Abstract
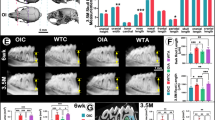
Recent non-placebo-controlled studies of the bisphosphonate pamidronate have shown it to be effective in reducing fractures and improving bone density in infants and children with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). To evaluate the effects of bisphosphonate treatment in a controlled study, the oim/oim mouse model of OI was studied. Nursing infant mouse pups (∼ 2 wk old) with moderate to severe OI (oim/oim mouse) and age- and background-matched control mice (+/+) were treated either with the third-generation bisphosphonate alendronate (ALN), or with saline. Fracture risk, bone quality, and growth were evaluated over a 12-wk treatment period. ALN at a dose of 0.03 mg/kg/d or saline was administered via s.c. injection to infant oim/oim and wild-type (+/+) mice from 2 to 14 wk of age (n = 20 per subgroup). The average number of fractures sustained by the ALN-treated oim/oim mice was reduced significantly compared with the untreated oim/oim mice (0.7 ± 0.7 fractures/mouse versus 2.0 ± 0.2 fractures/mouse). Bone density increased significantly in the femur and the spine with treatment (2.0 ± 0.5 versus 1.2 ± 0.5 in femur and 2.1 ± 0.5 versus 1.6 ± 0.5 in spine). Histologic evaluation revealed the percentage of metaphyseal tibial bone increased significantly with treatment in both +/+ and oim/oim mice. Mechanical testing revealed an increase in structural stiffness for both treated +/+ and oim/oim mice compared with untreated animals. None of the material properties examined were significantly altered with treatment, nor was spinal curvature affected. Weight gain and long bone growth were comparable in the treated and untreated oim/oim mice. In wild-type mice, femur lengths were significantly shorter in the treated mice compared with untreated counterparts. This animal study demonstrates that treatment of OI in mice as early as 2 wk of age with ALN appears to be effective in reducing fractures and increasing bone properties. Based on the data from this study, ALN therapy in infants with OI should prove to be effective.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- OI:
-
osteogenesis imperfecta
- oim/oim :
-
mice homozygous for spontaneous mutation causing the skeletal defects of OI
- +/+:
-
wild-type mice
- AP:
-
anteroposterior
- ML:
-
mediolateral
- BMD:
-
bone mineral density
- ALN:
-
alendronate
References
Smith R 1995 Osteogenesis imperfecta: the brittle bone syndrome. Curr Orthop 9: 28–33
Engelbert RHH, Pruijs JEH, Beemer FA, Helders PJM 1998 Osteogenesis imperfecta in childhood: treatment strategies. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 79: 1590–1593
Sillence DO, Senn A, Danks DM 1979 Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet 16: 101–116
Glorieux FH, Rauch F, Plotkin H, Ward L, Travers R, Roughley P, Lalic L, Glorieux DF, Fassier F, Bishop NJ 2000 Type V osteogenesis imperfecta: a new form of brittle bone disease. J Bone Miner Res 15: 1650–1658
Paterson CR, Ogston SA, Henry RM 1996 Life expectancy in osteogenesis imperfecta. BMJ 312: 351
Castells S 1973 New approaches to treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta. Clin Orthop 93: 239–249
Antoniazzi F, Mottes M, Fraschini P, Brunelli PC, Tato L 2000 Osteogenesis imperfecta: practical treatment guidelines. Paediatr Drugs 2: 465–488
Plotkin LI, Weinstein RS, Parfitt AM, Roberson PK, Manolagas SC, Bellido T 1999 Prevention of osteocyte osteoblast apoptosis by bisphosphonates calcitonon. J Clin Invest 104: 1363–1374
Rogers MJ, Frith JC, Luckman SP, Coxon FP, Benford HL, Monkkonen J, Suriola S, Chilton KM, Russell RGG 1999 Molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Bone 24( 5): 73S–79S
Devogelaer JP, Malghem J, Maldague B, Nagant de Deuxchaisnes C 1987 Radiological manifestations of bisphosphonate treatment with APD in a child suffering from osteogenesis imperfecta. Skeletal Radiol 16: 360–310
Huaux JP, Lokeitek W 1988 Is APD a promising drug in the treatment of severe osteogenesis imperfecta?. J Pediatr Orthop 8: 71–72
Lansmeer-Beker EA, Massa GG, Maaswinkel-Mooy PD, van de Kamp JJP, Papapoulos SE 1997 Treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta with the bisphosphonate olpadronate (dimethylaminohydroxypropylidene bisphosphonate). Eur J Pediatr 156: 792–794
Bembi B, Parma A, Bottega M, Ceschel S, Zanatta M, Martini C, Ciana G 1997 Intravenous pamidronate treatment in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr 131: 622–625
Astrom E, Soderhall S 1998 Beneficial effect of bisphosphonate during five years of treatment of severe osteogenesis imperfecta. Acta Paediatr 87: 64–68
Glorieux FH, Bishop N, Plotkin H, Chabot G, Lanoue G, Travers R 1998 Cyclic administration of pamidronate in children with severe osteogenesis imperfecta. N Engl J Med 339: 946–947
Plotkin H, Rauch F, Bishop NJ, Montpetit K, Ruck-Gibis J, Travers R, Glorieux FH 2000 Pamidronate treatment of severe osteogenesis imperfecta in children under 3 years of age. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 1846–1850
Lepola VT, Hannuniemi R, Kippo K, Lauren L, Jalovaara P, Vaanenen HK 1996 Long-term effects of clodronate on growing rat bone. Bone 18: 191–196
Ferretti JL, Mondelo N, Capozza RF, Cointry GR, Zanchetta JR, Montuori E 1995 Effects of large doses of olpadronate (dimethyl-pamidronate) on mineral density, cross-sectional architecture, mechanical properties of rat femurs. Bone 16: 285S–293S
Chipman SD, Sweet HO, McBride DJ, Davisson MT, Marks SC, Shuldiner AR, Wenstrup RJ, Rowe DW, Shapirt JR 1993 Defective pro alpha 2(I) collagen synthesis in a recessive mutation in mice: a model of human osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90: 1701–1705
Camacho NP, Raggio CL, Doty SB, Root L, Zraick V, Ilg WA, Toledano TR, Boskey AL 2001 A controlled study of the effects of alendronate in a growing mouse model of osteogenesis imperfecta. Calcif Tissue Int 69: 94–101
Cobb JR 1948 Outline for the study of scoliosis. Instructional course lectures. Am Acad Orthop Surg 5: 248–260
Turner CH, Burr DB 1993 Basic biomechanical measurements of bone: a tutorial. Bone 14: 595–608
Shimizu C, Coutts RD, Healey RM, Kubo T, Hirasawa Y, Amiel D 1997 Method of histomorphometric assessment of glycosaminoglycans in articular cartilage. J Orthop Res 15: 670–674
Zar JH 1999 Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice Hall, New Jersey, pp 260–261
Lanza FL, Hunt RH, Thomson AB, Provenza JM, Blank MA 2000 Endoscopic comparison of esophageal gastroduodenal effects of risedronate alendronate in postmenopausal women. Gastroenterology 119: 866–869
Glorieux FH 2001 The use of bisphosphonates in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 14( suppl 6): 1491–1495
Deak SB, van der Rest M, Prockop DJ 1985 Altered helical structure of a homotrimer of alpha 1 (I) chains synthesized by fibroblasts from a variant of osteogenesis imperfecta. Coll Relat Res 5: 305–313
Pysklywec MW, Moran EL, Bogoch ER 2000 Changes in cross-sectional geometry of the distal femoral metaphysis associated with inflammatory arthritis are reduced by a bisphosphonate (zoledronate). J Orthop Res 18: 734–738
Ferretti JL, Delgado CJ, Capozza RF, Cointry G, Montuori E, Roldan E, Perez Lloret A, Zanchetta JR 1993 Protective effects of disodium etidronate pamidronate against the biomechanical repercussion of betamethasone-induced osteopenia in growing rat femurs. Bone Miner 20: 265–276
Osterman T, Lauren L, Kuurtamo P, Hannuniemi R, Isaksson P, Kippo K, Peng Z, Vaananen HK, Sellman R 1998 The effect of orally administered clodronate on bone mineral density bone geometry in ovariectomized rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284: 312–316
Murphy MG, Weiss S, McClung M, Schnitzer T, Cerchio K, Connor J, Krupa D, Gertz BJ, MK-677/Alendronate Study Group 2001 Effect of alendronate MK-677 (a growth hormone secretagogue), individually in combination, on markers of bone turnover bone mineral density in postmenopausal osteoporotic women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 1116–1125
Boivin GY, Chavassieux PM, Santora AC, Yates J, Meunier PJ 2000 Alendronate increases bone strength by increasing the mean degree of mineralization of bone tissue in osteoporotic women. Bone 27: 687–694
Cummings SR, Black DM, Vogt TM 1996 Changes in BMD substantially under-estimate the anti-fracture effects of alendronate other antiresorptive drugs. J Bone Miner Res 11( suppl): S102( abstr)
Bullough PG 1992 Atlas of Orthopaedic Pathology with Clinical and Radiologic Correlations. Gower Medical Publishing, Philadelphia, pp 5.8–5.12
Orcel P, Beaudreuil J 2002 Bisphosphonates in bone diseases other than osteoporosis. Joint Bone Spine 69: 19–27
Zacharin M, Bateman J 2002 Pamidronate treatment of osteogenesis imperfecta—lack of correlation between clinical severity, age at onset of treatment, predicted collagen mutation treatment response. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 15: 163–174
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dalina Stiner, Kwadwo Boachie, and Vivien Zraick for the technical assistance, and the Mechanical Testing Core Facility of The Hospital for Special Surgery. We also thank Merck & Co., West Point, PA, for supplying the alendronate used in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by a grant from the Osteogenesis Imperfecta Foundation (The Michael Geisman Fellowship Award to E.A.M.) and by National Institutes of Health Grant numbers DE11803 (N.P.C.) and AR46121.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarthy, E., Raggio, C., Hossack, M. et al. Alendronate Treatment for Infants with Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Demonstration of Efficacy in a Mouse Model. Pediatr Res 52, 660–670 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200211000-00010
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200211000-00010
This article is cited by
-
Sclerostin-Antibody Treatment Decreases Fracture Rates in Axial Skeleton and Improves the Skeletal Phenotype in Growing oim/oim Mice
Calcified Tissue International (2020)
-
An update on the role of RANKL–RANK/osteoprotegerin and WNT-ß-catenin signaling pathways in pediatric diseases
World Journal of Pediatrics (2019)
-
Alendronate treatment induces IL-1B expression and apoptosis in glioblastoma cell line
Inflammopharmacology (2018)
-
Impaired bone remodeling in children with osteogenesis imperfecta treated and untreated with bisphosphonates: the role of DKK1, RANKL, and TNF-α
Osteoporosis International (2016)
-
Gender-Dependence of Bone Structure and Properties in Adult Osteogenesis Imperfecta Murine Model
Annals of Biomedical Engineering (2013)