Abstract
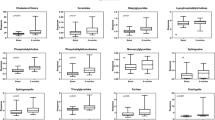
Summary: The effect of various lipids, proteins, and other substances on the adsorption rate of dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPC) was investigated. Each substance was added to a sonicated suspension of DPC in saline, and the surface pressure of the adsorbed surface film was measured using a platinum plate suspended from an electrobalance. Pure DPC adsorbed very slowly, being complete only after 8 hr; its half-adsorption time was 91.8 ± 8.3 min. Four additives markedly reduced the half-adsorption time of DPC: dipalmitoyl phosphatidylglycerol (1.1 ± 0.2 min), phosphatidylinositol (2.8 ± 0.4 min), serum high-density lipoprotein (1.0 ± 0.2 min), and surfactant apoprotein (0.9 ± 0.1 min). The half-adsorption times of mixtures of DPC and the other additives ranged from 15.3 ± 1.9 to 107.8 ± 12.1 min.
Speculation: The results suggest that dipalmitoyl phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylinositol, and serum high-density lipoprotein, in combination with dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine, may be of value in the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in the human neonate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Article PDF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meban, C. Effect of Lipids and Other Substances on the Adsorption of Dipalmitoyl Phosphatidylcholine. Pediatr Res 15, 1029–1031 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-198107000-00010
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-198107000-00010
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Changes of alveolar stability and phospholipids in pulmonary surfactant in acute pancreatitis
The Japanese Journal of Surgery (1983)