Abstract
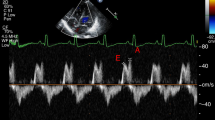
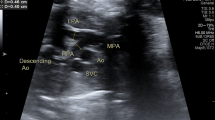
ABSTRACT: Maximum flow velocity waveforms were recorded in a longitudinal study from the fetal ascending aorta and fetal pulmonary artery in 46 normal pregnancies and, in addition, from the umbilical artery in 21 cases of intrauterine growth retardation between 19 and 33 wk gestation. In normal pregnancy, the mean peak systolic velocity (PSV) in the ascending aorta increased from 49.4 cm/s at 19 wk of gestation to 79.0 cm/s at 33 wk of gestation. The corresponding increase in PSV in the pulmonary artery was from 39.0 to 63.7 cm/s. The ratio for the PSV between the two arteries remained constant (1.25-1.29). Mean values of PSV in both arteries were linearly related to gestational age. Normal limits according to age were constructed by establishing the 5th and 95th percentiles. In intrauterine growth retardation, the PSV in the pulmonary artery was decreased (<5th percentile) in 95% of cases, PSV in the ascending aorta was reduced (<5th percentile) in only 57%. No relationship was established between PSV in both arteries and the presence or absence of end-diastolic flow velocities in the umbilical artery. The outcome of fetuses with intrauterine growth retardation, as expressed by Apgar score at 1 min and umbilical cord pH, bears no relationship to the PSV in ascending aorta and pulmonary artery.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Groenenberg, I., Stijnen, T. & Wladimiroff, J. Blood Flow Velocity Waveforms in the Fetal Cardiac Outflow Tract as a Measure of Fetal Well-Being in Intrauterine Growth Retardation. Pediatr Res 27, 379–382 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199004000-00011
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199004000-00011
This article is cited by
-
Pulmonary vascular reactivity in growth restricted fetuses using computational modelling and machine learning analysis of fetal Doppler waveforms
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Fluid mechanics of blood flow in human fetal left ventricles based on patient-specific 4D ultrasound scans
Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology (2016)
-
Fetal echocardiography: A review
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (1991)