Abstract
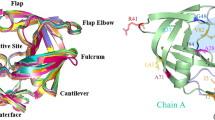
DNA binding by NFAT1 as a dimer has been implicated in the activation of host and viral genes. Here we report a crystal structure of NFAT1 bound cooperatively as a dimer to the highly conserved κB site from the human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) long terminal repeat (LTR). This structure reveals a new mode of dimerization and protein-DNA recognition by the Rel homology region (RHR) of NFAT1. The two NFAT1 monomers form a complete circle around the κB DNA through protein-protein interactions mediated by both their N- and C-terminal subdomains. The major dimer interface, formed by the C-terminal domain, is asymmetric and substantially different from the symmetric dimer interface seen in other Rel family proteins. Comparison to other NFAT structures, including NFAT5 and the NFAT1–Fos-Jun–ARRE2 complex, reveals that NFAT1 adopts different conformations and its protein surfaces mediate distinct protein-protein interactions in the context of different DNA sites.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to the full article PDF.
USD 39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Rao, A., Luo, C. & Hogan, P.G. Transcription factors of the NFAT family: regulation and function. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 707–747 (1997).
Crabtree, G.R. & Olson, E.N. NFAT signaling: choreographing the social lives of cells. Cell 109 (suppl.), S67–S79 (2002).
Northrop, J.P. et al. NF-AT components define a family of transcription factors targeted in T-cell activation. Nature 369, 497–502 (1994).
Chen, L., Glover, J.N., Hogan, P.G., Rao, A. & Harrison, S.C. Structure of the DNA-binding domains from NFAT, Fos and Jun bound specifically to DNA. Nature 392, 42–48 (1998).
Ghosh, G., van Duyne, G., Ghosh, S. & Sigler, P.B. Structure of NF-κB p50 homodimer bound to a κB site. Nature 373, 303–310 (1995).
Muller, C.W., Rey, F.A., Sodeoka, M., Verdine, G.L. & Harrison, S.C. Structure of the NF-κB p50 homodimer bound to DNA. Nature 373, 311–317 (1995).
Chen, F.E., Huang, D.B., Chen, Y.Q. & Ghosh, G. Crystal structure of p50/p65 heterodimer of transcription factor NF-κB bound to DNA. Nature 391, 410–413 (1998).
Stroud, J.C., Lopez-Rodriguez, C., Rao, A. & Chen, L. Structure of a TonEBP-DNA complex reveals DNA encircled by a transcription factor. Nat. Struct. Biol. 9, 90–94 (2002).
Lopez-Rodriguez, C. et al. Bridging the NFAT and NF-κB families: NFAT5 dimerization regulates cytokine gene transcription in response to osmotic stress. Immunity 15, 47–58 (2001).
Miyakawa, H., Woo, S.K., Dahl, S.C., Handler, J.S. & Kwon, H.M. Tonicity-responsive enhancer binding protein, a Rel-like protein that stimulates transcription in response to hypertonicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2538–2542 (1999).
Chen, L. et al. Only one of the two DNA-bound orientations of AP-1 found in solution cooperates with NFATp. Curr. Biol. 5, 882–889 (1995).
Chytil, M. & Verdine, G.L. The Rel family of eukaryotic transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 6, 91–100 (1996).
Hoey, T., Sun, Y.L., Williamson, K. & Xu, X. Isolation of two new members of the NF-AT gene family and functional characterization of the NF-AT proteins. Immunity 2, 461–472 (1995).
McCaffrey, P.G., Goldfeld, A.E. & Rao, A. The role of NFATp in cyclosporin A-sensitive tumor necrosis factor-α gene transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 30445–30450 (1994).
Chen, L. Combinatorial gene regulation by eukaryotic transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 9, 48–55 (1999).
Macian, F., Garcia-Rodriguez, C. & Rao, A. Gene expression elicited by NFAT in the presence or absence of cooperative recruitment of Fos and Jun. EMBO J. 19, 4783–4795 (2000).
Macian, F. et al. Transcriptional mechanisms underlying lymphocyte tolerance. Cell 109, 719–731 (2002).
Kinoshita, S. et al. The T cell activation factor NF-ATc positively regulates HIV-1 replication and gene expression in T cells. Immunity 6, 235–44 (1997).
Kinoshita, S., Chen, B.K., Kaneshima, H. & Nolan, G.P. Host control of HIV-1 parasitism in T cells by the nuclear factor of activated T cells. Cell 95, 595–604 (1998).
Cron, R.Q. et al. NFAT1 enhances HIV-1 gene expression in primary human CD4 T cells. Clin. Immunol. 94, 179–191 (2000).
Robichaud, G.A., Barbeau, B., Fortin, J.F., Rothstein, D.M. & Tremblay, M.J. Nuclear factor of activated T cells is a driving force for preferential productive HIV-1 infection of CD45RO-expressing CD4+ T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 23733–23741 (2002).
Chen, B.K., Feinberg, M.B. & Baltimore, D. The κB sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat enhance virus replication yet are not absolutely required for viral growth. J. Virol. 71, 5495–5504 (1997).
Jacobs, M.D. & Harrison, S.C. Structure of an IκBα/NF-κB complex. Cell 95, 749–758 (1998).
Huxford, T., Huang, D.B., Malek, S. & Ghosh, G. The crystal structure of the IκBα/NF-κB complex reveals mechanisms of NF-κB inactivation. Cell 95, 759–770 (1998).
Jin, L. et al. An asymmetric NFAT1 dimer on a pseudo-palindromic κB-like DNA site. Nat. Struct. Biol. advance online publication, 31 August 2003 (doi:10.1038/nsb975).
Oum, J.H. et al. Molecular mechanism of NFAT family proteins for differential regulation of the IL-2 and TNF-α promoters. Mol. Cell 13, 77–84 (2002).
McCaffrey, P.G., Jain, J., Jamieson, C., Sen, R. & Rao, A. A T cell nuclear factor resembling NF-AT binds to an NF-κB site and to the conserved lymphokine promoter sequence 'cytokine-1'. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 1864–1871 (1992).
Chen, Y.Q., Ghosh, S. & Ghosh, G. A novel DNA recognition mode by the NF-κB p65 homodimer. Nat. Struct. Biol. 5, 67–73 (1998).
Scully, K.M. et al. Allosteric effects of Pit-1 DNA sites on long-term repression in cell type specification. Science 290, 1127–1131 (2000).
Lefstin, J.A. & Yamamoto, K.R. Allosteric effects of DNA on transcriptional regulators. Nature 392, 885–888 (1998).
Escalante, C.R., Shen, L., Thanos, D. & Aggarwal, A.K. Structure of NF-κB p50/p65 heterodimer bound to the PRDII DNA element from the interferon-β promoter. Structure 10, 383–391 (2002).
Sen, R. & Baltimore, D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 46, 705–716 (1986).
Nabel, G. & Baltimore, D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature 326, 711–713 (1987).
Goldfeld, A.E., McCaffrey, P.G., Strominger, J.L. & Rao, A. Identification of a novel cyclosporin-sensitive element in the human tumor necrosis factor-α gene promoter. J. Exp. Med. 178, 1365–1379 (1993).
Okamoto, S. et al. The interleukin-8 AP-1 and κB-like sites are genetic end targets of FK506-sensitive pathway accompanied by calcium mobilization. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 8582–8589 (1994).
Zhou, P., Sun, L.J., Dotsch, V., Wagner, G. & Verdine, G.L. Solution structure of the core NFATC1/DNA complex. Cell 92, 687–696 (1998).
Schreiber, S.L. & Crabtree, G.R. The mechanism of action of cyclosporin A and FK506. Immunol. Today 13, 136–142 (1992).
Molkentin, J.D. et al. A calcineurin-dependent transcriptional pathway for cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 93, 215–228 (1998).
Kiani, A., Rao, A. & Aramburu, J. Manipulating immune responses with immunosuppressive agents that target NFAT. Immunity 12, 359–372 (2000).
Aramburu, J. et al. Affinity-driven peptide selection of an NFAT inhibitor more selective than cyclosporin A. Science 285, 2129–2133 (1999).
Otwinowski, Z. In Proceedings of the CCP4 Study Weekend (eds. Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Burley, S.) 56–62 (Daresbury Laboratories, Warrington, UK, 1993).
Brunger, A.T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A 54, 905–921 (1998).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47 (Pt. 2), 110–119 (1991).
Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4. CCP4 Suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Carson, M. Ribbons 2.0. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 11, 281–296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank H. Tong from APS beamline 14-BMC, A. Han for help in data collection and G. Murphy, J. Goodrich and T. Cech for critical reading of the manuscript. This research was supported by a scholar award from the Damon Runyon–Walter Winchell Foundation and grants from the W.M. Keck Foundation and the US National Institutes of Health (L.C.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giffin, M., Stroud, J., Bates, D. et al. Structure of NFAT1 bound as a dimer to the HIV-1 LTR κB element. Nat Struct Mol Biol 10, 800–806 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb981
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb981
This article is cited by
-
Current views on HIV-1 latency, persistence, and cure
Folia Microbiologica (2017)
-
NFATc1/αA: The other Face of NFAT Factors in Lymphocytes
Cell Communication and Signaling (2012)
-
Regulation of HIV-1 transcription in cells of the monocyte-macrophage lineage
Retrovirology (2009)
-
NFAT proteins: emerging roles in cancer progression
Nature Reviews Cancer (2009)
-
Induction of chromosomally integrated HIV-1 LTR requires RBF-2 (USF/TFII-I) and RAS/MAPK signaling
Virus Genes (2007)