gene silencing in activated leukocytes by targeting siRNAs to the integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 4095–4100 (2007).
Jabs, D. A. et al. Fomivirsen for the treatment of cytomegalovirus retinitis. Amer. J. Ophthalmol. 133, 552–556 (2002).
Gragoudas, E. S. et al. Pegaptanib for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 351, 2805–2816 (2004).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank their collaborators and colleagues for useful discussions. J.L. was supported by NIH grants AI056900 and AI070302.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Antonin de Fougerolles, Hans-Peter Vornlocher and John Maraganore are employees of Alnylam Pharmaceuticals and have financial interests in Alnylam. Judy Lieberman is a member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Alnylam.
Related links
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Fougerolles, A., Vornlocher, HP., Maraganore, J. et al. Interfering with disease: a progress report on siRNA-based therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6, 443–453 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2310
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2310
This article is cited by
-
Oral delivery of RNAi for cancer therapy
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2023)
-
Development of elastin-like polypeptide for targeted specific gene delivery in vivo
Journal of Nanobiotechnology (2020)
-
siRNA therapeutics: a clinical reality
Science China Life Sciences (2020)
-
The microgravity enhanced polymer-mediated siRNA gene silence by improving cellular uptake
Biophysics Reports (2020)
-
Selective Capture and Purification of MicroRNAs and Intracellular Proteins through Antisense-vectorized Magnetic Nanobeads
Scientific Reports (2019)