Abstract
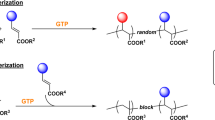
Group transfer polymerlzation (GTP) of methacrylate-terminated poly(2-alkyl-2-oxazoline) macromonomers (MA-PROZO-n 3; R = Me and n-Bu; n, degree of polymerization) was examined using 1-methoxy-1-(trimethylsiloxy)-2-methyl-1-propene and nucleophiles as the initiator and catalyst, respectively, at 24 or 50°C. MA-PROZO-n 3 (R=n-Bu; n=3, 14, and 31) was polymerized using tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride as the catalyst in tetrahydrofuran (THF) to provide poly(MA-PROZO-n)s (4; R=n-Bu) with Mn, up to 37600. GTP of 3 (R = Me; n=14 and 30) was carried out by use of KHF2 as the catalyst in CH3CN or CD3CN to produce 4 (R = Me) with maximum Mn, up to 17300. Mw/Mn of the 4 given from 3 of n≥14 was narrow (1.08—1.12). Rate of the GTP of the macromonomers 3 decreased with increase in n and concentrations of macromonomers. Maximum conversion of macromonomers 3 was obtained at relatively lower concentration of 3, generally 89—95%. Polymer 4 (R=n-Bu) was coupled in situ with p-bis(bromomethyl)benzene or propagating species of living poly(2-n-butyl-2-oxazoline)s, to provide chain extended poly(MA-PROZO-n)s (5; R=n-Bu) or block copolymers (6). From characteristics of the reactivity of 3 and 4 and narrow molecular weight distribution of 4, living nature of present polymerization was suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
References
S. Kobayashi and T. Saegusa, in “Ring-Opening Polymerization,” Vol. 2, K. J. Ivin and T. Saegusa, Eds., Elsevier Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London, 1984, p 764.
S. Kobayashi, Prog. Polym. Sci., 15, 751 (1990).
H. Uyama and S. Kobayashi, in “Catalysis in Precision Polymerization,” S. Kobayashi Ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Chichester, 1997, p 399.
S. Kobayashi, E. Masuda, S. Shoda, and Y. Shimano, Macromolecules, 22, 2878 (1989).
S. Shoda, E. Masuda, M. Furukawa, and S. Kobayashi, J. Polym. Sci., Part A, Polym. Chem., 30, 1489 (1992).
Y. Shimano, K. Sato, and S. Kobayashi, Polym. J., 31, 219 (1999).
Y. Shimano, K. Sato, D. Fukui, Y. Onodera, and Y. Kimura, Polym. J., 31, 296 (1999).
O. W. Webster, W. R. Hertler, D. Y. Sogah, W. B. Farnham, and T. V. Rajanbabu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 105, 5706 (1983).
R. Asami, M. Takaki, and Y. Moriyama, Polym. Bull., 16, 125 (1986).
H. Witte and W. Seeliger, Liebigs Ann. Chem., 996 (1974).
C. Ainsworth, F. Chen, and Y.-N. Kuo, J. Organomet. Chem., 46, 59 (1972).
D. Y. Sogah, W. R. Hertler, O. W. Webster, and G. M. Cohen, Macromolecules, 20, 1473 (1987).
Y. Tsukahara, K. Tsutsumi, Y. Yamashita, and S. Shimada, Macromolecules, 23, 5201 (1990).
A. H. E. Müller, Makromol. Chem., Makromol. Symp., 32, 87 (1990).
U. Schmalbrock, H. Sitz, and F. Bandermann, Makromol. Chem., 190, 2713 (1989).
S. Kobayashi, T. Mizutani, and T. Saegusa, Makromol. Chem., 185, 441 (1984).
Y. Shimano, K. Sato, and S. Kobayashi, J. Polym. Sci., Part A, Polym. Chem., 33, 2715 (1995).
M. Miyamoto, K. Naka, M. Tokumizu, and T. Saegusa, Macromolecules, 22, 1604 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimano, Y., Sato, K. & Kobayashi, S. Group Transfer Polymerization of Methacryl-Type Poly(2-oxazoline) Macromonomers. Polym J 31, 458–463 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.31.458
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1295/polymj.31.458