Abstract
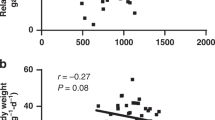
In adults, protein synthesis in skeletal muscle is reduced by as much as 50% after a septic challenge, and is associated with repression of translation initiation. Neonates are highly anabolic and their muscle protein synthesis rates are elevated and uniquely sensitive to amino acid and insulin stimulation. In the present study, neonatal piglets were infused with Endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide, LPS) for 20 h at 0 (n = 6) and 13 μg/kg•h (n = 8). During the last 2 h, dextrose and an amino acid mixture were infused to attain fed plasma concentrations of amino acids, glucose, and insulin. Fractional protein synthesis rates and translational control mechanisms were examined. LPS reduced protein synthesis in glycolytic muscles by only 13% and had no significant effect in oxidative muscles. This depression was associated with reductions in the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 (−31%) and S6 K1 (−78%), and a decrease in eIF4G binding to eIF4E (−62%), an event required for formation of the active mRNA binding complex. By comparison, LPS increased protein synthesis in the liver (+29%), spleen (+32%), and kidney (+27%), and in the liver, this increase was associated with augmented eIF4G to eIF4E binding (+88%). In muscle and liver, LPS did not alter eIF2B activity, an event that regulates initiator met-tRNAi binding to the 40S ribosomal complex. These findings suggest that during sustained endotoxemia, the high rate of neonatal muscle protein synthesis is largely maintained in the presence of substrate supply, despite profound changes in translation initiation factors that modulate the mRNA binding step in translation initiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide, endotoxin
- μg:
-
microgram
- Kg:
-
kilogram
- 4E-BP1:
-
eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4E binding protein 1
- eIF4G:
-
eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4G
- eIF4E:
-
eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4E
- S6 K1:
-
ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1
- mRNA:
-
mRNA
- met-tRNAi:
-
initiator methionyl-tRNA
References
Proulx F, Fayon M, Farrell CA, Lacroix J, Gauthier M 1996 Epidemiology of sepsis and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in children. Chest 109: 1033–1037
Angus DC, Linde-Zwirble WT, Lidicker J, Clermont G, Carcillo J, Pinsky MR 2001 Epidemiology of severe sepsis in the United States: analysis of incidence outcome and associated costs of care. Crit Care Med 29: 1303–1310
Agwunobi AO, Reid C, Maycock P, Little RA, Carlson GL 2000 Insulin resistance and substrate utilization in human endotoxemia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85: 3770–3778
Lang CH 2001 Sepsis-induced changes in pancreatic hormone secretion. In: Jefferson LS and Cherrington AD (eds) Handbook of Physiology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 999–1014.
Lang CH, Dobrescu C, Meszaros K 1990 Insulin-mediated glucose uptake by individual tissues during sepsis. Metabolism 39: 1096–1107
Lang CH, Frost RA, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR, Vary TC 2000 Endotoxin-induced decrease in muscle protein synthesis is associated with changes in eIF2B, eIF4E, and IGF-I. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 278: E1133–E1143
Oberholzer A, Oberholzer C, Moldawer LL 2000 Cytokine signaling–regulation of the immune response in normal and critically ill states. Crit Care Med 28: N3–N12
Wesley J 1998 Nutrient metabolism in relation to the systemic stress response. In: Fuhrman BP and Zimmerman JJ (eds) Pediatric Critical Care. Mosby, St Louis, 799–819.
Webel DM, Finck BN, Baker DH, Johnson RW 1997 Time course of increased plasma cytokines, cortisol, and urea nitrogen in pigs following intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide. J Anim Sci 75: 1514–1520
Wolfe RR 1997 Substrate utilization/insulin resistance in sepsis/trauma. Bailliere's Clin Endocrinol Metab 11: 645–657
Yelich MR, Witek-Janusek L 1994 Glucose, lactate, insulin, and somatostatin responses to endotoxin in developing rats. Shock 6: 438–444
Chorinchath BB, Kong LY, Mao L, McCallum RE 1996 Age-associated differences in TNF-α and nitric oxide production in endotoxic mice. J Immunol 156: 1525–1530
Li JX, Oliver JR, Lu CY, Grantham KD, Philips JB 1993 Age related differences in responses to endotoxin in unanesthetized piglets. Circulatory Shock 41: 40–47
Orellana RA, O'Connor PMJ, Nguyen HV, Bush JA, Suryawan AS, Thivierge MC, Fiorotto ML, Davis TA 2002 Endotoxemia reduces skeletal muscle protein synthesis in neonates. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283: E909–E916
Cooney RN, Kimball SR, Vary TC 1997 Regulation of skeletal muscle protein turnover during sepsis: mechanisms and mediators. Shock 7: 1–16
Vary TC, Kimball SR 1992 Sepsis-induced changes in protein synthesis: differential effects on fast- and slow-twitch muscles. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 262: C1513–C1519
Davis TA, Burrin DG, Fiorotto ML, Nguyen HV 1996 Protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and jejunum is more responsive to feeding in 7- than 26-day-old pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 270: E802–E809
Davis TA, Burrin DG, Fiorotto ML, Reeds PJ, Jahoor F 1998 Role of insulin and amino acids in the regulation of protein synthesis in the neonate. J Nutr 128: 347S–350S
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Beckett PR, Burrin DG, Reeds PJ, Wray-Cahen D, Nguyen HV 2001 Differential effects of insulin on peripheral and visceral tissue protein synthesis in neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 280: E770–E779
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Burrin DG, Reeds PJ, Nguyen HV, Beckett PR, Vann RC, O'Connor PM 2002 Stimulation of protein synthesis by both insulin and amino acids is unique to skeletal muscle in neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282: E880–890
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Nguyen HV, Reeds PJ 1993 Enhanced response of muscle protein synthesis and plasma insulin to food intake in suckling rats. Am J Physiol 265: R334–R340
Preedy VR, Garlick PJ 1993 Response of muscle protein synthesis to parenteral administration of amino acid mixtures in growing rats. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 17: 113–118
Tessari P, Zannetti M, Barazzoni R, Vettore M, Michielan F 1996 Mechanism of postprandial protein accretion in human skeletal muscle. Insight from leucine and phenylalanine forearm kinetics. J Clin Invest 98: 1361–1372
Kimball SR, Farrell PA, Nguyen HV, Jefferson LS, Davis TA 2002 Developmental decline in components of signal transduction pathways regulating protein synthesis in pig muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282: E585–E592
Davis TA, Nguyen HV, Suryawan AS, Bush JA, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR 2000 Developmental changes in the feeding-induced stimulation of translation initiation in muscle of neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 279: E1226–1234
Vary TC, Jefferson LS, Kimball SR 2001 Insulin fails to stimulate protein synthesis in sepsis despite unimpaired signaling to 4E-BP1 and S6K1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 281: E1045–E1053
Kimball SR 2002 Regulation of global and specific mRNA translation by amino acids. J Nutr 132: 883–886
Proud CG, Denton RM 1998 Molecular mechanisms for the control of translation by insulin. Biochem J 328: 329–341
Kimball SR, Horetsky RL, Jefferson LS 1998 Signal transduction pathways involved in the regulation of protein synthesis by insulin in L6 myoblasts. Am J Physiol 274: C221–228
Kimball SR, Orellana RA, O'Connor PMJ, Suryawan AS, Bush JA, Nguyen HV, Thivierge MC, Jefferson LS, Davis TA 2003 Endotoxin induces differential regulation of mTOR–dependent signaling in skeletal muscle and liver of neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 285: E637–E644
Fink MP, Heard SO 1990 Laboratory models of sepsis and septic shock. J Surg Res 49: 186–196
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Burrin DG, Vann RC, Reeds PJ, Nguyen HV, Beckett PR, Bush JA 2002 Acute IGF-I infusion stimulates protein synthesis in skeletal muscle and other tissues of neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283: E638–47
Wray-Cahen D, Beckett PR, Nguyen HV, Davis TA 1997 Insulin-stimulated amino acid utilization during glucose and amino acid clamps decreases with development. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 273: E305–E314
Beckett PR, Hardin DS, Davis TA, Nguyen HV, Wray-Cahen D, Copeland KC 1996 Spectrophometric assay for measuring branched chain amino acid concentrations: applications for measuring the sensitivity of protein metabolism to insulin. Anal Biochem 240: 48–53
Siggaard-Andersen O 1966 Titratable acid or base of body fluids. Ann NY Acad Sci 133: 41–58
Garlick PJ, McNurlan MA, Preedy VR 1980 A rapid and convenient technique for measuring the rate of protein synthesis in tissues by injection of 3H-phenylalanine. Biochem J 192: 719–723
Davis TA, Fiorotto ML, Nguyen HV, Burrin DG 1999 Aminoacyl-tRNA and tissue free amino acid pools are equilibrated after a flooding dose of phenylalanine. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 277: E103–109
Bush JA, Kimball SR, O'Connor PMJ, Suryawan AS, Orellana RA, Nguyen HV, Jefferson LS, Davis TA 2003 Translational control of protein synthesis in muscle and liver of growth-hormone-treated pigs. Endocrinology 144: 1273–1283
Fish RE, Lang CH, Spitzer JA 1986 Regional blood flow during continuous endotoxin infusion. Circ Shock 18: 267–275
McCowen KC, Ling PR, Ciccarone A, Mao Y, Chow JC, Bistrian BR, Smith RJ 2001 Sustained endotoxemia leads to marked down-regulation of early steps in the insulin-signaling cascade. Crit Care Med 29: 839–846
Ertel W, Morrison MH, Wang P, Ba ZF, Ayala A, Chaudry IH 1991 The complex pattern of cytokines in sepsis. Associations between prostaglandins, cachectin, and interleukins. Ann Surg 214: 141–148
Shangraw RE, Jahoor F, Miyoshi H, Neff WA, Stuart CA, Herndon DN, Wolfe R 1989 Differentiation between septic and post burn insulin resistance. Metabolism 38: 983–989
Goto M, Zeller WP, Lichtemberg RC 1994 Decreased gluconeogenesis and increased glucose disposal without hyperinsulinemia in 10 day-old rats with endotoxic shock. Metabolism 43: 1248–1254
Battelino T, Goto M, Krzisnik C, Zeller WP 1996 Tissue glucose transport and glucose transporters in suckling rats with endotoxic shock. Shock 6: 259–262
Jurasinski CU, Gray K, Vary TC 1995 Modulation of skeletal muscle protein synthesis by amino acids and insulin during sepsis. Metabolism 44: 1130–1138
Hasselgren PO, Pedersen P, Sax HC, Warner BW, Fischer JE 1988 Current concepts of protein turnover and amino acid transport in liver and skeletal muscle during sepsis. Arch Surg 123: 992–999
Breuillé D, Arnal M, Rambourdin F, Bayle G, Levieux D, Obled C 1998 Sustained modifications of protein metabolism in various tissues in a rat model of long-lasting sepsis. Clin Sci 94: 413–423
Keeton AB, Amsler MO, Venable DY, Messina JL 2002 Insulin signal transduction pathways and insulin induced gene expression. J Biol Chem 277: 48565–48573
Acknowledgements
The authors thank William Liu and Susan Nguyen for technical assistance, Frankie Biggs and Jerome Stubblefield for assistance with care of animals, Adam Gillum for graphics assistance, and Leslie Loddeke for editorial assistance, and Linda Weiser for secretarial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported, in part, by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) AR4447 (T.A.D.), United States Department of Agriculture/Agricultural Research Service 6250-51000-031 (T.A.D.), NIH DK15658 (L.S.J.), NIH DK13499 (L.S.J.) and the NIH training grant T32 HD07445.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orellana, R., Kimball, S., Nguyen, H. et al. Regulation of Muscle Protein Synthesis in Neonatal Pigs During Prolonged Endotoxemia. Pediatr Res 55, 442–449 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000110526.02282.F3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000110526.02282.F3
This article is cited by
-
Amino acids, independent of insulin, attenuate skeletal muscle autophagy in neonatal pigs during endotoxemia
Pediatric Research (2016)
-
Analysis of Porcine Transcriptional Response to Salmonella enterica serovar Choleraesuis suggests novel targets of NFkappaB are activated in the Mesenteric Lymph Node
BMC Genomics (2008)