Abstract
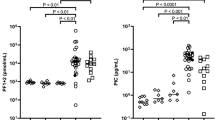
Intravascular and intraalveolar fibrin depositions in preterm infants with severe respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) have been attributed to activation of clotting. We questioned whether in the face of activated clotting, fibrinolysis is sufficient in these infants. We found, in infants with severe RDS within 6 to 12 h of birth, increased median thrombin-antithrombin III complex formation (11.1 versus1.3 ng/mL in the group with mild-to-moderate RDS, p < 0.001), indicating activation of clotting. Simultaneously, we found increased tissue-type plasminogen activator antigen (t-PA) release in plasma of these infants represented by increased median t-PA plasma concentrations (8.3 versus 2.5 ng/mL in the group with mild-to-moderate RDS, p < 0.01). This increased t-PA release was not accompanied with more plasminogen and antiplasmin consumption and with more fibrin and fibrinogen degradation than in the infants with mild-to-moderate RDS because plasma plasminogen and antiplasmin activity and total fibrin and fibrinogen degradation product concentrations were similar in both groups. We have found that activated clotting and t-PA plasma concentrations are positively correlated with arterial-to-alveolar oxygen tension ratio and ventilator efficiency index values. Plasminogen and antiplasmin activity, and total fibrin and fibrinogen degradation product concentrations were not correlated with these continuous measures of RDS severity. In neonatal RDS, clotting activity contributes to disease severity. Insufficient fibrinolysis likely facilitates the deleterious effects of activated clotting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- RDS:
-
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
- AT III:
-
antithrombin III
- T-AT III:
-
thrombin-antithrombin III complex
- t-PA:
-
tissue-type plasminogen activator antigen
- PAI-1:
-
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
- total FDP:
-
total fibrin and fibrinogen degradation products
- FiO2:
-
fraction of inspired oxygen
- PIP:
-
peak inspiratory pressure
- PaO2/PAO2:
-
arterial-to-alveolar oxygen tension ratio
- VEI:
-
ventilator efficiency index
References
Peters M, Ten Cate JW, Breederveld C, De Leeuw R, Emeis J, Koppe J 1984 Low antithrombin III levels in neonates with idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome: poor prognosis. Pediatr Res 18: 273–276.
Stark CR, Abramson D, Erkan V 1968 Intravascular coagulation and hyaline membrane disease of the newborn. Lancet 2: 1180–1181.
Schmidt B, Vegh P, Weitz J, Johnston M, Caco C, Roberts R 1992 Thrombin/antithrombin III complex formation in the neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 145: 767–770.
Brus F, van Oeveren W, Okken A, Bambang Oetomo S 1994 Activation of the plasma clotting, fibrinolytic and kinin-kallikrein system in preterm infants with severe idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Res 36: 647–653.
Brus F, van Oeveren W, Okken A, Bambang Oetomo S 1997 Disease severity is correlated with plasma clotting, fibrinolytic, and kinin-kallikrein activity in preterm infants wit respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Res 41: 120–127.
Brus F, van Oeveren W, Okken A, Bambang Oetomo S 1997 Increased release of elastase and thromboxane by a decreased number of circulating polymorphonuclear leukocytes and platelets in preterm infants with severe idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatrics 99: 672–680.
Berg W, van den B, Breederveld C, Ten Cate JW, Peters M, Borm JJJ 1989 Low antithrombin III: accurate predictor of idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome in premature neonates. Eur J Pediatr 148: 455–458.
Peters M, Ten Cate JW, Jansen E, Breederveld C 1985 Coagulation and fibrinolytic factors in the first week of life in healthy infants. J Pediatr 106: 292–295.
Malik AB, Horgan MJ 1987 Mechanisms of thrombin-induced lung vascular injury and edema. Am Rev Respir Dis 136: 467–470.
Fuchimukai T, Fujiwara T, Takahashi A, Enhörning G 1987 Artificial pulmonary surfactant inhibited by proteins. J Appl Physiol 62: 429–437.
Ueda T, Ikegami M, Jobe A 1994 Surfactant subtypes. In vitro conversion, in vivo function, and effects of serum proteins. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149: 1254–1259.
Corrigan JJ Jr 1992 Normal hemostasis in the fetus and newborn: coagulation. In: Polin RA, Fox WW (eds) Fetal and Neonatal Physiology, Vol 2. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 1368–1371.
Corrigan JJ Jr 1988 Neonatal thrombosis and the thrombolytic system: pathophysiology and therapy. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 10: 83–91.
Corrigan JJ Jr, Sleeth JJ, Jeter M, Lox CD 1989 Newborn's fibrinolytic mechanism: components and plasmin generation. Am J Hematol 32: 273–278.
Collen D 1985 Human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Circulation 72: 18–20.
Andrew M 1995 Developmental hemostasis: relevance to hemostatic problems during childhood. Semin Thromb Hemost 2: 341–356.
Aoki N, Saito H, Kamiya T, Koie K, Sakata Y, Kobakura M 1979 Congenital deficiency of α2-plasmin inhibitor associated with severe hemorrhagic tendency. J Clin Invest 63: 877–884.
Sprengers ED, Klutt C 1987 Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood 69: 381–387.
Giedion A, Haefliger H, Dangel P 1973 Acute pulmonary x-ray changes in hyaline membrane disease treated with artificial ventilation and positive end expiratory pressure. Pediatr Radiol 1: 145–152.
Brazy JE, Grimm JK, Little VA 1982 Neonatal manifestations of severe maternal hypertension occurring before the thirty-sixth week of pregnancy. J Pediatr 100: 265–271.
Jansen NJG, van Oeveren W, van Vliet M, Stoutenbeek CP, Eysman L, Wildevuur Ch RH 1991 The role of different types of corticosteroids in the inflammatory mediators in cardiopulmonary bypass. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 5: 211–217.
Levene MI, Williams JL, Fawer CL 1985 Ultrasound of the Infant Brain. Clinics in Developmental Medicine, Vol 92. Blackwell Scientific Publications Ltd, Oxford
Gu YJ, Obster R, de Haan J, Gallandat Huet RCG, van Oeveren W 1992 Biocompatibility of leukocyte removal filters during bedside leukocyte filtration of red cell concentrates. Transfusion Sci 13: 467–472.
van Lingen RA, Hofhuis WDJ, Dekker I, Baerts W, Hählen K, Sauer PJJ 1992 The effect of heparin in arterial catheters on the coagulation in preterm infants. J Perinat Med 20: 39–46.
Notter RH, Egan EA, Kwong MS, Holm BA, Shapiro DL 1985 Lung surfactant replacement in premature lambs with extracted lipid from bovine lung lavage: effects of dose, dispersion technique and gestational age. Pediatr Res 19: 569–577.
Kohelet D, Perlman M, Hanna G, Ballin A 1990 Reduced platelet counts in neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Biol Neonate 57: 334–342.
Corrigan JJ, Jeter MA 1992 Tissue-type plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor, and histidine-rich glycoproteins in stressed human newborns. Pediatrics 89: 43–46.
Plötz FB, van Oeveren W, Barlett RH, Wildevuur CHRH 1993 Blood activation during neonatal extracorporeal life support (ECLS). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 105: 823–832.
Viscardi RM, Broderick K, Sun CJ, Yale-Loehr AJ, Hessamfar A, Taciak V, Burke KC, Koenig KB, Idell S 1992 Disordered pathways of fibrin turnover in lung lavage of premature infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 146: 492–499.
Singhal KK, Parton LA 1996 Plasminogen activator activity in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: relationship to the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Pediatr Res 39: 299–235.
Idell S, Kumar A, Koenig KB, Coalson JJ 1994 Pathways of fibrin turnover in lavage of premature baboons with hyperoxic lung injury. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149: 767–775.
Haynes JB, Hyers TM, Giclas PC, Franks JJ, Petty TL 1988 Elevated fibrin degradation products in ARDS. Am Rev Respir Dis 122: 841–847.
Sarnaik AP, Lieh-Lai M 1994 Adult respiratory distress syndrome in children. Pediatr Clin North Am 41: 337–364.
Nemerson Y 1992 The tissue factor pathway of blood coagulation. Semin Hematol 29: 170–176.
Manco-Johnson M 1992 Pathophysiology of neonatal disseminated intravascular coagulation and thrombosis. In: Polin RA, Fox WW (eds) Fetal and Neonatal Physiology, Vol 2. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 1394–1399.
Collen D 1980 On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Thromb Haemost 43: 77–89.
Nilsson R, Grossmann G, Robertson B 1978 Lung surfactant and the pathogenesis of neonatal bronchiolar lesions induced by artificial ventilation. Pediatr Res 12: 249–255.
Saugstad OD 1990 Oxygen toxicity in the neonatal period. Acta Paediatr Scand 79: 881–892.
Saugstad OD, Buo L, Johansen HT, Roise O, Aasen AO 1992 Activation of the plasma kallikrein-kinin system in respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatr Res 32: 431–435.
Kaplan AP, Silverberg M 1987 The coagulation-kinin pathway of human plasma. Blood 70: 1–15.
Hathaway WE 1992 Normal hemostatic mechanisms. In: Polin RA, Fox WW (eds) Fetal Neonatal Physiology, Vol 2. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 1365–1368.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Johan Haan for his excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brus, F., Oetomo, S., Schieving, J. et al. Increased Tissue-Type Plasminogen Activator Antigen Release Is Not Accompanied by Increased Systemic Fibrinolytic Activity in Severe Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Pediatr Res 45, 588–594 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199904010-00020
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199904010-00020
This article is cited by
-
Activatie van plasma-eiwitten en bloedcellen bij het neonataal respiratoir distress-syndroom: pathogenetische en therapeutische aspecten
Tijdschrift voor kindergeneeskunde (2000)