Abstract
Apnea is a common complication of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection in young infants. The purpose of this study was to determine whether this infection affects apnea triggered by sensorineural stimulation in weanling rats. We also studied which neurotransmitters are involved in this response and whether passive prophylaxis with a specific neutralizing antibody (palivizumab) confers protection against it. Weanling rats were inoculated intranasally with RSV, adenovirus, or virus-free medium. Changes in respiratory rate and apnea in response to nerve stimulation with increasing doses of capsaicin were measured by plethysmography. Capsaicin-induced apnea was significantly longer in RSV-infected rats at postinoculation days 2 (upper airways infection) and 5 (lower airways infection), and apnea-related mortality occurred only in the RSV-infected group. Reduction in the duration of apnea was observed after selective inhibition of central γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type A receptors and neurokinin type 1 receptors for substance P. Prophylactic palivizumab protected against apnea and apnea-related mortality. These results suggest that sensorineural stimulation during RSV infection is associated with the development of apnea and apnea-related death in early life, whose mechanism involves the release of GABA acting on central GABA type A receptors and substance P acting on neurokinin type 1 receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- CGRP:
-
calcitonin gene-related peptide
- GABA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid
- GABAA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid receptor type A
- NK1:
-
neurokinin 1
- RSV:
-
respiratory syncytial virus
- SID:
-
sudden infant death
- TRPV:
-
transient receptor potential channel, vanilloid subfamily
References
Simoes EA 1999 Respiratory syncytial virus infection. Lancet 354: 847–852
Piedimonte G 2002 Origins of reactive airways disease in early life: do viral infections play a role?. Acta Paediatr Suppl 91: 6–11
Bruhn FW, Mokrohisky ST, McIntosh K 1977 Apnea associated with respiratory syncytial virus infection in young infants. J Pediatr 90: 382–386
Anas N, Boettrich C, Hall CB, Brooks JG 1982 The association of apnea and respiratory syncytial virus infection in infants. J Pediatr 101: 65–68
Kneyber MC, Brandenburg AH, de Groot R, Joosten KF, Rothbarth PH, Ott A, Moll HA 1998 Risk factors for respiratory syncytial virus associated apnoea. Eur J Pediatr 157: 331–335
Ferris JA, Aherne WA, Locke WS, McQuillin J, Gardner PS 1973 Sudden and unexpected deaths in infants: histology and virology. BMJ 2: 439–442
Ogra PL, Ogra SS, Coppola PR 1975 Secretory component and sudden-infant-death syndrome. Lancet 2: 387–390
Williams AL, Uren EC, Bretherton L 1984 Respiratory viruses and sudden infant death. BMJ 288: 1491–1493
Piedimonte G 2001 Neural mechanisms of respiratory syncytial virus-induced inflammation and prevention of respiratory syncytial virus sequelae. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163: S18–S21
Piedimonte G 2003 Contribution of neuroimmune mechanisms to airway inflammation and remodeling during and after respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatr Infect Dis J 22: S66–S75
Piedimonte G, Rodriguez MM, King KA, McLean S, Jiang X 1999 Respiratory syncytial virus upregulates expression of the substance P receptor in rat lungs. Am J Physiol 277: L831–L840
King KA, Hu C, Rodriguez MM, Romaguera R, Jiang X, Piedimonte G 2001 Exaggerated neurogenic inflammation and substance P receptor upregulation in RSV-infected weanling rats. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24: 101–107
Piedimonte G, Hegele RG, Auais A 2004 Persistent airway inflammation after resolution of respiratory syncytial virus infection in rats. Pediatr Res 55: 657–665
Hu C, Wedde-Beer K, Auais A, Rodriguez MM, Piedimonte G 2002 Nerve growth factor and nerve growth factor receptors in respiratory syncytial virus-infected lungs. Am J Physiol 283: L494–L502
Gray PA, Rekling JC, Bocchiaro CM, Feldman JL 1999 Modulation of respiratory frequency by peptidergic input to rhythmogenic neurons in the preBotzinger complex. Science 286: 1566–1568
Holzer P 1991 Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev 43: 143–201
Hedner J, Hedner T, Wessberg P, Jonason J 1984 An analysis of the mechanism by which gamma-aminobutyric acid depresses ventilation in the rat. J Appl Physiol 56: 849–856
Bauman NM, Wang D, Jaffe DA, Sandler AD, Luschei ES 1999 Effect of intravenous calcitonin gene-related peptide antagonist on the laryngeal chemoreflex in piglets. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 121: 1–6
Bauman NM, Wang D, Jaffe DM, Sandler AD, Luschei ES 1999 Effect of intravenous substance P on laryngeal adductor activity in young dogs. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 108: 112–118
Johnson S, Oliver C, Prince GA, Hemming VG, Pfarr DS, Wang SC, Dormitzer M, O'Grady J, Koenig S, Tamura JK, Woods R, Bansal G, Couchenour D, Tsao E, Hall WC, Young JF 1997 Development of a humanized monoclonal antibody (MEDI-493) with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against respiratory syncytial virus. J Infect Dis 176: 1215–1224
The IMpact-RSV Study Group 1998 Palivizumab, a humanized respiratory syncytial virus monoclonal antibody, reduces hospitalization from respiratory syncytial virus infection in high-risk infants. Pediatrics 102: 531–537
Piedimonte G, Pickles RJ, Lehmann JR, McCarty D, Costa DL, Boucher RC 1997 Replication-deficient adenoviral vector for gene transfer potentiates airway neurogenic inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16: 250–258
Abu-Shaweesh JM, Dreshaj IA, Haxhiu MA, Martin RJ 2001 Central GABAergic mechanisms are involved in apnea induced by SLN stimulation in piglets. J Appl Physiol 90: 1570–1576
McLean S, Ganong A, Seymour PA, Bryce DK, Crawford RT, Morrone J, Reynolds LS, Schmidt AW, Zorn S, Watson J, Fossa A, DePasquale M, Rosen T, Nagahisa A, Tsuchiya M, Heym J 1996 Characterization of CP-122,721; a nonpeptide antagonist of the neurokinin NK1 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277: 900–908
Pericic D, Bujas M 1997 Sex differences in the response to GABA antagonists depend on the route of drug administration. Exp Brain Res 115: 187–190
Huang J, Suguihara C, Hehre D, Lin J, Bancalari E 1994 Effects of GABA receptor blockage on the respiratory response to hypoxia in sedated newborn piglets. J Appl Physiol 77: 1006–1010
Siber GR, Leombruno D, Leszczynski J, McIver J, Bodkin D, Gonin R, Thompson CM, Walsh EE, Piedra PA, Hemming VG, Prince GA 1994 Comparison of antibody concentrations and protective activity of respiratory syncytial virus immune globulin and conventional immune globulin. J Infect Dis 169: 1368–1373
Zar JH 1984 Biostatistical Analysis. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Wallenstein S, Zucker CL, Fleiss JL 1980 Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res 47: 1–9
Napchan G, Sabogal C, Piedimonte G 2002 Early effect of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection on capsaicin-induced apnea in conscious F-344 rats. [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165: A204
Samuels M 2003 Viruses and sudden infant death. Pediatr Respir Rev 4: 178–183
Lindgren C 1993 Respiratory syncytial virus and the sudden infant death syndrome. Acta Paediatr Suppl 82: 67–69
Joshi VV, Escobar MR, Stewart L, Bates RD 1973 Fatal influenza A2 viral pneumonia in a newborn infant. Am J Dis Child 126: 839–840
Caterina MJ, Julius D 2001 The vanilloid receptor: a molecular gateway to the pain pathway. Annu Rev Neurosci 24: 487–517
O'Neil RG, Brown RC 2003 The vanilloid receptor family of calcium-permeable channels: molecular integrators of microenvironmental stimuli. News Physiol Sci 18: 226–231
Kaczynska K, Szereda-Przestaszewska M 2000 Respiratory effects of capsaicin occur beyond the lung vagi in anaesthetized rats. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 60: 159–165
Pickens DL, Schefft G, Thach BT 1988 Prolonged apnea associated with upper airway protective reflexes in apnea of prematurity. Am Rev Respir Dis 137: 113–118
Downing SE, Lee JC 1975 Laryngeal chemosensitivity: a possible mechanism for sudden infant death. Pediatrics 55: 640–649
Xia Y, Haddad GG 1992 Ontogeny and distribution of GABAA receptors in rat brainstem and rostral brain regions. Neuroscience 49: 973–989
Burton MD, Kazemi H 2000 Neurotransmitters in central respiratory control. Respir Physiol 122: 111–121
Wei F, Zhao ZQ 1996 Blockade of capsaicin-induced reduction of GABA-immunoreactivity by spantide in cat spinal superficial dorsal horn. Neuroscience 71: 277–283
Castro-Lopes JM, Tavares I, Tolle TR, Coimbra A 1994 Carrageenan-induced inflammation of the hind foot provokes a rise of GABA-immunoreactive cells in the rat spinal cord that is prevented by peripheral neurectomy or neonatal capsaicin treatment. Pain 56: 193–201
Byard RW, Krous HF 2003 Sudden infant death syndrome: overview and update. Pediatr Dev Pathol 6: 112–127
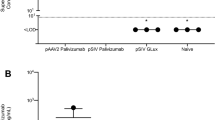
Sabogal C, Auais A, Mager E, Zhou B, Piedimonte G 2004 Protective effect of Numax against capsaicin-induced apnea in respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)-infected Fischer-344 (F344) weanling rats. [abstract]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169: A757
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the technical assistance of Dorothy Hehre and Carlos Devia. We also thank Judith McCullough, Ph.D., and James Wilkinson, M.D., M.P.H., for help with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported in part by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (NHLBI HL-61007) and a research grant from MedImmune, Inc., to G.P.
Some of the findings reported in this paper were presented at the American Thoracic Society Conference; Seattle, WA; May 16–21, 2003.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabogal, C., Auais, A., Napchan, G. et al. Effect of Respiratory Syncytial Virus on Apnea in Weanling Rats. Pediatr Res 57, 819–825 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000157679.67227.11
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000157679.67227.11
This article is cited by
-
Comparison of airway measurements during influenza-induced tachypnea in infant and adult cotton rats
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2009)
-
Erregerbedingte Atemregulationsstörungen bei Säuglingen
Somnologie - Schlafforschung und Schlafmedizin (2007)
-
Erregerbedingte Atemregulationsstörungen bei Säuglingen
Somnologie - Schlafforschung und Schlafmedizin (2006)