Abstract
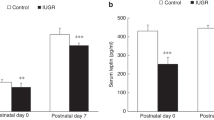
Low birth weight has been associated with elevated arterial pressure in later life but mechanisms are unknown. Our aim was to determine the effects of low birth weight resulting from intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) on fetal and postnatal arterial pressures and the potential roles of circulating cortisol and renin. We induced IUGR by umbilico-placental embolization (UPE) in fetal sheep from 120 d of gestation until birth (approximately 147 d); postnatal lambs (8 IUGR, 8 controls) were studied for 8 wk. Fetal and postnatal arterial pressures were measured and blood samples taken for measurement of gas tensions, cortisol concentrations and renin activity. In IUGR fetuses, mean arterial pressure (MAP) initially increased with UPE, but near term was not different to values in controls. IUGR lambs weighed 33% less than controls at birth and remained lighter than controls during the 8 postnatal weeks; their growth pattern was different to that of controls. IUGR lambs had lower MAP than controls, and this relative hypotension (−4 mm Hg) persisted throughout the 8 postnatal weeks. Covariate analysis showed that the relative hypotension of IUGR lambs could have resulted from their smaller size. Plasma cortisol concentrations were not different between IUGR and control animals before or after birth. Plasma renin activity was not different in postnatal IUGR lambs compared with controls. Thus, postnatal cortisol and renin levels were not consistent with the development of hypotension or hypertension. We conclude that late gestational IUGR in sheep leads to relative hypotension in the early postnatal period, probably a result of reduced body size.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- UPE:
-
umbilico-placental embolization
- IUGR:
-
intrauterine growth restriction
- MAP:
-
mean arterial pressure
References
Barker DJ 1995 Fetal origins of coronary heart disease. BMJ 311: 171–174.
Law CM, Shiell AW 1996 Is blood pressure inversely related to birth weight? The strength of evidence from a systematic review of the literature. J Hypertens 14: 935
Barker DJ, Godfrey KM, Osmond C, Bull A 1992 The relation of fetal length, ponderal index and head circumference to blood pressure and the risk of hypertension in adult life. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 6: 35–44.
Gennser G, Rymark P, Isberg PE 1988 Low birth weight and risk of high blood pressure in adulthood. BMJ 296: 1498–1500.
Williams S, St George IM, Silva PA 1992 Intrauterine growth retardation and blood pressure at age seven and eighteen. J Clin Epidemiol 45: 1257–1263.
Nilsson PM, Ostergren PO, Nyberg P, Soderstrom M, Allebeck P 1997 Low birth weight is associated with elevated systolic blood pressure in adolescence: a prospective study of a birth cohort of 149 378 Swedish boys. J Hypertens 15: 1627–1631.
Matthes JW, Lewis PA, Davies DP, Bethel JA 1994 Relation between birth weight at term and systolic blood pressure in adolescence. BMJ 308: 1074–1077.
Law CM, de Swiet M, Osmond C, Fayers PM, Barker DJ, Cruddas AM, Fall CH 1993 Initiation of hypertension in utero and its amplification throughout life. BMJ 306: 24–27.
Persson E, Jansson T 1992 Low birth weight is associated with elevated adult blood pressure in the chronically catheterized guinea-pig. Acta Physiol Scand 145: 195–196.
Langley SC, Jackson AA 1994 Increased systolic blood pressure in adult rats induced by fetal exposure to maternal low protein diets. Clin Sci 86: 217–222.
Murotsuki J, Challis JR, Han VK, Fraher LJ, Gagnon R 1997 Chronic fetal placental embolization and hypoxemia cause hypertension and myocardial hypertrophy in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol 272: R201–R207.
Cock ML, Harding R 1997 Renal and amniotic fluid responses to umbilicoplacental embolization for 20 days in fetal sheep. Am J Physiol 273: R1094–1102.
Gagnon R, Challis J, Johnston L, Fraher L 1994 Fetal endocrine responses to chronic placental embolization in the late-gestation ovine fetus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 170: 929–938.
Trudinger BJ, Stevens D, Connelly A, Hales JR, Alexander G, Bradley L, Fawcett A, Thompson RS 1987 Umbilical artery flow velocity waveforms and placental resistance: the effects of embolization of the umbilical circulation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 157: 1443–1448.
Nicolaides KH, Economides DL, Soothill PW 1989 Blood gases, pH, and lactate in appropriate- and small-for-gestational-age fetuses. Am J Obstet Gynecol 161: 996–1001.
Lumbers ER 1995 Functions of the renin-angiotensin system during development. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 22: 499–505.
Edwards CR, Benediktsson R, Lindsay RS, Seckl JR 1993 Dysfunction of placental glucocorticoid barrier: link between fetal environment and adult hypertension?. Lancet 341: 355
Bocking AD, McMillen IC, Harding R, Thorburn GD 1986 Effect of reduced uterine blood flow on fetal and maternal cortisol. J Dev Physiol 8: 237–245.
Woods RL, Anderson WP, Korner PI 1986 Renal and systemic effects of enalapril in chronic one-kidney hypertension. Hypertension 8: 109–116.
Hawkins P, Steyn C, Ozaki T, Saito T, Noakes DE, Hanson MA 2000 Effect of maternal undernutrition in early gestation on ovine fetal blood pressure and cardiovascular reflexes. Am J Physiol 279: R340–348.
Contis G, Lind J 1963 Study of systolic blood pressure, heart rate, body temperature of normal newborn infants through the first week of life. Acta Paediatr Suppl 146: 41–47.
Lee YH, Rosner B, Gould JB, Lowe EW, Kass EH 1976 Familial aggregation of blood pressures of newborn infants and their mother. Pediatrics 58: 722–729.
O'Sullivan MJ, Kearney PJ, Crowley MJ 1996 The influence of some perinatal variables on neonatal blood pressure. Acta Paediatr 85: 849–853.
Robinson JS, McMillen IC, Fielke S, Evans L, Lok F, Owens JA 1998 Role of the placenta: development and function. Equine Vet J 30: 456
Williams S, Poulton R 1999 Twins and maternal smoking: ordeals for the fetal origins hypothesis?. A cohort study BMJ 318: 897
Dwyer T, Blizzard L, Morley R, Ponsonby AL 1999 Within pair association between birth weight and blood pressure at age 8 in twins from a cohort study. BMJ 319: 1325–1329.
Poulter NR, Chang CL, MacGregor AJ, Snieder H, Spector TD 1999 Association between birth weight and adult blood pressure in twins: historical cohort study. BMJ 319: 1330–1333.
Broughton Pipkin F, Lumbers ER, Mott JC 1974 Factors influencing plasma renin and angiotensin II in the conscious pregnant ewe and its foetus. J Physiol 243: 619–636.
Konje JC, Bell SC, Morton JJ, de Chazal R, Taylor DJ 1996 Human fetal kidney morphometry during gestation and the relationship between weight, kidney morphometry and plasma active renin concentration at birth. Clin Sci 91: 169–175.
Edwards LJ, Simonetta G, Owens JA, Robinson JS, McMillen IC 1999 Restriction of placental and fetal growth in sheep alters fetal blood pressure responses to angiotensin II and captopril. J Physiol 515: 897–904.
Benediktsson R, Lindsay RS, Noble J, Seckl JR, Edwards CR 1993 Glucocorticoid exposure in utero: new model for adult hypertension. Lancet 341: 339–341.
Dodic M, May CN, Wintour EM, Coghlan JP 1998 An early prenatal exposure to excess glucocorticoid leads to hypertensive offspring in sheep. Clin Sci 94: 149–155.
Richardson BS, Bocking AD 1998 Metabolic and circulatory adaptations to chronic hypoxia in the fetus. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 119: 717–723.
Gagnon R, Murotsuki J, Challis JR, Fraher L, Richardson BS 1997 Fetal sheep endocrine responses to sustained hypoxemic stress after chronic fetal placental embolization. Am J Physiol 272: E817–823.
Deyl Z, Juricova M, Rosmus J, Adam M 1971 The effect of food deprivation on collagen accumulation. Exp Gerontol 6: 383–390.
Spanheimer R, Zlatev T, Umpierrez G, DiGirolamo M 1991 Collagen production in fasted and food-restricted rats: response to duration and severity of food deprivation. J Nutr 121: 518–524.
Berk JL, Massoomi N, Hatch C, Goldstein RH 1999 Hypoxia downregulates tropoelastin gene expression in rat lung fibroblasts by pretranslational mechanisms. Am J Physiol 277: L566–572.
Rizzo G, Arduini D 1991 Fetal cardiac function in intrauterine growth retardation. Am J Obstet Gynecol 165: 876–882.
Hokken-Koelega AC, De Ridder MA, Lemmen RJ, Den Hartog H, De Muinck Keizer-Schrama SM, Drop SL 1995 Children born small for gestational age: do they catch up?. Pediatr Res 38: 267
Albertsson-Wikland K, Wennergren G, Wennergren M, Vilbergsson G, Rosberg S 1993 Longitudinal follow-up of growth in children born small for gestational age. Acta Paediatr 82: 438–443.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Mr. Ale- Satragno for surgical assistance, Ms. Belinda Joyce for assistance in animal e-perimentation, and Mrs. Jan Loose and Mrs. Katrina Worthy for performing, respectively, the cortisol and renin assays. We are also appreciative of the interest of Dr. Ruth Morley in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Louey, S., Cock, M., Stevenson, K. et al. Placental Insufficiency and Fetal Growth Restriction Lead to Postnatal Hypotension and Altered Postnatal Growth in Sheep. Pediatr Res 48, 808–814 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200012000-00018
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200012000-00018
This article is cited by
-
Altered Placental Chorionic Arterial Biomechanical Properties During Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Mean Arterial Pressure in Concordant and Discordant Triplets during the First Week of Life
Journal of Perinatology (2005)