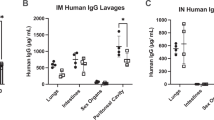
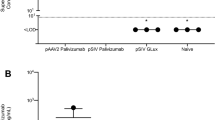
Abstract
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most important respiratory pathogen in infancy and early childhood and may predispose to subsequent lower respiratory tract illness. Recent data indicate that RSV up-regulates the substance P receptor, making the airways abnormally susceptible to the proinflammatory effects of this peptide released from sensory nerves. The present study was designed to determine whether the administration of RSV antibodies prevents the potentiation of neurogenic inflammation in rat airways. Five days after inoculation, sensory nerve-mediated extravasation of Evans blue-labeled albumin was significantly greater in the airways of RSV-infected rats than in pathogen-free controls. Polyclonal immune globulin enriched for RSV-neutralizing antibodies (RSVIG) reduced neurogenic extravasation when injected 24 h before intranasal inoculation of the virus but not when injected before endotracheal inoculation. A humanized MAb against RSV fusion protein (palivizumab) was twice as potent as RSVIG when given before intranasal inoculation and also caused significant inhibition after endotracheal inoculation. Furthermore, palivizumab inhibited neurogenic inflammation in RSV-infected rats when given 72 h after virus inoculation. These data suggest that palivizumab protects the respiratory tract from RSV-induced inflammation when given before or in the early phase of the viral infection. The administration of palivizumab to high-risk infants may limit the severity of the acute airway inflammation and may protect against subsequent lower respiratory tract illness.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- MEM:
-
Eagle's minimum essential medium
- RSV:
-
respiratory syncytial virus
- TCID50:
-
50% tissue culture infective dose
- RSVIG:
-
polyclonal immune globulin enriched for RSV-neutralizing antibodies
References
Hall CB 1998 Respiratory syncytial virus. In: Feigin RD, Cherry JD (eds) Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Diseases. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 2084–2111
Eigen H 1999 The RSV-asthma link: the emerging story. J Pediatr 135: S1–S50
Stein RT, Sherril D, Morgan WJ, Holberg CJ, Halonen M, Taussig LM, Wright AL, Martinez FD 1999 Respiratory syncytial virus in early life and risk of wheeze and allergy by age 13 years. Lancet 354: 541–545
Piedimonte G 1995 Tachykinin peptides, receptors, and peptidases in airway disease. Exp Lung Res 21: 809–834
Piedimonte G, Nadel JA 1996 Role of peptidases in airway defense mechanisms. In: Chretien J, Dusser D (eds) Airways and Environment: From Injury to Repair. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 123–153
Barnes PJ 1992 Neurogenic inflammation and asthma. J Asthma 29: 165–180
Piedimonte G, Rodriguez MM, King KA, McLean S, Jiang X 1999 Respiratory syncytial virus upregulates expression of the substance P receptor in rat lungs. Am J Physiol 277: L831–L840
Piedimonte G, King KA, Perez Z, Jiang X 1999 Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes long-term potentiation of neurogenic inflammation in rat airways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159: A245 abstr
The PREVENT Study Group. 1997 Reduction of respiratory syncytial virus hospitalization among premature infants and infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia using respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin prophylaxis. Pediatrics 99: 93–99
The IMpact-RSV Study Group 1998 Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. Pediatrics 102: 531–537
Piedimonte G, Pickles RJ, Lehmann JR, McCarty D, Costa DL, Boucher RC 1997 Replication-deficient adenoviral vector for gene transfer potentiates airway neurogenic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16: 250–258
Routledge EG, McQuillin J, Samson ACR, Toms GL 1985 The development of monoclonal antibodies to respiratory syncytial virus and their use in diagnosis by indirect immunofluorescence. J Med Virol 15: 305–320
Piedimonte G, Nadel JA, Umeno E, McDonald DM 1990 Sendai virus infection potentiates neurogenic inflammation in the rat trachea. J Appl Physiol 68: 754–760
Piedimonte G, McDonald DM, Nadel JA 1990 Glucocorticoids inhibit neurogenic plasma extravasation and prevent virus-potentiated extravasation in the rat trachea. J Clin Invest 86: 1409–1415
Prince GA, Jenson AB, Horswood RL 1978 The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in cotton rats. Am J Pathol 93: 771–792
Saria A, Lundberg JM, Skofitsch G, Lembeck F 1983 Vascular protein leakage in various tissues induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, serotonin, histamine, and by antigen challenge. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 324: 212–218
Holzer P 1991 Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev 43: 143–201
Siber GR, Leombruno D, Leszczynski J, McIver J, Bodkin D, Gonin R, Thompson CM, Walsh EE, Piedra PA, Hemming VG, Prince GA 1994 Comparison of antibody concentrations and protective activity of respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin and conventional immune globulin. J Infect Dis 169: 1368–1373
Johnson S, Oliver C, Prince GA, Hemming VG, Pfarr DS, Wang SC, Dormitzer M, O'Grady J, Koenig S, Tamura JK, Woods R, Bansal G, Couchenour D, Tsao E, Hall WC, Young JF 1997 Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody (MEDI-493) with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). J Infect Dis 176: 1215–1224
Zar JH 1984 Two-Factor Analysis of Variance. Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall Inc, Englewood Cliffs NJ, pp 206–235
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL 1980 Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47: 1–9
Groothuis JR, Simoes EAF, Levin MJ, Hall CB, Long CE, Rodriguez WJ, Arrobio J, Meissner HC, Fulton DR, Welliver RC, Tristram DA, Siber GR, Prince GA, Van Raden M, Hemming VG 1993 Prophylactic administration of respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin to high-risk infants and young children. N Engl J Med 329: 1524–1530
Rodriguez WJ, Gruber WC, Welliver RC, Groothuis JR, Simoes EAF, Meissner HC, Hemming VG, Levin MJ, Hall CB, Lepow ML, Rosas AJ, Robertsen C, Kramer AA 1997 Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) immune globulin intravenous therapy for RSV lower respiratory tract infection in infants and young children at risk for severe RSV infections. Pediatrics 99: 454–461
Malley R, DeVincenzo J, Ramilo O, Dennehy PH, Meissner HC, Gruber WC, Sanchez PJ, Jafri H, Balsley J, Carlin D, Buckingham S, Vernacchio L, Ambrosino DM 1998 Reduction of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in tracheal aspirates in intubated infants by use of humanized monoclonal antibody to RSV F protein. J Infect Dis 178: 1555–1561
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Xiaobo Jiang for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NHLBI HL-61007), the 1997 Career Investigator Award of the American Lung Association of Florida, and a research grant from MedImmune, Inc. to Dr. Giovanni Piedimonte.
Presented in part at the 1999 Annual Meeting, Pediatric Academic Societies, San Francisco, CA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piedimonte, G., King, K., Holmgren, N. et al. A Humanized Monoclonal Antibody against Respiratory Syncytial Virus (Palivizumab) Inhibits RSV-Induced Neurogenic-Mediated Inflammation in Rat Airways. Pediatr Res 47, 351–356 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200003000-00011
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200003000-00011
This article is cited by
-
One-domain CD4 Fused to Human Anti-CD16 Antibody Domain Mediates Effective Killing of HIV-1-Infected Cells
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Pathophysiological mechanisms for the respiratory syncytial virus-reactive airway disease link
Respiratory Research (2002)
-
An epidemiological study of respiratory syncytial virus associated hospitalizations in Denmark
Respiratory Research (2002)