Abstract
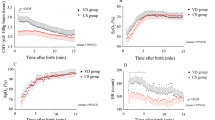
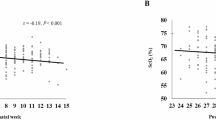
Measurements of cerebral oxygen consumption (CVo2) may improve our understanding of cerebral oxygenation, but there are few published data for sick neonates. Although cerebral maturation is associated with an increase in cerebral glucose consumption, the relationship between CVo2 and increasing gestational age has not previously been assessed in humans. The aims of this study were to evaluate a noninvasive method for the estimation of CVo2 in the neonate using near infrared spectroscopy, and to investigate the relationship between gestational age and CVo2. Twenty babies who were undergoing intensive care in the neonatal period were studied. Cerebral hemoglobin flow (CHbF) and cerebral venous oxyhemoglobin saturation (CSvo2) were measured using near infrared spectroscopy. Arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation was measure by pulse oximetry (Spo2). CVo2 was calculated from the equation: CVo2 = CHbF ×(Spo2 - Svo2 × 4. The median (range) CVo2 was 0.9(0.52-1.76) mL·100 g-1 min-1. There was an increase in CVo2 with advancing gestational age (n = 20, ρ = 0.55,p = 0.014). We conclude that CVo2 can be estimated in sick neonates using noninvasive optical methods. The values obtained are similar to those obtained in other studies by more invasive methods, and are in agreement with values which would be expected from the known rate of cerebral glucose consumption in neonates. Mean (SD) CVo2 at 24-26 wk was 0.5 (0.18) mL·100 g-1 min-1 and rose with increasing gestation to term by 0.03 mL·100 g-1 min-1 per wk.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- Cao 2 :
-
arterial oxygen content
- CBF :
-
cerebral blood flow
- CDo 2 :
-
cerebral oxygen delivery
- CHbF :
-
cerebral hemoglobin flow
- CSvo 2 :
-
cerebral venous oxyhemoglobin saturation
- Cvo 2 :
-
venous oxygen content
- CVo 2 :
-
cerebral oxygen consumptiony
- Hb :
-
deoxyhemoglobin
- Hbo 2 :
-
oxyhemoglobin
- [Hb] :
-
hemoglobin concentration in the blood
- NIRS :
-
near infrared spectroscopy
- Sao 2 :
-
arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation
- So 2 :
-
oxyhemoglobin saturation
- Spo 2 :
-
arterial oxyhemoglobin saturation by pulse oximetry
- Svo 2 :
-
venous oxyhemoglobin saturation
References
Wyatt JS, Edwards AD, Azzopardi D, Reynolds EOR 1989 Magnetic resonance and near infrared spectroscopy for investigation of perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Arch Dis Child 64: 953–963.
Van Bel F, Dorrepaal CA, Benders MJNL, Zeeuve PEM, van der Bor M, Berger HM 1993 Changes in cerebral hemodynamics and oxygenation in the first twenty four hours after birth asphyxia. Pediatrics 92: 365–372.
Matcher SJ, Elwell CE, Cooper CE, Cope M, Delpy DT 1995 Performance comparison of several published tissue near-infrared spectroscopy algorithms. Anal Biochem 227: 54–68.
Gagnon RE, Gagnon FA, Macnab AJ 1996 Identification of software errors in near infrared spectroscopic measurement of changes in oxidised cytochrome aa3. Eur J Appl Physiol 74: 487–495.
Marks KA, Mallard EC, Roberts I, Williams CE, Sirimanne ES, Johnstone B, Gluckman PD, Edwards AD 1996 Delayed vasodilation and altered oxygenation after cerebral ischaemia in fetal sheep. Pediatr Res 39: 48–54.
Madsen PL, Vorstrup S, Schmidt JF, Paulson OB 1990 Effect of acute and prolonged treatment with propranolol on cerebral blood flow and cerebral oxygen metabolism in healthy volunteers. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 39: 395–297.
Schmidt JF, Waldemar G, Paulson OB 1990 The acute effect of captopril on cerebral blood flow, its CO2 reactivity, and cerebral oxygen metabolism in human volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 16: 1007–1010.
Jakobsen J, Schmidt JF, Waldemar G, Paulson OB 1990 The acute effect of dilevalol on cerebral blood flow and oxygen consumption in normotensive humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 15: 574–578.
Madsen PL, Schmidt JF, Holm S, Vorstrup S, Lassen NA, Wildschiodtz G 1991 Cerebral oxygen metabolism and cerebral blood flow in man during light sleep (stage 2). Brain Res 557: 217–220.
Hino A, Ueda S, Mizukawa N, Imahori Y, Tenjin H 1992 Effect of haemodilution on cerebral haemodynamics and oxygen metabolism. Stroke 23: 423–426.
Madsen PL, Schmidt JF, Holm S, Jorgensen H, Wildschiodtz G, Christensen NJ, Friberg L, Vorstrup S, Lassen NA 1992 Mental stress and cognitive performance do not increase overall level of cerebral O2 uptake in humans. J Appl Physiol 72: 420–426.
Madsen PL, Holm S, Herning M, Lassen NA 1993 Average blood flow and oxygen uptake in the human brain during resting wakefulness: a critical appraisal of the Kety-Schmidt technique. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13: 646–655.
Baron JC, Rougemont D, Bousser MG, Lebrun-Grandie P, Iba-Zizan MT, Chivas JC 1983 Local CBF, oxygen extraction fraction and CMRO2: prognostic value in recent supratentorial infarction. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3( suppl 1): s1–s3.
Powers WJ, Grubb RL, Darriet D, Raichle ME 1985 Cerebral blood flow and cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen for cerebral function in humans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5: 600–608.
Altman DJ, Perlman JM, Volpe JJ, Powers WJ 1993 Cerebral oxygen metabolism in newborns. Pediatrics 92: 99–104.
Duncan A, Meek JH, Clemence M, Elwell C, Tyszczuk L, Cope M, Delpy DT 1995 Optical pathlength measurements on adult head, calf and forearm and the head of the newborn infant using phase resolved spectroscopy. Phys Med Biol 40: 295–304.
Yoxall CW, Dawani N, Weindling AM, Peart I 1995 Measurement of cerebral venous oxyhaemoglobin saturation in children by near infrared spectroscopy and partial jugular venous occlusion. Pediatr Res 38: 319–323.
Edwards AE, Wyatt J, Richardson C, Delpy DT, Cope M, Reynolds EOR 1988 Cotside measurement of cerebral blood flow in ill newborn infants by near infrared spectroscopy. Lancet 2: 770–771.
Edwards AD, Richardson C, Van der Zee P, Elwell C, Wyatt JS, Cope M, Delpy DT, Reynolds EOR 1993 Measurement of haemoglobin flow and blood flow by near infrared spectroscopy. J Appl Physiol 75: 1884–1889.
Bland JM, Altman DG 1995 Calculating correlation coefficients with repeated observations. 1. Correlation within subjects. BMJ 310: 446
Bland JM, Altman DG 1995 Calculating correlation coefficients with repeated observations. 2. Correlation between subjects. BMJ 310: 633
Garfunkel JM, Baird HW, Zeigler J 1954 The relationship of oxygen consumption to cerebral functional activity. J Pediatr 44: 64–72.
Frewen TC, Kissoon N, Kronick J, Fox M, Lee R, Bradwin N, Chance G 1991 Cerebral blood flow, cross brain oxygen extraction and fontanelle pressure after hypoxic-ischaemic injury in newborn infants. J Pediatr 118: 265–271.
Skov L, Pryds O, Greisen G, Lou H 1993 Estimation of cerebral venous saturation in newborn infants by near infrared spectroscopy. Pediatr Res 33: 52–55.
Fanconi S, Tschupp A 1994 Accuracy of a new transmittance-reflectance pulse oximetry sensor in critically ill neonates. Crit Care Med 22: 1142–1146.
Skov L, Pryds O, Greisen 1993 Estimating cerebral blood flow in newborn infants: comparison of near infrared spectroscopy and133 Xe clearance. Pediatr Res 30: 570–573.
Bucher HU, Edwards AD, Lipp AE, Duc G 1993 Comparison between near infrared spectroscopy and 133Xe clearance for estimation of cerebral blood flow in critically ill, preterm infants. Pediatr Res 33: 56–60.
Edwards AD, Wyatt JS, Richardson CE, Delpy DT, Cope M, Reynolds EOR 1989 Precision of cerebral blood flow measurement by near infrared spectroscopy. Pediatr Res 26: 520
Brun N, Greisen G 1994 Cerebrovascular responses to carbon dioxide as detected by near infrared spectrophotometry: comparison of three different measures. Pediatr Res 36: 20–24.
Roberts I, Fallom P, Kirkham FJ, Lloyd Thomas A, Cooper C, Maynard R, Elliott M, Edwards AD 1993 Estimation of cerebral blood flow with near infrared spectroscopy and indocyanine green. Lancet 342: 1425
Wyatt JS, Cope M, Delpy DT, van der Zee P, Arridge SR, Edwards AD, Reynolds EOR 1990 Measurement of optical pathlength for near infrared spectroscopy in newborn infants. Dev Neurosci 12: 140–144.
Van der Zee P, Cope M, Arridge AR, Essenpreis M, Potter LA, Edwards AD, Wyatt JS, McCormick DC, Roth SC, Reynolds EOR, Delpy DT 1992 Experimentally measured optical pathlengths for the adult head, calf and forearm and the head of the newborn infant as a function of interoptode spacing. Adv Exp Med Biol 316: 143–153.
Cooke RW, Rolfe P, Howat P 1977 A technique for estimation of cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant. J Med Eng Technol 1: 263–266.
Cross KW, Dear PR, Hathorn MK, Hyams A, Kerslake DM, Milligan DW, Rahilly PM, Stothers JK 1979 An estimation of cerebral blood flow in the newborn infant. J Physiol 289: 329–345.
Weindling AM, Rolfe P, Tarassenko L, Costeloe K 1983 Cerebral haemodynamics in newborn babies studied by electrical impedance. Preliminary results. Acta Paediatr Suppl 311: 14–19.
England MA 1995 Anatomical development of the central nervous system. In Levene MI, Lilford RJ (eds) Fetal and Neonatal Neurology and Neurosurgery. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 3–27.
Koyangi T, Nakano H 1995 Functional development of the fetal nervous system. In Levene MI, Lilford RJ (eds) Fetal and Neonatal Neurology and Neurosurgery. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 31–44.
Gleason CA, Hamm C, Jones MD 1989 Cerebral blood flow, oxygenation, and carbohydrate metabolism in immature fetal sheep in utero. Am J Physiol 256:R1246–R1268.
Himwich WA, Benaron HB, Tucker BE, Babuna C, Stripe MC 1959 Metabolic studies on perinatal human brain. Physiol 14: 873–877.
Kinnala A, Suhonen-Polvi H, Äärimma T, Kero P, Korvenranta H, Ruotsalainen U, Bergman J, Haaparanta M, Solin O, Nuutila P 1996 Cerebral metabolic rate for glucose during the first six months of life: an FDG positron emission tomography study. Arch Dis Child 74: 153–157.
Seisjo BK 1978 Brain Energy Metabolism. John Wiley& Sons, New York, 103–106.
Frackowiak RSJ, Herold S, Petty RKH, Morgan-Hughes JA 1988 The cerebral metabolism of oxygen and glucose measured by positron emission tomography in patients with mitochondrial diseases. Brain 111: 1009–1024.
Ogawa M, Fukuyama H, Ouchi Y, Yamauchi H, Kimura J 1996 Altered energy metabolism in Alzheimers disease. J Neurol Sci 139: 78–82.
Madsen PL, Hasselbalch SG, Hageman LP, Olsen K, Persistent resetting of the cerebral oxygen/glucose uptake ratio by brain activation: evidence obtained with the Kety-Schmidt technique. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15: 485–491.
Greeley WJ, Bracey VA, Ungerleider RM, Griebel JA, Kern FH, Boyd JL, Reves JG, Piantadosi CA 1991 Recovery of cerebral metabolism and mitochondrial oxidation state is delayed after hypothermic circulatory arrest. Circulation 84: suppl III 400–406.
Settergren G, Lindblad BS, Persson B 1976 Cerebral blood flow and exchange of oxygen, glucose, ketone bodies, lactate, pyruvate and amino acids in babies. Acta Paediatr Scand 65: 343–353.
Connors R, Frewen TC, Kissoon N, Kronick J, Sommeraur J, Lee R, Singh N, Tiffin N, Brown T 1992 Relationship of cross-brain oxygen content difference, cerebral blood flow and metabolic rate to neurologic outcome after near drowning. J Pediatr 121: 839–844.
Kennedy C, Sokoloff L 1957 An adaptation of the nitrous oxide method to the study of the cerebral circulation in children; normal values for cerebral blood flow and cerebral metabolic rate in childhood. J Clin Invest 36: 1130–1137.
Chugani HT, Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC 1987 Positron emission tomography study of human brain functional development. Ann Neurol 22: 487–497.
Marchal G, Rioux P, Petit-Taboue MC, Sette G, Travere JM, LePoec C, Courtheoux P, Derlon JM, Baron JC 1992 Regional cerebral oxygen consumption, blood flow and blood volume in healthy human aging. Arch Neurol 49: 1013–1020.
Vaz M Rajkumar C Wong J Mazzeo RS Turner AG Cox HS Jennings GL Esler MD 1996 Oxygen consumption in the heart, hepatomesenteric bed and brain in young and elderly human subjects and accompanying sympathetic nervous activity. Metabolism 45: 1487–1492.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
CDO2 and CVO2 can be calculated from the standard equation Equation A1, Equation A2 where CDO2 is milliliters of O2·100 g of brain-1 min-1, CBF is milliliters of blood·100 g of brain-1 min-1), CaO2 is milliliters of O2/mL of blood, CVO2 is milliliters of O2·100 g of brain-1 min-1, and CvO2 is milliliters of O2/mL of blood.


The oxygen content of blood (milliliters of O2/mL of blood) can be calculated from: Equation A3 or, Equation A4 where [Hb] = grams/mL, SO2 = percentage HbO2 saturation, 1.39 = the stoichiometric value of oxygen for hemoglobin (milliliters/g), PO2 = partial pressure of O2 (mm Hg), and 0.00003 = coefficient of oxygen solubility(milliliters of O2/mL of blood).


Within the range of hemoglobin concentrations seen in neonates, at physiologic oxygen tensions approximately 99% of the oxygen in the blood is carried bound to hemoglobin. Dissolved oxygen can therefore be reasonably disregarded in the calculation of blood oxygen content. Blood oxygen content can therefore be calculated from: Equation A5 CDO2 and CVO2 can then be calculated by rearrangingEquations A1, A2, and A5Equation A6, Equation A7 where CHbF is grams of hemoglobin·100 g of brain-1 min-1, SaO2 and CSvO2 are percent.



Because each molecule of hemoglobin binds 4 molecules of O2, if the concentration of hemoglobin in blood is expressed in micromoles/mL, the blood oxygen content can be calculated in micromoles/mL using a modification of Equation A5: Equation A8 CDO2 and CVO2 can then be calculated in micromoles·100 g-1 min-1 from:Equation A9, Equation A10



To express CVO2 in milliliters of O2·100 mL of brain-1 min-1, the CHbF value was converted to grams·100 mL-1 min-1 from:Equation A11 where 64 500 = molecular weight of hemoglobin (grams/mol).

CVO2 and CDO2 were then recalculated in milliliters/100 g/min using Equations A6 and A7.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoxall, C., Weindling, A. Measurement of Cerebral Oxygen Consumption in the Human Neonate Using Near Infrared Spectroscopy: Cerebral Oxygen Consumption Increases with Advancing Gestational Age. Pediatr Res 44, 283–290 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199809000-00004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199809000-00004
This article is cited by
-
Proteomic phenotype of cerebral organoids derived from autism spectrum disorder patients reveal disrupted energy metabolism, cellular components, and biological processes
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
Brain Oximetry and the Quest for Quantified Metabolic Rate: Applications Using MRI and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Applied Magnetic Resonance (2021)
-
Elevated brain oxygen extraction fraction in preterm newborns with anemia measured using noninvasive MRI
Journal of Perinatology (2018)
-
Investigating the effects of cerebrospinal fluid removal on cerebral blood flow and oxidative metabolism in infants with post-hemorrhagic ventricular dilatation
Pediatric Research (2017)
-
Magnetic resonance imaging based noninvasive measurements of brain hemodynamics in neonates: a review
Pediatric Research (2016)