Abstract
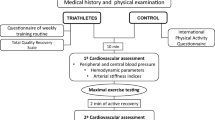
Exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia (EIAH) is a recognized phenomenon in highly trained adults. Like adult athletes, prepubescent trained children may develop high-level metabolic demand but with a limited lung capacity in comparison with adults. The purpose of this investigation was to search for evidence of EIAH in prepubescent trained children. Twenty-four prepubescent (age: 10.3 ± 0.2 y) trained children (10.0 ± 0.7 h of weekly physical activity) performed pulmonary function tests and a graded maximal exercise test on a cycle ergometer. EIAH was defined as a drop of at least 4% from resting level arterial oxygen saturation (Sao2) measured by pulse oximetry. EIAH was observed in seven children. Forced vital capacity (FVC), ventilatory response to exercise (ΔV˙E/ΔV˙co2), and breathing reserve at maximal exercise were significantly lower, whereas tidal volume relative to FVC was higher in hypoxemic children than in nonhypoxemic children; weekly physical activity and maximal oxygen uptake were similar. Moreover, positive relationships were found between Sao2 at maximal exercise and breathing reserve (r = 0.56; p < 0.05) or volume relative to FVC (r = 0.70; p < 0.01). EIAH may occur in prepubescent trained children with a relatively low maximal oxygen uptake (42 mL · min−1 · kg−1); however, the mechanisms remain unclear and need to be investigated more accurately.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BR:
-
breathing reserve at maximal exercise
- EIAH:
-
exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia
- f :
-
breathing frequency
- FEV1:
-
forced expiratory volume in 1 s
- FVC:
-
forced vital capacity
- MEF:
-
maximal expiratory flow
- MVV:
-
maximal voluntary ventilation
- Pao2:
-
partial arterial oxygen
- Petco2:
-
end-tidal carbon dioxide partial pressure
- Peto2:
-
end-tidal oxygen partial pressure
- Sao2:
-
arterial oxygen saturation
- V˙co2:
-
carbon dioxide output
- V˙o2:
-
oxygen uptake
- V˙o2max:
-
maximal oxygen uptake
- V˙E:
-
ventilation
- Vt:
-
tidal volume
- ΔV˙E/ΔV˙co2:
-
slope of ventilation versus CO2 output in progressive exercise
References
Dempsey JA, Hanson PG, Henderson KS 1984 Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in healthy human subjects at sea level. J Physiol 355: 161–175
Dempsey JA, Wagner PD 1999 Exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia. J Appl Physiol 87: 1997–2006
Powers SK, Martin D, Dodd S 1993 Exercise-induced hypoxaemia in elite endurance athletes. Incidence, causes and impact on on V˙ o2max . Sports Med 16: 14–22
Harms CA, McClaran SR, Nickele GA, Pegelow DF, Nelson WB, Dempsey JA 1998 Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in healthy young women. J Physiol 507: 619–628
Prefaut C, Durand F, Mucci P, Caillaud C 2000 Exercise-induced arterial hypoxaemia in athletes: a review. Sports Med 30: 47–61
Powers SK, Lawler J, Dempsey JA, Dodd S, Landry G 1989 Effects of incomplete pulmonary gas exchange on V˙ o2max . J Appl Physiol 66: 2491–2495
Durand F, Mucci P, Prefaut C 2000 Evidence for an inadequate hyperventilation inducing arterial hypoxemia at submaximal exercise in all highly trained endurance athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32: 926–932
Harms CA, Stager JM 1995 Low chemoresponsiveness and inadequate hyperventilation contribute to exercise-induced hypoxemia. J Appl Physiol 79: 575–580
Hopkins SR, Gavin TP, Siafakas NM, Haseler LJ, Olfert IM, Wagner H, Wagner PD 1998 Effect of prolonged, heavy exercise on pulmonary gas exchange in athletes. J Appl Physiol 85: 1523–1532
Rice AJ, Thornton AT, Gore CJ, Scroop GC, Greville HW, Wagner H, Wagner PD, Hopkins SR 1999 Pulmonary gas exchange during exercise in highly trained cyclists with arterial hypoxemia. J Appl Physiol 87: 1802–1812
Wetter TJ, St Croix CM, Pegelow DF, Sonetti DA, Dempsey JA 2001 Effects of exhaustive endurance exercise on pulmonary gas exchange and airway function in women. J Appl Physiol 91: 847–858
Rowland T 1996 Developmental Exercise Physiology. Human Kinetics, Champaign, IL, 27–157.
Laursen PB, Tsang GC, Smith GJ, van Velzen MV, Ignatova BB, Sprules EB, Chu KS, Coutts KD, McKenzie DC 2002 Incidence of exercise-induced arterial hypoxemia in prepubescent females. Pediatr Pulmonol 34: 37–41
Tanner J 1962 Growth at Adolescence. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford 325
Durnin JV, Rahaman MM 1967 The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness. Br J Nutr 21: 681–689
Deheeger M, Rolland-Cachera MF, Fontvieille AM 1997 Physical activity and body composition in 10 year old French children: linkages with nutritional intake?. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 21: 372–379
Buchfuhrer MJ, Hansen JE, Robinson TE, Sue DY, Wasserman K, Whipp BJ 1983 Optimizing the exercise protocol for cardiopulmonary assessment. J Appl Physiol 55: 1558–1564
American Thoracic Society 1987 Standardization of spirometry–1987 update. Statement of the American Thoracic Society. Am Rev Respir Dis 136: 1285–1298
Johnson BD, Weisman IM, Zeballos RJ, Beck KC 1999 Emerging concepts in the evaluation of ventilatory limitation during exercise: the exercise tidal flow-volume loop. Chest 116: 488–503
Medoff BD, Oelberg DA, Kanarek DJ, Systrom DM 1998 Breathing reserve at the lactate threshold to differentiate a pulmonary mechanical from cardiovascular limit to exercise. Chest 113: 913–918
Cooper DM, Kaplan MR, Baumgarten L, Weiler-Ravell D, Whipp BJ, Wasserman K 1987 Coupling of ventilation and CO2production during exercise in children. Pediatr Res 21: 568–572
Martin D, Powers S, Cicale M, Collop N, Huang D, Criswell D 1992 Validity of pulse oximetry during exercise in elite endurance athletes. J Appl Physiol 72: 455–458
Powers SK, Dodd S, Freeman J, Ayers GD, Samson H, McKnight T 1989 Accuracy of pulse oximetry to estimate HbO2fraction of total Hb during exercise. J Appl Physiol 67: 300–304
American Association for Respiratory Care 1992 Clinical practice guideline. Exercise testing for evaluation of hypoxemia and/or desaturation. Respir Care 37: 907–912
Mucci P, Prioux J, Hayot M, Ramonatxo M, Prefaut C 1998 Ventilation response to CO2and exercise-induced hypoxaemia in master athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 77: 343–351
Rice AJ, Scroop GC, Gore CJ, Thornton AT, Chapman MA, Greville HW, Holmes MD, Scicchitano R 1999 Exercise-induced hypoxaemia in highly trained cyclists at 40% peak oxygen uptake. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 79: 353–359
Aguilaniu B, Flore P, Maitre J, Ochier J, Lacour JR, Perrault H 2002 Early onset of pulmonary gas exchange disturbance during progressive exercise in healthy active men. J Appl Physiol 92: 1879–1884
Ohuchi H, Kato Y, Tasato H, Arakaki Y, Kamiya T 1999 Ventilatory response and arterial blood gases during exercise in children. Pediatr Res 45: 389–396
Harms CA, McClaran SR, Nickele GA, Pegelow DF, Nelson WB, Dempsey JA 2000 Effect of exercise-induced arterial O2 desaturation in V˙ o2max in women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32: 1101–1108
Nagano Y, Baba R, Kuraishi K, Yasuda T, Ikoma M, Nishibata K, Yokota M, Nagashima M 1998 Ventilatory control during exercise in normal children. Pediatr Res 43: 704–707
McConnell AK, Semple ES, Davies CT 1993 Ventilatory responses to exercise and carbon dioxide in elderly and younger humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 66: 332–337
McConnell AK, Semple ES, Davies CT 1996 Ventilatory sensitivity to carbon dioxide: the influence of exercise and athleticism. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28: 685–691
Pianosi P, Wolstein R 1996 Carbon dioxide chemosensitivity and exercise ventilation in healthy children and in children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res 40: 508–513
Acknowledgements
We thank our subjects for enthusiastic participation in this study and Yannick Castannet, Audrey Koïtka, and Grégory Dupont for technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nourry, C., Fabre, C., Bart, F. et al. Evidence of Exercise-Induced Arterial Hypoxemia in Prepubescent Trained Children. Pediatr Res 55, 674–681 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000114481.58902.FB
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000114481.58902.FB
This article is cited by
-
Significant exercise limitations after recovery from MIS-C related myocarditis
World Journal of Pediatrics (2023)