Abstract
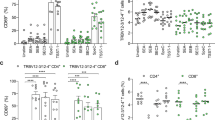
We previously reported that the frequency of TCRBV2 and TCRBV6S5-bearing T-cells was high in patients in the acute phase of Kawasaki disease (KD) and that streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C (SPE-C) was a potent stimulator of these TCRBV-bearing T-cells. To further elucidate the pathogenesis of KD, we examined the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire, human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DRB1 genotype, and antibody responses to recombinant(r) SPE-C in patients with KD. We also performed in vitro stimulation with rSPE-A and rSPE-C of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy donors and characterized the reacting T-cells. The percentage of T-cells bearing TCRBV2 and TCRBV6S5 was high in patients in the acute stage of KD. rSPE-C stimulation of PBMC from healthy donors induced expansion of TCRBV2 and TCRBV6S5-bearing T-cells. Furthermore, serum levels of anti-SPEC antibodies, which did not display antimitogenic activity, were higher in patients with acute KD than in age-matched controls. The frequencies of the DRB1*04051, 0406, and 0901 were high, whereas that of the DRB1*1101 was low among patients with KD as compared with the healthy adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- HLA:
-
human leukocyte antigen
- IVIg:
-
intravenous immunoglobulin
- KD:
-
Kawasaki disease
- SPE-A:
-
streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin A
- SPE-C:
-
streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C
- SSOPs:
-
sequence-specific oligonucleotide probes
- TCR:
-
T-cell receptor
- TSS:
-
toxic shock syndrome
- SA:
-
superantigen
References
Kawasaki T 1967 Acute febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of the fingers and toes in children [Japanese]. Jpn J Allergy 16: 178–222
Terai M, Kohono Y, Nizawa K, Toba T, Sakurai N, Nakajima H 1987 Imbalance among T-cell subsets in patients with coronary arterial aneurysms in Kawasaki disease. Am J Cardiol 60: 555–559
Furukawa S, Matubara T, Yabuta K 1992 Mononuclear cell subsets and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 67: 706–708
Leung DYM, Kurt-Jones E, Newburger JW, Cotran RS, Burns JC, Pober JS 1989 Endothelial cell activation and high interleukin-1 secretion in the pathogenesis of acute Kawasaki disease. Lancet 338: 1298–1302
Maury CPJ, Salo E, Pelkonen E 1989 Elevated circulating tumor necrosis factor-a in patients with Kawasaki disease. J Lab Clin Med 113: 651–654
Matsubara T, Furukawa S, Yabuta S 1990 Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor, interleukin 2 receptor, and interferon-g in Kawasaki disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 56: 29–36
Todd J, Fishaut M 1978 Toxic shock syndrome associated phage-group 1-staphylococci. Lancet 2: 1116–1118
Torres-Martinez C, Mehta D, Butt A, Levin M 1992 Streptococcus associated toxic shock. Arch Dis Child 67: 126–130
Cone LA, Woodard DR, Schlievert PM, Tomory GS 1987 Clinical and bacteriological observations of toxic shock-like syndrome due to Streptococcus pyogenes. N Engl J Med 317: 146–149
Abe J, Kotzin BL, Jujo K, Melish ME, Glode MP, Kohsaka T, Leung DYM 1992 Selective expansion of T cells expressing T-cell receptor variable regions V beta 2 and V beta 8 in Kawasaki disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89: 4066–4070
Abe J, Kotzin BL, Meissner C, Melish ME, Masato T, Fuluton D, Romagne F, Malissen B, Leung DYM 1993 Characterization of T cell repertoire changes in acute Kawasaki disease. J Exp Med 177: 791–796
Curtis N, Zheng R, Lamb JR, Levin M 1995 Evidence for superantigen mediated process in Kawasaki disease. Arch Dis Child 72: 308–311
Leung DY, Giorno RC, Kazemi LV, Flynn PA, Busse JB 1995 Evidence for superantigen involvement in cardiovascular injury due to Kawasaki syndrome. J Immunol 155: 5018–5021
Choi Y, Lafferty JA, Clements JR, Todd JK, Gelfand EW, Kappler J, Marrack P, Kotzin BL 1990 Selective expansion of T cells expressing V beta 2 in toxic shock syndrome. J Exp Med 172: 981–984
Kotzin B, Leung D, Kappler J, Marrack P 1994 Superantigens and their potential role in human disease. Adv Immunol 57: 99–166
Toyosaki T, Yoshioka T, Tsuruta Y, Yutsudo T, Iwasaki M, Suzuki R 1996 Definition of the mitogenic factor (MF) as a novel streptococcal superantigen that is different from streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins A, B, and C. Eur J Immunol 26: 2693–2701
Yoshioka T, Matsutani T, Iwagami S, Toyosaki-Maeda T, Yutsudo T, Tsuruta Y, Suzuki H, Uemura T, Takeuchi T, Koike M, Suzuki R 1999 Polyclonal expansion of TCRBV2- and TCRBV6-bearing T cells in patients with Kawasaki disease. Immunology 96: 465–472
Tsuruta Y, Iwagami S, Furue S, Teraoka H, Yosida T, Sakata T, Suzuki R 1993 Detection of human T cell receptor cDNAs (a, b, g and d) by ligation of a universal adaptor to variable region. J Immunol Methods 161: 7–21
Tsuruta Y, Yoshioka T, Suzuki R, Sakata T 1994 Analysis of the population of human T cell receptor γ and δ chain variable region subfamilies by reverse dot blot hybridization. J Immunol Methods 169: 17–23
Yoshioka T, Matsutani T, Iwagami S, Tsuruta Y, Kanesige T, Toyosaki T, Suzuki R 1997 Quantitative analysis of the usage of human T cell receptor a and b chain variable regions by reverse dot blot hybridization. J Immunol Methods 201: 145–155
Matsutani T, Yoshioka T, Tsuruta Y, Iwagami S, Suzuki R 1997 Analysis of TCRAV and TCRBV repertoires in healthy individuals by microplate hybridization assay. Hum Immunol 56: 57–69
Horiuchi T, Hirokawa M, Kawabata Y, Kitabayashi A, Matsutani T, Yoshioka T, Tsuruta Y, Suzuki R, Miura AB 2001 Identification of the T cell clones expanding within both CD8+CD28+ and CD8+CD28- T cell subsets in recipients of allogenic hematopoietic cell grafts and its implication in post-transplant skewing of T cell receptor repertoire. Bone Marrow Transplant 27: 731–739
Kaneshige T, Hashimoto M, Matsumoto Y, Kinoshita T, Hirasawa T, Uchida K, Inoko H 1994 Serological and nucleotide sequencing analysis of novel DR52-asociated DRB1 allele with ‘NJ25' specificity, designated DRB*1307. Hum Immunol 41: 151–159
Bodmer JB, Steven GE, Ekkehard D, Albert ED, Bodmer WF, Bontrop RE, Charron D, Dupont B, Erlich HA, Mach B, Mayr WR, Pharman P, Sasazuki T, Schreudr GMTH, Strominger JL, Svejgaard A, Terasaki PI 1997 Nomenclature for factors of HLA system, 1996. Tissue Antigens 49: 297–321
Morita A, Imada Y, Igarashi H, Yutsudo T 1997 Serologic evidence that streptococcal superantigens are not in the pathogenesis of Kawasaki disease. Microbiol Immunol 41: 895–900
Melish ME 1981 Kawasaki syndrome: a new infectious disease. J Infect Dis 143: 317–324
Li Y, Li H, Dimasi N, McCormick JK, Martin R, Schuck P, Schlievert PM, Mariuzza RA 2001 Crystal structure of a superantigen bound to the high-affinity, zinc-dependent site on MHC class II. Immunity 14: 93–104
Takata H, Suzuki M, Ishii T, Sekiguchi S, Iri H 1987 Influence of major histocompatibility complex region genes on human longevity among Okinawan-Japanese centenarians and nonagerians. Lancet 2: 824–826
Higuchi T, Seki N, Yamada S, Kimura A, Kato H, Itoh K 1998 Polymorphism of 5′-flanking region of the human tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha gene in Japanese. Tissue Antigens 51: 605–612
Watanabe-Ohnishi R, Low DE, McGeer A, Stevens DL, Schlievert PM, Newton D, Schwartz B, Kreiswirth B, Kotb M 1995 Selective depletion of V beta-bearing T cells in patients with severe invasive group A streptococcal infections and streptococcal toxic shock syndrome. Ontario Streptococcal Study Project. J Infect Dis 171: 274–275
Mascini EM 1997 Association with a lack of anti-exotoxin antibodies. In: Horaud R (ed) Streptococci and the Host. Plenum Press, New York, 921–922.
Abe Y, Nakano S, Nakahara T, Kamezawa Y, Kato I, Ushijima H, Yoshino K, Ito S, Noma S, Okitsu S 1990 Detection of serum antibody by the antimitogen assay against streptococcal erythrogenic toxins. Age distribution in children and the relation to Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Res 27: 11–15
Bonventre PF, Heeg H, Cullen C, Lian CJ 1993 Toxicity of recombinant toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 and mutant toxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus in rabbit infection model of toxic shock syndrome. Infect Immun 61: 793–799
Miethke T, Gaus H, Wahl C, Heeg K, Wagner H 1992 T cell dependent shock induced by a bacterial superantigen. Chem Immunol 55: 172–184
Yamaoka J, Nakamura E, Takeda Y, Imamura S, Minato N 1998 Mutational analysis of superantigen activity responsible for the induction of skin erythema by streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxin C. Infect Immun 66: 5020–5026
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Ichiro Kurane (Department of Virology 1, National Institute of Infection Disease, Tokyo, Japan) for the critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shionogi & Co., Ltd. and Wakayama Medical University supported this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshioka, T., Matsutani, T., Toyosaki-Maeda, T. et al. Relation of Streptococcal Pyrogenic Exotoxin C as a Causative Superantigen for Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr Res 53, 403–410 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000049668.54870.50
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000049668.54870.50
This article is cited by
-
Sex Differences in Pediatric Rheumatology
Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology (2019)
-
Comprehensive analysis and characterization of the TCR α chain sequences in the common marmoset
Immunogenetics (2010)
-
Current perspectives on Kawasaki disease
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (2005)
-
The Epidemiology of Kawasaki Disease in an Urban Hospital: Does African American Race Protect Against Coronary Artery Aneurysms?
Pediatric Cardiology (2005)