Abstract
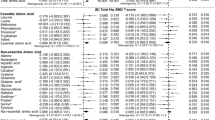
Bone turnover, collagen metabolism, and bone mineral status were investigated in 59 patients with cystic fibrosis and in 72 sex- and age-matched control subjects. In all patients and control subjects serum concentrations of osteocalcin (OC), carboxy-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen (PICP), amino-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen(PIIINP), and cross-linked carboxy-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen(ICTP), and urinary values of cross-linked N-telopeptides of type I collagen (NTX), as well as total body bone mineral content (TBBM) were measured. Higher ICTP (μg/L) and NTX (bone collagen equivalent/urinary creatinine (nmol/mmol) values were found in prepubertal, pubertal, and young adult patients than in control subjects (ICTP: 15.4 ± 2.1 and 13.2± 1.8, p < 0.001; 23.3 ± 5.3 and 20.1 ± 4.1,p < 0.02; 4.8 ± 1.1 and 4.0 ± 1.0, p < 0.05, respectively; NTX: 1047.5 ± 528.6 and 227.8 ± 71.8,p < 0.01; 997.8 ± 391.7 and 376.3 ± 91.0,p < 0.01; 993.2 ± 398.0 and 73.9 ± 28.5,p < 0.01, respectively). Lower OC and PICP levels (μg/L) were showed in pubertal patients in comparison with control subjects (OC: 20.2± 12.3 and 39.0 ± 15.1, p < 0.01; PICP: 305.8± 130.4 and 436.2 ± 110.1, p < 0.02, respectively). Lower OC and higher PIIINP levels (μg/L) were found in young adult patients than in control subjects (OC: 4.4 ± 3.0 and 7.0 ± 3.1,p < 0.05; PIIINP: 4.8 ± 1.1 and 3.1 ± 1.0,p < 0.001, respectively). TBBM (z score) was reduced in prepubertal, pubertal, and young adult patients (-0.8 ± 0.4, -1.0± 0.4, -1.1 ± 0.5, respectively). Patients with cystic fibrosis have bone demineralization and imbalance between bone formation and degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- PIIINP:
-
amino-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- PICP:
-
carboxy-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen
- ICTP:
-
cross-linked carboxy-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen
- NTX:
-
cross-linked N-telopeptides of type I collagen
- CF:
-
cystic fibrosis
- OC:
-
osteocalcin
- TBBM:
-
total body bone mineral content
- BCE:
-
bone collagen equivalent
References
Mischler EH, Chesney PJ, Chesney RW, Mazess RB 1979 Demineralization in cystic fibrosis. Detected by direct photon absorptiometry. Am J Dis Child 133: 632–635
Reiter EO, Brugman SM, Pike JW, Pitt M, Dokoh S, Haussler MR, Gerstle RS, Taussing LM 1985 Vitamin D metabolites in adolescent and young adult with cystic fibrosis: effects of sun and season. J Pediatr 106: 21–26
Gibbens DT, Gilsanz V, Boechat MI, Dufer D, Carlson ME, Wang C-I 1988 Osteoporosis in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 113: 295–300
Stamp TCB, Geddes DM 1993 Osteoporosis and cystic fibrosis. Thorax 48: 585–586
Grey AB, Ames RW, Matthews RD, Reid IR 1993 Bone mineral density and body composition in adult patients with cystic fibrosis. Thorax 48: 589–593
De Schepper J, Smitz J, Dab I, Piepsz A, Jonckheer M, Bergmann P 1993 Low serum bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid protein concentrations in patients with cystic fibrosis: correlation with hormonal parameters and bone mineral density. Horm Res 39: 197–201
Bachrach LK, Loutit CW, Moss RB, Marcus R 1994 Osteopenia in adults with cystic fibrosis. Am J Med 96: 27–34
Henderson RC, Specter BB 1994 Kyphosis and fractures in children and young adults with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 125: 208–212
Bhudhikanok GS, Lim J, Marcus R, Harkins A, Moss RB, Bachrach LK 1996 Correlates of osteopenia in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatrics 97: 103–111
Reiter EO, Stern RC, Root AW 1981 The reproductive endocrine system in cystic fibrosis. Am J Dis Child 135: 422–426
Reiter EO, Stern RC, Root AW 1982 The reproductive endocrine system in cystic fibrosis: 2. Changes in gonadotropins and sex sterods following LHRH. Clin Endocrinol 16: 127–137
Delmas PD, Malaval L, Arlot ME, Meunier PJ 1985 Serum bone Gla-protein compared to bone hystomorphometry in endocrine diseases. Bone 6: 339–341
Prockop DJ, Kivirikko KJI, Tuderman L, Guzman NA 1979 The biosynthesis of collagen and its disorders. N Engl J Med 301: 13–23, 777-85
Risteli J, Risteli L 1989 Growth and collagen. Curr Med Lit Growth Growth Factors 4: 159–164
Parfitt AM, Simon LS, Villanueva AR, Krane SM 1987 Procollagen type I carboxy-terminal extension peptide in serum as a marker of collagen biosynthesis in bone. Correlation with iliac bone formation rates and comparison with total alkaline phosphatase. J Bone Miner Res 2: 427–436
Trivedi P, Cheeseman P, Portmann B, Hegarthy J, Mowat AP 1985 Variation in serum type III procollagen peptide with age in healthy subjects and its comparative value in the assessment of disease activity in children and adults with chronic active hepatitis. Eur J Clin Invest 15: 69–74
Teare JP, Sherman D, Greenfield SM, Simpson J, Bray G, Catterall AP, Murray-Lyon IM, Peters TJ, Williams R, Thompson RPH 1993 Comparison of serum procollagen III peptide concentrations and PGA index for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Lancet 342: 895–898
Entzian P, Huckstadt A, Kreipe H, Barth J 1990 Determination of serum concentrations of type III procollagen peptide in mechanically ventilated patients. Pronounced augmented concentrations in adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 142: 1079–1082
Heikinheimo M, Halila R, Marttinen E, Raivio K 1992 N-terminal propeptide of type III collagen in tracheal fluid and serum in preterm infants at risk for bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res 31: 340–344
Okazaki R, Matsuoka K, Horiuchi A, Maruyama K, Okazaki I 1988 Assays of serum laminin and type III procollagen peptide for monitoring the clinical course of diabetic microangiopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 5: 163–170
Saggese G, Bertelloni S, Baroncelli GI, Calisti L, Ghirri P 1991 Amino-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen in insulin dependent diabetes mellitus. A possible marker of diabetic microangiopathy. Riv Ital Pediatr 17: 23–27
Risteli J, Elomaa I, Niemi S, Novamo A, Risteli L 1993 Radioimmunoassay for the pyridinoline cross-linked carboxy-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen: a new serum marker of bone collagen degradation. Clin Chem 39: 635–640
Rosen HN, Dresner-Pollak R, Moses AC, Rosenblatt M, Zeind AJ, Clemens JD, Greenspan SL 1994 Specificity of urinary excretion of cross-linked N-telopeptides of type I collagen as a marker of bone turnover. Calcif Tissue Int 54: 26–29
Bollen A-M, Eyre DR 1994 Bone resorption rates in children monitored by the urinary assay of collagen type I cross-linked peptides. Bone 15: 31–34
Saggese G, Baroncelli GI, Bertelloni S, Buggiani B 1989 Osteocalcin values in childhood. Relationship with bone mineralization and with 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D variations. Riv Ital Pediatr 15: 109–112
Saggese G, Bertelloni S, Baroncelli GI, Di Nero G 1992 Serum levels of carboxy-terminal propeptide of type I procollagen in healthy children from 1st year of life to adulthood and in metabolic bone disease. Eur J Pediatr 151: 764–768
Trivedi P, Hindmarsh PC, Risteli J, Risteli L, Mowat AP, Brook CGD 1989 Growth velocity, growth hormone therapy, and serum concentrations of the amino-terminal propeptide of type III procollagen. J Pediatr 114: 225–230
Risteli L, Risteli J 1996 New markers of collagen synthesis and degradation. In: Schonau E (ed) Paediatric Osteology-New Developments in Diagnostic and Therapy. Elsevier Science BV, Amsterdam, pp 193–202.
Shwachman H, Kulczycki L 1958 Long-term study of one hundred five patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Dis Child 96: 6–15
Chrispin AR, Norman AP 1974 The systematic evaluation of the chest radiograph in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Radiol 2: 101–106
Food and Nutrition Board. National Research Council 1989 Recommended Dietary Allowances, 10th Ed. National Academy Press, Washington DC, pp 174–184
Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH, Takaishi M 1966 Standards from birth to maturity for height, weight, height velocity and weight velocity: British children-1965. Arch Dis Child 41: 454–471, 61613–634
Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH 1976 Clinical longitudinal standards for height, weight, height velocity, weight velocity and stages of puberty. Arch Dis Child 51: 170–179
Greulich WW, Pyle SI 1959 Radiographic Atlas of Skeletal Development of the Hand and Wrist, 2nd Ed. Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA
Colombo C, Apostolo MG, Ferrari M, Seia M, Genoni S, Giunta A, Piceni Sereni L 1994 Analysis of risk factors for the development of liver disease associated with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 124: 393–399
Risteli J, Niemi S, Trivedi P, Maentausta O, Mowat AP, Risteli L 1988 Rapid equilibrium radioimmunoassay for the amino-terminal propeptide of human type III procollagen. Clin Chem 34: 715–718
Hanson DA, Weis MAE, Bollen A-M, Maslan SL, Singer FR, Eyre DR 1992 A specific immunoassay for monitoring human bone resorption: quantitation of type I collagen cross-linked N-telopeptides in urine. J Bone Miner Res 7: 1251–1258
Faulkner RA, Bailey DA, Drinkwater DT, Wilkinson AA, Houston CS, McKay HA 1993 Regional and total body bone mineral content, bone mineral density, and total body tissue composition in children 8-16 years of age. Calcif Tissue Int 53: 7–12
Rico H, Revilla M, Villa LF, Hernandez ER, Alvarez de Buergo M, Villa M 1993 Body composition in children and Tanner's stages: a study with dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. Metabolism 42: 967–970
Rico H, Revilla M, Hernandez ER, Villa LF, Alvarez de Buergo M 1992 Sex differences in the acquisition of total bone mineral mass peak assessed through dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Calcif Tissue Int 51: 251–254
Kleerekoper M, Avioli LV 1993 Evaluation and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. In: Favus MJ (ed) Primer on the Metabolic Bone Diseases and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism, 2nd Ed. Raven Press, New York, pp 223–229
Ramsey BW, Boat TF 1994 Outcome measures for clinical trials in cystic fibrosis. Summary of a cystic fibrosis foundation consensus conference. J Pediatr 124: 177–192
Melton LJ, Atkinson EJ, O'Fallon WM, Wahner HW, Riggs BL 1993 Long-term fracture prediction by bone mineral assessed at different skeletal sites. J Bone Miner Res 8: 1227–1233
Sorva R, Turpeinen M, Juntunen-Backman K, Karonen SL, Sorva A 1992 Effects of inhaled budesonide on serum markers of bone metabolism in children with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 90: 808–815
Boulet L-P, Giguère M-C, Milot J, Brown J 1994 Effects of long-term use of high-dose inhaled steroids on bone density and calcium metabolism. J Allergy Clin Immunol 94: 796–803
Birkebaek NH, Esberg G, Andersen K, Wolthers O, Hassager C 1995 Bone and collagen turnover during treatment with inhaled dry powder budesonide and beclomethasone dipropionate. Arch Dis Child 73: 524–527
Packe GE, Douglas JG, McDonald AF, Robins SP, Reid DM 1992 Bone density in asthmatic patients taking high dose inhaled beclomethasone dipropionate and intermittent systemic corticosteroids. Thorax 47: 414–417
Maharaj B, Maharaj RJ, Leary WP, Cooppan RM, Naran AD, Pirie D, Pudifin DJ 1986 Sampling variability and its influence on the diagnostic yield of percutaneous needle biopsy of the liver. Lancet 1: 523–525
Frei A, Zimmermann A, Weigand K 1983 Serum procollagen III aminopeptide (PP) as index of liver fibrosis-new morphometric evidence. Hepatology 2: 46A
Mitchell D, Smith A, Rowan B, Warnes TW, Haboubi NY, Lucas SB, Chalmers RJG 1990 Serum type III procollagen peptide, dynamic liver function tests and hepatic fibrosis in psoriatic patients receiving methotrexate. Br J Dermatol 122: 1–7
Rojkind M, Giambrone MA, Biempica L 1979 Collagen types in normal and cirrhotic liver. Gastroenterology 76: 710–719
Haukipuro K, Melkko J, Risteli L, Kairaluoma MI, Risteli J 1991 Synthesis of type I collagen in healing wounds in humans. Ann Surg 213: 75–80
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baroncelli, G., De Luca, F., Magazzú, G. et al. Bone Demineralization in Cystic Fibrosis: Evidence of Imbalance between Bone Formation and Degradation. Pediatr Res 41, 397–403 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199703000-00016
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199703000-00016
This article is cited by
-
IL-8 correlates with reduced baseline femoral neck bone mineral density in adults with cystic fibrosis: a single center retrospective study
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Die Knochenmarker BSP, CTX und NTX und deren Publikationscharakteristika im Rahmen einer bibliometrischen Analyse
Zentralblatt für Arbeitsmedizin, Arbeitsschutz und Ergonomie (2021)
-
Reduced bone volumetric density and weak correlation between infection and bone markers in cystic fibrosis adult patients
Osteoporosis International (2016)
-
Bone disease in cystic fibrosis: new pathogenic insights opening novel therapies
Osteoporosis International (2016)
-
Bone and body composition analyzed by Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) in clinical and nutritional evaluation of young patients with Cystic Fibrosis: a cross-sectional study
BMC Pediatrics (2009)