Abstract
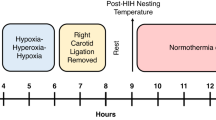
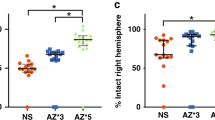
Various therapeutic interventions after hypoxia-ischemia (HI) have been shown to reduce brain injury in the short-term perspective, but it remains uncertain whether such findings are accompanied by long-term functional and structural improvements. HI was induced in 7-d-old rats as follows. The left carotid artery was ligated, and the rat was exposed to 100 min of hypoxia (7.70% oxygen in nitrogen). At postnatal d 42 the rats were assessed using four sensorimotor tests. The results were correlated with the extent of brain damage expressed as volume of deficit of the left hemisphere as percent of the right hemisphere. In the grip-traction test, the time to falling was 2.2 times shorter in the HI animals compared with controls (p < 0.01). Asymmetries of limb-placing and foot-faults (p < 0.001) were detected in HI animals, and the motor function was abnormal in the postural reflex test (p < 0.001). We found a moderate correspondence between functional and neuropathologic outcome (r = 0.842, p < 0.001). A set of four easily performed sensorimotor tests is presented for the long-term evaluation of neurologic function in the 7-d-old rat model of HI.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- HI:
-
hypoxia-ischemia
- MAP:
-
microtubule-associated protein
- H&E:
-
hematoxylin and eosin
References
Bågenholm R, Andiné P, Hagberg H 1996 Effects of the 21-aminosteroid tirilazad mesylate (U-74006F) on brain damage and edema after perinatal hypoxic-ischemia in the rat. Pediatr Res 40: 399–403.
Bona E, Ådén U, Fredholm BB, Hagberg H 1995 The effect of long term caffeine treatment on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the neonate. Pediatr Res 38: 312–318.
Hagberg H, Gilland E, Diemer NH, Andiné P 1994 Hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat brain: histopathology after post-treatment with NMDA and non-NMDA receptor antagonists. Biol Neonate 66: 206–213.
Nozaki K, Finklestein SP, Beal F 1993 Basic fibroblast growth factor protects against hypoxia ischemia and NMDA neurotoxicity in neonatal rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13: 221–228.
Silverstein FS, Buchanan K, Hudson C, Johnston MV 1986 Flunarizine limits hypoxia-ischemia induced morphologic injury in immature rat brain. Stroke 17: 477–482.
Thordstein M, Bågenholm R, Thiringer K, Kjellmer I 1993 Scavengers of free oxygen radicals in combination with magnesium ameliorate perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Pediatr Res 34: 23–26.
Kirino T 1982 Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following transient ischemia. Brain Res 239: 57–69.
McRae A, Gilland E, Bona E, Hagberg H 1995 Microglia activation after neonatal hypoxic-ischemia. Dev Brain Res 84: 245–252.
Towfighi J, Zec N, Yager J, Housman C, Vannucci RC 1995 Temporal evolution of neuropathologic changes in an immature rat model of cerebral hypoxia: a light microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol 90: 375–386.
Gilland E, Hagberg H 1996 NMDA-receptor dependent increase of cerebral glucose utilization after hypoxia-ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16: 1005–1013.
Beilharz EJ, Williams CE, Dragunow M, Sirimanne ES, Gluckman PD 1995 Mechanisms of delayed cell death following hypoxic-ischemic injury in the immature rat: evidence for apoptosis during selective neuronal loss. Mol Brain Res 29: 1–14.
Williams CE, Gunn AJ, Mallard C, Gluckman PD 1992 Outcome after ischemia in the developing sheep brain: an electroencephalografic and histological study. Ann Neurol 31: 14–21.
Iizuka H, Sakatani K, Young W 1990 Neural damage in the rat thalamus after cortical infarcts. Stroke 21: 790–794.
Fujie W, Kirino T, Tomukai N, Iwasawa T, Tamura A 1990 Progressive shrinkage of the thalamus following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 21: 1485–1488.
Nyakas C, Buwalda B, Luiten PGM 1996 Hypoxia and brain development. Progr Neurobiol 49: 1–51.
Kolb B, Elliott W 1987 Recovery from early cortical damage in rats. III. Effects of experience on anatomy and behavior following frontal lesions at 1 or 5 days of age. Behav Brain Res 26: 119–137.
Barth TM, Stanfield BB 1990 The recovery of forelimb-placing behavior in rats with neonatal unilateral cortical damage involves the remaining hemisphere. J Neurosci 10: 3449–3459.
Sørensen JC, Castro AJ, Klausen B, Zimmer J 1992 Projections from fetal neocortical transplants placed in the frontal neocortex of newborn rats. A Phaseolus vulgaris-leucoagglutinin tracing study. Exp Brain Res 92: 299–309.
Levene MI 1991 Outcome after asphyxial and circulatory disturbances in the brain. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 7: 113–117.
Hagberg B, Hagberg G 1993 The origins of cerebral palsy. In: David TJ (eds) Recent Advances in Paediatrics, Vol XI. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburg, pp 67–83.
Dietrich WD, Busto R, Alonso O, Globus MYT, Ginsberg MD 1993 Intraischemic but not postischemic brain hypothermia protects chronically following global forebrain ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13: 541–549.
Johansson BB, Ohlsson A-L 1996 Environment, social interaction, and physical activity as determinants of functional outcome after cerebral infarction in the rat. Exp Neurol 139: 322–327.
Ohlsson A-L, Johansson BB 1995 Environment influences functional outcome of cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke 26: 644–649.
Shuaib A, Murabit MA, Kanthan R, Howlett W, Wishart T 1996 The neuroprotective effects of γ-vinyl GABA in transient global ischemia: a morphological study with early and delayed evaluations. Neurosci Lett 204: 1–4.
Kolb B, Holmes C, Whishaw IQ 1987 Recovery from early cortical lesions in rats. III. Neonatal removal of posterior parietal cortex has greater behavioral and anatomical effects than similar removals in adulthood. Behav Brain Res 26: 119–137.
Huttenlocher PR, Raichelson RM 1989 Effects of neonatal hemispherectomy on location and number of corticospinal neurons in the rat. Dev Brain Res 47: 59–69.
Rice JE, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB 1981 The influence of immaturity on hypoxicischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9: 131–141.
Hall RD, Lindholm EP 1974 Organization of motor and somatosensory neocortex in the albino rat. Brain Res 66: 23–38.
Donatelle JM 1977 Growth of the corticospinal tract and the development of placing reactions in the postnatal rat. J Comp Neurol 175: 207–232.
De Ryck M, Van Reempts J, Duytschaever H, Van Deuren B, Clincke G 1992 Neocortical localization of tactile/proprioceptive limb placing reactions in the rat. Brain Res 573: 44–60.
Hicks SP, D'Amanto CJ 1975 Motor-sensory cortex - corticospinal system and developing locomotion and placing in rats. Am J Anat 143: 1–34.
Barth TM, Jones TA, Schallert T 1990 Functional subdivisions of the rat somatic sensorimotor cortex. Behav Brain Res 39: 73–95.
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H 1986 Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17: 472–476.
Combs DJ, D'Alecy LG 1987 Motor performance in rats exposed to severe forebrain ischemia: effect of fasting and 1,3-butanediol. Stroke 18: 503–511.
De Ryck M, Van Reempts J, Borgers M, Wauquier A, Janssen AJ 1989 Photochemical stroke model: flunarizine prevents sensorimotor deficits after neocortical infarcts in rats. Stroke 20: 1383–1390.
Grabowski M, Nordborg C, Johansson BB 1991 Sensorimotor performance and rotation correlate to lesion size in right but not left hemisphere brain infarcts in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Brain Res 547: 249–257.
Kolb B, Mackintosh A, Whishaw IQ, Sutherland RJ 1984 Evidence for anatomical but not functional asymmetry in the hemidecorticate rat. Behav Neurosci 98: 44–58.
Castro AJ, Tonder N, Sunde NA, Zimmer J 1987 Fetal cortical transplants in the cerebral hemisphere of newborn rats: a retrograde fluorescent analysis of connections. Exp Brain Res 66: 533–542.
Sørensen JC, Grabowski M, Zimmer J, Johansson BB 1996 Fetal neocortical tissue blocks implanted in brain infarcts of adult rats interconnect with the host brain. Exp Neurol 138: 227–235.
Johansson BB, Grabowski M 1994 Functional recovery after brain infarction: plasticity and neuronal transplantation. Brain Pathol 4: 85–95.
Sharp FR, Gonzalez MF 1986 Fetal cortical transplants ameliorate thalamic atrophy ipsilateral to neonatal frontal cortex lesions. Neurosci Lett 71: 247–251.
Sørensen JC, Zimmer J, Castro AJ 1989 Fetal cortical transplants reduce the thalamic atrophy induced by frontal cortical lesions in newborn rats. Neurosci Lett 98: 33–38.
Plumet J, Cadusseau J, Roberg M 1991 Skilled forelimb use in the rat: amelioration of functional deficits resulting from neonantal damage to the frontal cortex by neonatal transplantation of fetal cortical tissue. Restor Neurol Neurosci 3: 135–147.
Towfighi J, Yager JY, Housman C, Vannucci RC 1991 Neuropathology of remote hypoxic-ischemic damage in the immature rat. Acta Neuropathol 81: 578–587.
Silverstein F, Johnston MV 1984 Effects of hypoxia-ischemia on monoamine metabolism in the immature brain. Ann Neurol 15: 342–347.
Young RSK, Kolnich J, Woods CL, Yagel SK 1986 Behavioral performance of rats following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Stroke 17: 1313–1316.
Ford LM, Sanberg PR, Norman AB, Fogelson H 1989 MK-801 prevents hippocampal neurodegeneration in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic rats. Arch Neurol 46: 1090–1096.
Andiné P, Thordstein M, Kjellmer I, Nordborg C, Thiringer K, Wennberg E, Hagberg H 1990 Evaluation of brain damage in a rat model of neonatal hypoxic-ischemia. J Neurosci Methods 35: 253–260.
Johansson BB 1995 Functional recovery after brain infarction. Corebrovasc Dis 5: 278–281.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Malgorzata Puka-Sundvall for expert assistance and express gratitude to Liselotte Öhman for the professional illustrations of the functional tests. E.B. gives special thanks to Anna-Lena Ohlsson for the introduction to the advanced functional animal tests at the laboratory in Lund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Swedish Medical Research Council (Grant 9455), the Sven Jerring Foundation, the 1987 Foundation for Strokeresearch, the Åke Wiberg Foundation, the Åhlén Foundation, the Magnus Bergwall Foundation, the Konung Gustaf V's 80 års Foundation, the Frimurare Barnhus Foundation, the Linnéa and Josef Carlsson Foundation, the Göteborg Medical Society, the Sahlgrenska Hospital Foundation for Medical Research, the Medical Faculty of Göteborg, University of Göteborg, and the Swedish Society for Medical Research.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bona, E., Johansson, B. & Hagberg, H. Sensorimotor Function and Neuropathology Five to Six Weeks after Hypoxia-Ischemia in Seven-Day-Old Rats. Pediatr Res 42, 678–683 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199711000-00021
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199711000-00021
This article is cited by
-
Deficits in motor and cognitive functions in an adult mouse model of hypoxia-ischemia induced stroke
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Nafamostat Mesilate Improves Neurological Outcome and Axonal Regeneration after Stroke in Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
Docosahexaenoic Acid Reduces Cerebral Damage and Ameliorates Long-Term Cognitive Impairments Caused by Neonatal Hypoxia–Ischemia in Rats
Molecular Neurobiology (2017)
-
Combined use of spatial restraint stress and middle cerebral artery occlusion is a novel model of post-stroke depression in mice
Scientific Reports (2015)
-
Assessment of Long-Term Sensorimotor Deficit after Cerebral Ischemia/Hypoxia in Neonatal Rats
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (2014)