Abstract
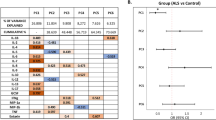
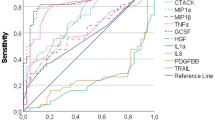
Neutrophils in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) increase during the initial stage of meningitis. Some cytokines induce the accumulation of such neutrophils, and we and other investigators have revealed transient increases in the levels of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-csf) and IL-8 in the CSF of patients with meningitis. To explore the coordination of other cytokines with G-csf and IL-8 in the neutrophil accumulation in the CSF, we herein investigated macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α), which can induce the infiltration of neutrophils. The modulation of MIP-1α levels in the CSF in children with bacterial (n = 10) and aseptic (n = 22) meningitis was examined using an ELISA. MIP-1α levels in the CSF were detectable at the stage with symptoms of meningitis: 289.9 ± 270.7 ng/L in the bacterial meningitis group and 16.1 ± 12.5 ng/L in the aseptic meningitis group. These levels decreased with the improvement of symptoms. MIP-1α was not detectable(<6 ng/L) in all of the control patients without meningitis (n = 19). The MIP-1α levels in the CSF showed a significant correlation with the CSF neutrophil counts (r = 0.750, p < 0.0001;n = 80) of meningitis, and the values of MIP-1α (log ng/L)/neutrophil counts (log/L) ratio were calculated (1.003 ± 0.576). The MIP-1α levels in the serum were significantly lower than those in the CSF (p = 0.0464). We found MIP-1α mRNA in the CSF cells by the reverse transcriptase-PCR method, and high levels of MIP-1α protein in the culture media from mononuclear cells in the CSF in vitro. In summary, The MIP-1α level increases in the CSF at the symptomatic stage of meningitis in children, and its cellular source is, in part, mononuclear cells which have infiltrated the CSF. We propose that MIP-1α, in addition to G-csf and IL-8, plays an important role in the accumulation of neutrophils in the CSF of patients with meningitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CSF:
-
cerebrospinal fluid
- csf:
-
colony-stimulating factor
- G-csf:
-
ganulocyte-csf
- M-csf:
-
macrophage-csf
- GM-csf:
-
granulocyte/macrophage csf
- MIP:
-
macrophage inflammatory protein
- MNC:
-
mononuclear cell
- RT:
-
reverse transcriptase
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
References
van Meir E, Ceska M, Effenberger F, Walz A, Grouzmann E, Desbaillets I, Frei K, Fontana A, de Tribolet N 1992; Interleukin-8 is produced in neoplastic and infectious disease of the human central nervous system. Cancer Res 52: 4297–4305.
Halstensen A, Ceska M, Brandtzaeg P, Redl H, Naess A, Waage A 1993; Interleukin-8 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid from patients with meningococcal disease. J Infect Dis 167: 471–475.
Fukushima K, Ishiguro A, Nakamura T, Suzuki Y, Nagayama S, Abe M, Umezawa T, Nakahata T, Komiyama A, Shimbo T 1993; Elevated levels of interleukin 6 in the cerebrospinal fluid in childhood aseptic meningitis(Japanese with English summary). Jpn J Inflamm 13: 263–268.
Shimoda K, Okamura S, Omori F, Mizuno Y, Hara T, Aoki T, Akeda H, Ueda K, Niho Y 1991; Detection of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with aseptic meningitis. Acta Haematol 86: 36–39.
Sáez-Llorens X, Ramilo O, Mustafa MM, Mertsola J, McCracken GH 1990; Molecular pathophysiology of bacterial meningitis: current concepts and therapeutic implications. J Pediatr 116: 671–684.
Fukushima K, Ishiguro A, Shimbo T 1995; Transient elevation of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels in the cerebrospinal fluid at the initial stage of aseptic meningitis in children. Pediatr Res 37: 160–164.
Shimoda K, Okamura S, Omori F, Mizuno Y, Hara T, Aoki T, Ueda K, Niho Y 1991; Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with meningitis. Blood 77: 2214–2217.
Wolpe SD, Davatelis G, Sherry B, Beutler B, Hesse DG, Nguyen HT, Moldawer LL, Nathan CF, Lowry SF, Cerami A 1988; Macrophages secrete a novel heparin-binding protein with inflammatory and neutrophil chemokinetic properties. J Exp Med 167: 570–580.
Graham GJ, Wright EG, Hewick R, Wolpe SD, Wilkie NM, Donaldson D, Lorimore S, Pragnell IB 1990; Identification and characterization of an inhibitor of haemopoietic stem cell proliferation. Nature 344: 442–444.
Saukkonen K, Sande S, Cioffe C, Wolpe S, Sherry B, Cerami A, Tuomanen E 1990; The role of cytokines in the generation of inflammation and tissue damage in experimental gram-positive meningitis. J Exp Med 171: 439–448.
Minano FJ, Myers RD 1991; Anorexia and adipsia: dissociation from fever after MIP-1 injection in ventromedial hypothalamus and preoptic area of rats. Brain Res Bull 27: 273–278.
Fahey TJ 3rd, Sherry B Tracey KJ van Deventer S, Fahey TJ 3; Cytokine production in a model of wound healing: the appearance of MIP-1, MIP-2, cachectin/TNF and IL-1. Cytokine 2: 92–99.
Koch AE, Kunkel SL, Harlow LA, Mazarakis DD, Haines GK, Burdick MD, Pope RM, Strieter RM 1994; Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α. A novel chemotactic cytokine for macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest 93: 921–928.
Standiford TJ, Rolfe MW, Kunkel SL, Lynch JP 3; Macrophage inflammatory protein-1α expression in interstitial lung disease. J Immunol 151: 2852–2863.
Hunter CA, Jennings FW, Kennedy PGE, Murrey M 1992; Astrocyte activation correlates with cytokine production in central nervous system of Trypanosoma brucei brucei-infected mice. Lab Invest 67: 635–642.
Ishiguro A, Suzuki Y, Inaba Y, Komiyama A, Koeffler HP, Shimbo T 1996; Production of interleukin-10 in the cerebrospinal fluid in aseptic meningitis of children. Pediatr Res 40: 610–614.
Burdick MD, Kunkel SL, Lincoln PM, Wilke CA, Strieter RM 1993; Specific ELISAs for the detection of human macrophage inflammatory protein-1α and β. Immunol Invest 22: 441–449.
Ishiguro A, Inoue K, Nakahata T, Nishihira H, Kojima S, Ueda K, Suzuki Y, Shimbo T 1996; Reference intervals for serum granulocyte colony-stimulating factor levels in children. J Pediatr 128: 208–212.
Davis LG, Kuehl WM, Battey JF 1994; Basic Methods in Molecular Biology, 2nd Ed. Prentice Hall, London
Obaru K, Fukuda M, Maeda S, Shimada K 1986; A cDNA clone used to study mRNA inducible in human tonsillar lymphocytes by a tumor promoter. J Biochem 99: 885–894.
Ishiguro A, Spirin K, Shiohara M, Tobler A, gombert F, Israel MA, Norton JD, Koeffler HP 1996; Id2 expression increases with differentiation of human myeloid cells. Blood 87: 5225–5231.
Ishiguro A, Spirin K, Shiohara M, Tobler A, Norton JD, Rigolet M, Shimbo T, Koeffler HP 1995; Expression of Id2 and Id3 mRNA in human lymphocytes. Leuk Res 19: 989–996.
Cook DN, Beck MA, Coffman TM, Kirby SL, Sheridan JF, Pragnell IB, Smithies O 1995; Requirement of MIP-1α for an inflammatory response to viral infection. Science 269: 1583–1585.
Hosaka S, Akahoshi C, Wada C, Kondo H 1994; Expression of the chemokine super family in arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 97: 451–457.
Schall TJ, Bacon K, Camp RD, Kaspari JW, Goeddel DV 1993; Human macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α) and MIP-1β chemokines attract distinct populations of lymphocytes. J Exp Med 177: 1821–1826.
Wang JM, Sherry B, Fivash MJ, Kelvin DJ, Oppenheim JJ 1993; Human recombinant macrophage inflammatory protein-1α and -β and monocyte chemotactic and activating factor utilize common and unique receptors on human monocytes. J Immunol 150: 3022–3029.
Khan S, Wigley C 1994; Different effect of a macrophage cytokine on proliferation in astrocytes and Schwann cells. Neuroreport 5: 1381–1385.
Oppenheim JJ, Zachariae COC, Mukaida N, Matsushima K 1991; Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene“intercrine” cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol 9: 617–648.
Lord BI, Heyworth CM, Woolford LB 1993; Macrophage inflammatory protein: its characteristics, biological properties and role in the regulation of haemopoiesis. Int J Hematol 57: 197–206.
Zipfel PF, Balke J, Irving SG, Kelly K, Sienbenlist U 1989; Mitogenic activation of human T cells induced two closely related genes which share structural similarities with a new family of secreted factors. J Immunol 142: 1582–1590.
Kasama T, Strieter RM, Standiford TJ, Burdick MD, Kunkel SL 1993; Expression and regulation of human neutrophil-derived macrophage inflammatory protein 1α. J Exp Med 178: 63–72.
Costa JJ, Matossian K, Resnick MB, Beil WJ, Wong DT, Gordon JR, Dvorak AM, Weller PF, Galli SJ 1993; Human eosinophils can express the cytokines tumor necrosis factor-α and macrophage inflammatory protein-1α. J Clin Invest 91: 2673–2684.
Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Elner VM, Evanoff HL, Burdick M, Kunkel SL 1994; Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 mediates the expression of monocyte derived MIP-1α during monocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Blood 83: 1174–1178.
Lukacs NW. Chensue SW, Smith RE, Strieter RM, Warmington K, Wilke C, Kunkel SL 1994; Production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 by inflammatory granuloma fibroblasts. Am J Pathol 144: 711–718.
Hunter CA, Gow JW, Kennedy PGE, Jennings FW, Murray M 1991; Immunopathology of experimental African sleeping sickness: detection of cytokine mRNA in the Brains of Trypanosoma brucei brucei-induced mice. Infect Immun 59: 4636–4640.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Professor Atsushi Komiyama, Department of Pediatrics, Shinshu University School of Medicine, Matsumoto, Japan, for his encouragement and critical suggestions throughout this work. We also thank Y. Suzuki, A. Wakita, and R. Kiriyama for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported, in part, by a grant in aid for Fundamental Scientific Research from the Education Ministry of Japan (07770606, 07670899).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inaba, Y., Ishiguro, A. & Shimbo, T. The Production of Macrophage Inflammatory Protein-1α in the Cerebrospinal Fluid at the Initial Stage of Meningitis in Children. Pediatr Res 42, 788–793 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199712000-00012
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199712000-00012