Abstract
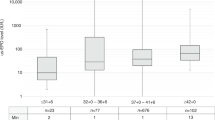
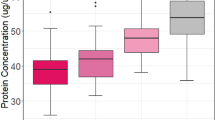
Apoptotic neuronal loss may be responsible for altered brain development associated with prematurity and perinatal insults. Neurotrophins play crucial roles in protecting neurons from entering or progressing along an apoptotic pathway. The present study examined levels of neurotrophins in human umbilical cord blood from infants at different gestational ages and clinical conditions. We collected 60 samples of cord blood and categorized them accordingly into three gestational age groups: group A (24–28 wk), group B (29–35 wk), and group C (≥36 wk). Neurotrophin levels were determined by using brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and neurotrophin 3 (NT3) ELISA. Clinical data were obtained by medical chart analysis. The BDNF levels were 884 ± 386, 1421 ± 616, and 2190 ± 356 pg/mL in group A, group B, and group C, respectively. Significant differences were found between groups A and B (p = 0.038), groups A and C (p = 0.0001), and groups B and C (p = 0.001). Infants with severe intraventricular hemorrhage had significantly lower cord blood BDNF levels (925 ± 513 pg/mL) compared with their normal counterparts (1650 ± 674 pg/mL;p = 0.021). NT3 levels did not show significant change either across gestational ages or with the presence of intraventricular hemorrhage. Cord blood levels of BDNF may reflect the degree of neural maturity in premature infants. Interestingly, when a complete course of antenatal steroids was given, BDNF and NT3 cord blood levels were higher than when no steroid was given. Increased neurotrophins levels may also mediate improved neurodevelopmental outcome in infants who received antenatal steroids.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BDNF:
-
brain-derived neurotrophic factor
- NT3:
-
neurotrophin 3
- IVH:
-
intraventricular hemorrhage
- PROM:
-
premature rupture of membranes
- SGA:
-
small for gestational age
- PIH:
-
pregnancy-induced hypertension
REFERENCES
Murphy DJ, Sellers S, MacKenzie IZ 1995 Case-control study of antenatal and intrapartum risk factors for cerebral palsy in very preterm singleton babies. Lancet 346: 1449–1454
Verma U, Tejani N, Klein SR 1997 Obstetric antecedents of intraventricular hemorrhage and periventricular leukomalacia in the low-birth-weight neonate. Am J Obstet Gynecol 176: 275–281
Gaudet LM, Smith GN 2001 Cerebral palsy and chorioamnionitis: the inflammatory cytokine link. Obstet Gynecol Surv 56: 433–436
Acien P, Lloret G, Lloret M 1990 Perinatal morbidity and mortality in pregnancy hypertensive disorders: prognostic value of the clinical and laboratory findings. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 32: 229–235
Danielian PJ, Allman AC, Steer PJ 1992 Is obstetric and neonatal outcome worse in fetuses who fail to reach their own growth potential?. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 99: 452–454
Billaud N, Lemarie P 2001 Negative effects of maternal smoking during the course of pregnancy. Arch Pediatr 8: 875–881
Salokorpi T, Sajaniemi N, Hallback H, Kari A, Rita H, von Wendt L 1997 Randomized study of the effect of antenatal dexamethasone on growth and development of premature children at the corrected age of 2 years. Acta Paediatr 86: 294–298
Lemons JA, Bauer CR, Oh W, Korones SB, Papile LA, Stoll BJ, Verter J, Temprosa M, Wright LL, Ehrenkranz RA, Fanaroff AA, Stark A, Carlo W, Tyson JE, Donovan EF, Shankaran S, Stevenson DK 2001 Very low birth weight outcomes of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network, January 1995 through December 1996. NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Pediatrics 107( 1). Available at: www.pediatrics.org/cgi/content/full/107/1/e1
Inder TE, Huppi PS, Warfield S, Kikinis R, Zientara GP, Barnes PD, Jolesz F, Volpe JJ 1999 Periventricular white matter injury in the premature infant is followed by reduced cerebral cortical gray matter volume at term. Ann Neurol 46: 755–760
Huppi PS, Warfield S, Kikinis R, Barnes PD, Zientara GP, Jolesz FA, Tsuji MK, Volpe JJ 1998 Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of brain development in premature and mature newborns. Ann Neurol 43: 224–235
Hetman M, Xia Z 2000 Signaling pathways mediating anti-apoptotic action of neurotrophins. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Warsz) 60: 531–545
Tucker KL, Meyer M, Barde YA 2001 Neurotrophins are required for nerve growth during development. Nat Neurosci 4: 29–37
Chao MV 2000 Trophic factors: an evolutionary cul-de-sac or door into higher neuronal function?. J Neurosci Res 59: 353–355
Takei N, Nawa H 1998 Roles of neurotrophins on synaptic development and functions in the central nervous system. Hum Cell 11: 157–165
Korhonen L, Riikonen R, Nawa H, Lindholm D 1998 Brain derived neurotrophic factor is increased in cerebrospinal fluid of children suffering from asphyxia. Neurosci Lett 16: 151–154
Cheng Y, Gidday JM, Yan Q, Shah AR, Holtzman DM 1997 Marked age-dependent neuroprotection by brain-derived neurotrophic factor against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Ann Neurol 41: 521–529
Ferrer I, Krupinski J, Goutan E, Marti E, Ambrosio S, Arenas E 2001 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces cortical cell death by ischemia after middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 101: 229–238
Karege F, Schwald M, Cisse M 2002 Postnatal developmental profile of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat brain and platelets. Neurosci Lett 328: 261–264
Haddad J, Vilge V, Juif JG, Maitre M, Donato L, Messer J, Mark J 1994 Beta-nerve growth factor levels in newborn cord sera. Pediatr Res 35: 637–639
Polin RA, Fox WW 1998 Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 2106–2107.
Kricka LJ 1994 Selected strategies for improving sensitivity and reliability of immunoassays. Clin Chem 40: 347–357
Papile LA, Burstein J, Burstein R, Koffler H 1978 Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr 92: 529–534
Gibbs RS, Blanco JD, St Clair PJ, Castaneda YS 1982 Quantitative bacteriology of amniotic fluid from women with clinical intraamniotic infection at term. J Infect Dis 145: 1–8
Yoon BH, Romero R, Park JS, Kim CJ, Kim SH, Choi JH 2000 Fetal exposure to an intra-amniotic inflammation and the development of cerebral palsy at the age of three years. Am J Obstet Gynecol 182: 675–681
Williams RL, Creasy RK, Cunningham GC 1982 Fetal growth and perinatal viability in California. Obstet Gynecol 59: 624–632
Campbell S, Newman GB 1971 Growth of the fetal biparietal diameter during normal pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw 78: 513–519
Mongelli M, Wilcox M, Gardosi J 1996 Estimating the date of confinement: ultrasonographic biometry versus certain menstrual dates. Am J Obstet Gynecol 174: 278–281
Tunon K, Eik-Nes SH, Grottum P, Von During V, Kahn JA 2000 Gestational age in pregnancies conceived after in vitro fertilization: a comparison between age assessed from oocyte retrieval, crown-rump length and biparietal diameter. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 15: 41–46
Ballard JL, Novak K, Driver M 1979 A simplified score for assessment of fetal maturation of newly born infants. J Pediatr 95: 769–774
Ballard JL, Khoury JC, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman BL, Lipp R 1991 New Ballard Score expanded to include extremely premature infants. J Pediatr 119: 417–423
Alexander GA, de Caunes F, Hulsey TC, Tompkins ME, Allen M 1992 Validity of postnatal assessments of gestational age: a comparison of the method of Ballard et al. and early ultrasonography. Am J Obstet Gynecol 166: 891–895
Henderson CE 1996 Role of neurotrophic factors in neuronal development. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6: 64–70
Barde YA 1994 Neurotrophins: a family of proteins supporting the survival of neurons. Prog Clin Biol Res 390: 45–56
Lewin GR, Barde YA 1996 Physiology of the neurotrophins. Annu Rev Neurosci 19: 289–317
Nelson KB, Grether JK, Croen LA, Dambrosia JM, Dickens BF, Jelliffe LL, Hansen RL, Phillips TM 2001 Neuropeptides and neurotrophins in neonatal blood of children with autism or mental retardation. Ann Neurol 49: 597–606
Conover JC, Yancopoulos GD 1997 Neurotrophin regulation of the developing nervous system: analyses of knockout mice. Rev Neurosci 8: 13–27
Ernfors P, Kucera J, Lee KF, Loring J, Jaenisch R 1995 Studies on the physiological role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 in knockout mice. Int J Dev Biol 39: 799–807
Farinas I, Jones KR, Backus C, Wang XY, Reichardt LF 1994 Severe sensory and sympathetic deficits in mice lacking neurotrophin-3. Nature 23369: 658–661
Lu B, Figurov A 1997 Role of neurotrophins in synapse development and plasticity. Rev Neurosci 8: 1–12
Ward NL, Hagg T 2000 BDNF is needed for postnatal maturation of basal forebrain and neostriatum cholinergic neurons in vivo. Exp Neurol 162: 297–310
Ringstedt T, Linnarsson S, Wagner J, Lendahl U, Kokaia Z, Arenas E, Ernfors P, Ibanez CF 1998 BDNF regulates reelin expression and Cajal-Retzius cell development in the cerebral cortex. Neuron 21: 305–315
Chalazonitis A 1996 Neurotrophin-3 as an essential signal for the developing nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 12: 39–53
ElShamy WM, Ernfors P 1997 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4 complement and cooperate with each other sequentially during visceral neuron development. J Neurosci 17: 8667–8675
Coppola V, Kucera J, Palko ME, Martinez-De Velasco J, Lyons WE, Fritzsch B, Tessarollo L 2001 Dissection of NT3 functions in vivo by gene replacement strategy. Development 128: 4315–4327
Postigo A, Calella AM, Fritzsch B, Knipper M, Katz D, Eilers A, Schimmang T, Lewin GR, Klein R, Minichiello L 2002 Distinct requirements for TrkB and TrkC signaling in target innervation by sensory neurons. Genes Dev 16: 633–645
Ciccolini F, Svendsen CN 2001 Neurotrophin responsiveness is differentially regulated in neurons and precursors isolated from the developing striatum. J Mol Neurosci 17: 25–33
Oppenheim RW 1996 Neurotrophic survival molecules for motorneurons: an embarrassment of riches. Neuron 17: 195–197
Acknowledgements
We thank the employees of the clinical blood bank of the University of Kentucky, Lexington.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by Children's Miracle Network grant, Children's Hospital, University of Kentucky, Lexington.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chouthai, N., Sampers, J., Desai, N. et al. Changes in Neurotrophin Levels in Umbilical Cord Blood From Infants With Different Gestational Ages and Clinical Conditions. Pediatr Res 53, 965–969 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000061588.39652.26
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000061588.39652.26
This article is cited by
-
Postnatal serum IGF-1 levels associate with brain volumes at term in extremely preterm infants
Pediatric Research (2023)
-
The placenta protects the fetal circulation from anxiety-driven elevations in maternal serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Effect of maternal iron deficiency anemia on fetal neural development
Journal of Perinatology (2018)
-
Perinatal hypoxia as a risk factor for psychopathology later in life: the role of dopamine and neurotrophins
Hormones (2018)
-
Placental and cord blood brain derived neurotrophic factor levels are decreased in nondiabetic macrosomia
Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics (2017)