Abstract
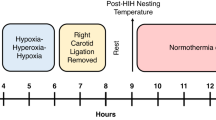
Hypothermia may be an ideal neuroprotective intervention in hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy after perinatal asphyxia. The present study describes the long-term effects of prolonged resuscitative whole-body hypothermia initiated 2 h after hypoxic-ischemic injury on brain morphology and neuropsychological behavior in 7-d-old rats. After right common carotid artery ligation and exposure to hypoxia of 8% O2 for 105 min, 10 animals were kept normothermic at 37°C and 10 animals were cooled to 30°C rectal temperature for 26 h, starting 2 h after the hypoxic-ischemic insult. All hypoxic-ischemic animals were gavage fed to guarantee long-term survival. Neuroprotection was evaluated by magnetic resonance imaging and behavioral testing. Hypothermia significantly reduced the final size of cerebral infarction by 23% at 6 wk after the insult. The most extended tissue rescue was found in the hippocampus (21%, p = 0.031), followed by the striatum (13%, p = 0.143) and the cortex (11%, p = 0.160). Cooling salvaged spatial memory deficits verified at 5 wk of recovery with Morris Water Maze test; whereas circling abnormalities after apomorphine injection and sensory motor dysfunctions on rotating treadmill improved, yet did not reach statistical significance. When compared with controls, hypoxic-ischemic animals performed worse in all behavioral tests. Hypothermia did not influence functional outcome in controls. Significant correlations between behavioral performance and corresponding regional brain volumes were found. We conclude that 26 h of mild to moderate resuscitative hypothermia leads not only to brain tissue rescue, but most important to long-lasting behavioral improvement throughout brain maturation despite severity of injury and delayed onset of cooling.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- MRI:
-
magnetic resonance imaging
- HI:
-
hypoxia-ischemia
- T2WI:
-
T2-weighted imaging
- DWI:
-
diffusion weighted imaging
- MWM:
-
Morris Water Maze
- IH:
-
ischemia with hypothermia
- IN:
-
ischemia with normothermia
- CH:
-
control with hypothermia
- CN:
-
control with normothermia
References
Committee on Fetus and Newborn, American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Obstetric Practice, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 1996 Use and abuse of the Apgar score. Pediatrics 98: 141–142
Roland EH, Poskitt K, Rodriguez E, Lupton BA, Hill A 1998 Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic thalamic injury: clinical features and neuroimaging. Ann Neurol 44: 161–166
Vannucci RC, Perlman JM 1997 Interventions for perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Pediatrics 100: 1004–1014
Dunn JM, Miller JA Jr 1969 Hypothermia combined with positive pressure ventilation in resuscitation of the asphyxiated neonate. Clinical observations in 28 infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol 104: 58–67
Cordey R, Chiolero R, Miller JA 1973 Resuscitation of neonates by hypothermia: report on 20 cases with acid-base determination on 10 cases and the long-term development of 33 cases. Resuscitation 2: 169–181
Williams GR, Spencer JA 1958 The clinical use of hypothermia following cardiac arrest. Ann Surg 148: 462–466
Silverman WA, Fertig JW, Berger AP 1958 The influence of the thermal environment upon the survival of newly born premature infants. Pediatrics 22: 876–885
Busto R, Dietrich WD, Globus MY, Ginsberg MD 1989 Postischemic moderate hypothermia inhibits CA1 hippocampal ischemic neuronal injury. Neurosci Lett 101: 299–304
Dietrich WD, Busto R, Alonso O, Globus MY, Ginsberg MD 1993 Intraischemic but not postischemic brain hypothermia protects chronically following global forebrain ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13: 541–549
Weinrauch V, Safar P, Tisherman S, Kuboyama K, Radovsky A 1992 Beneficial effect of mild hypothermia and detrimental effect of deep hypothermia after cardiac arrest in dogs. Stroke 23: 1454–1462
Colbourne F, Corbett D 1995 Delayed postischemic hypothermia: a six month survival study using behavioral and histological assessments of neuroprotection. J Neurosci 15: 7250–7260
Colbourne F, Sutherland GR, Auer RN 1999 Electron microscopic evidence against apoptosis as the mechanism of neuronal death in global ischemia. J Neurosci 19: 4200–4210
Bona E, Hagberg H, Loberg EM, Banasiak K, Thoresen M 1998 Protective effects of moderate hypothermia after neonatal hypoxia-ischemia: short- and long-term outcome. Pediatr Res 43: 738–745
Sirimanne ES, Blumberg RM, Bossano D, Gunning M, Edwards AD, Gluckman PD, Williams CE 1996 The effect of prolonged modification of cerebral temperature on outcome after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the infant rat. Pediatr Res 39: 591–597
Gunn AJ, Gunn TR, de Haan HH, Williams CE, Gluckman PD 1997 Dramatic neuronal rescue with prolonged selective head cooling after ischemia in fetal lambs. J Clin Invest 99: 248–256
Gunn AJ, Gunn TR, Gunning MI, Williams CE, Gluckman PD 1998 Neuroprotection with prolonged head cooling started before postischemic seizures in fetal sheep. Pediatrics 102: 1098–1106
Doppenberg EM, Bullock R 1997 Clinical neuro-protection trials in severe traumatic brain injury: lessons from previous studies. J Neurotrauma 14: 71–80
Fisher M, Bogousslavsky J 1998 Further evolution toward effective therapy for acute ischemic stroke. JAMA 279: 1298–1303
Muir KW, Grosset DG 1999 Neuroprotection for acute stroke: making clinical trials work. Stroke 30: 180–182
Nedelcu J, Klein MA, Aguzzi A, Boesiger P, Martin E 2000 Resuscitative hypothermia protects the neonatal brain from hypoxic-ischemic injury. Brain Pathol 10: 61–71
Rice JE Jr, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB 1981 The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9: 131–141
Rumpel H, Buchli R, Gehrmann J, Aguzzi A, Illi O, Martin E 1995 Magnetic resonance imaging of brain edema in the neonatal rat: a comparison of short and long term hypoxia-ischemia. Pediatr Res 38: 113–118
Rumpel H, Nedelcu J, Aguzzi A, Martin E 1997 Late glial swelling after acute cerebral hypoxia-ischemia in the neonatal rat: a combined magnetic resonance and histochemical study. Pediatr Res 42: 54–59
Nedelcu J, Klein MA, Aguzzi A, Boesiger P, Martin E 1999 Biphasic edema after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats reflects early neuronal and late glial damage. Pediatr Res 46: 297–304
Yager J, Towfighi J, Vannucci RC 1993 Influence of mild hypothermia on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the immature rat. Pediatr Res 34: 525–529
Thoresen M, Bagenholm R, Lindberg EM, Apricena F, Kjellmer I 1996 Posthypoxic cooling of neonatal rats provides protection against brain injury. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 74: F3–F9
Zaloga GP, Roberts P 1994 Permissive underfeeding. New Horiz 2: 257–263
Young RS, Kolonich J, Woods CL, Yagel SK 1986 Behavioral performance of rats following neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Stroke 17: 1313–1316
Bona E, Johansson BB, Hagberg H 1997 Sensorimotor function and neuropathology five to six weeks after hypoxia-ischemia in seven-day-old rats. Pediatr Res 42: 678–683
Hennig J, Nauerth A, Friedburg H 1986 RARE imaging: a fast imaging method for clinical MR. Magn Reson Med 3: 823–833
Merboldt KD, Hänicke W, Frahm J 1985 Self-diffusion NMR imaging using stimulated echoes. J Magn Reson 64: 479–486
Jansen EM, Low WC 1996 Long-term effects of neonatal ischemic-hypoxic brain injury on sensorimotor and locomotor tasks in rats. Behav Brain Res 78: 189–194
Meyer M, Widmer HR, Wagner B, Guzman R, Evtouchenko L, Seiler RW, Spenger C 1998 Comparison of mesencephalic free-floating tissue culture grafts and cell suspension grafts in the 6-hydroxydopamine- lesioned rat. Exp Brain Res 119: 345–355
Brück K 1998 Neonatal thermal regulation. In: Polin RA, Fox WF (eds) Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 676–702
Yager JY, Asselin J 1996 Effect of mild hypothermia on cerebral energy metabolism during the evolution of hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the immature rat. Stroke 27: 919–925
Haaland K, Lindberg EM, Steen PA, Thoresen M 1997 Posthypoxic hypothermia in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res 41: 505–512
Edwards AD, Yue X, Squier MV, Thoresen M, Cady EB, Penrice J, Cooper CE, Wyatt JS, Reynolds EO, Mehmet H 1995 Specific inhibition of apoptosis after cerebral hypoxia- ischaemia by moderate post-insult hypothermia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217: 1193–1199
Thoresen M, Penrice J, Lorek A, Cady EB, Wylezinska M, Kirkbride V, Cooper CE, Brown GC, Edwards AD, Wyatt JS 1995 Mild hypothermia after severe transient hypoxia-ischemia ameliorates delayed cerebral energy failure in the newborn piglet. Pediatr Res 37: 667–670
Amess PN, Penrice J, Cady EB, Lorek A, Wylezinska M, Cooper CE, DSouza P, Tyszczuk L, Thoresen M, Edwards AD, Wyatt JS, Reynolds EO 1997 Mild hypothermia after severe transient hypoxia-ischemia reduces the delayed rise in cerebral lactate in the newborn piglet. Pediatr Res 41: 803–808
Laptook AR, Corbett RJ, Sterett R, Burns DK, Garcia D, Tollefsbol G 1997 Modest hypothermia provides partial neuroprotection when used for immediate resuscitation after brain ischemia. Pediatr Res 42: 17–23
Trescher WH, Ishiwa S, Johnston MV 1997 Brief post-hypoxic-ischemic hypothermia markedly delays neonatal brain injury. Brain Dev 19: 326–338
Silverstein F, Johnston MV 1984 Effects of hypoxia-ischemia on monoamine metabolism in the immature brain. Ann Neurol 15: 342–347
Moser E, Moser MB, Andersen P 1993 Spatial learning impairment parallels the magnitude of dorsal hippocampal lesions, but is hardly present following ventral lesions. J Neurosci 13: 3916–3925
Shuaib A, Murabit MA, Kanthan R, Howlett W, Wishart T 1996 The neuroprotective effects of gamma-vinyl GABA in transient global ischemia: a morphological study with early and delayed evaluations. Neurosci Lett 204: 1–4
Green EJ, Pazos AJ, Dietrich WD, McCabe PM, Schneiderman N, Lin B, Busto R, Globus MY, Ginsberg MD 1995 Combined postischemic hypothermia and delayed MK-801 treatment attenuates neurobehavioral deficits associated with transient global ischemia in rats. Brain Res 702: 145–152
Kawamata T, Alexis NE, Dietrich WD, Finklestein SP 1996 Intracisternal basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) enhances behavioral recovery following focal cerebral infarction in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16: 542–547
Canevari L, Console A, Tendi EA, Clark JB, Bates TE 1999 Effect of postischaemic hypothermia on the mitochondrial damage induced by ischaemia and reperfusion in the gerbil. Brain Res 817: 241–245
Thoresen M, Satas S, Puka SM, Whitelaw A, Hallström A, Lindberg EM, Ungerstedt U, Steen PA, Hagberg H 1997 Post-hypoxic hypothermia reduces cerebrocortical release of NO and excitotoxins. Neuroreport 8: 3359–3362
Baldwin WA, Kirsch JR, Hurn PD, Toung WS, Traystman RJ 1991 Hypothermic cerebral reperfusion and recovery from ischemia. Am J Physiol 261: H774–H781
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. H.R. Widmer, Division of Neurosurgical Research, and Dr. R, Amman, Medical Statistics of the Department of Pediatrics, University of Berne, for critical review of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, B., Nedelcu, J. & Martin, E. Delayed Postischemic Hypothermia Improves Long-Term Behavioral Outcome after Cerebral Hypoxia-Ischemia in Neonatal Rats. Pediatr Res 51, 354–360 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200203000-00015
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-200203000-00015
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic hypothermia for the treatment of neonatal hypoxia-ischemia: sex-dependent modulation of reactive astrogliosis
Metabolic Brain Disease (2022)
-
Potential biomarkers for neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration at short and long term after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic insult in rat
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2019)
-
Effects of therapeutic hypothermia on white matter injury from murine neonatal hypoxia–ischemia
Pediatric Research (2017)
-
Therapeutic effect of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in rats
World Journal of Pediatrics (2015)
-
Comparison of Three Hypothermic Target Temperatures for the Treatment of Hypoxic Ischemia: mRNA Level Responses of Eight Genes in the Piglet Brain
Translational Stroke Research (2013)