Abstract
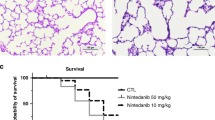
Pulmonary oxygen toxicity is believed to play a prominent role in the lung injury that leads to the development of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). To determine whether human recombinant erythropoietin (rhEPO) treatment reduces the risk of developing BPD, we investigated the effect of rhEPO treatment on the histopathologic changes seen in hyperoxia-induced lung injury of BPD. Twenty-five rat pups were divided into four groups: air-exposed control group (n = 5), hyperoxia-exposed placebo group (n = 7), hyperoxia-exposed rhEPO-treated group (n = 6), and air-exposed rhEPO-treated group (n = 7). Measurement of alveolar surface area, quantification of secondary crest formation, microvessel count, evaluation of alveolar septal fibrosis, and smooth muscle actin immunostaining were performed to assess hyperoxia-induced changes in lung morphology. Treatment of hyperoxia-exposed animals with rhEPO resulted in a significant increase in the mean alveolar area, number of secondary crests formed, and the microvessel count in comparison with hyperoxia-exposed placebo-treated animals. There was significantly less fibrosis in rhEPO-treated animals. However, treatment of hyperoxia-exposed animals with rhEPO did not result in a significant change in smooth muscle content compared with hyperoxia-exposed placebo treated animals. Our results suggest treatment with rhEPO during hyperoxia exposure is associated with improved alveolar structure, enhanced vascularity, and decreased fibrosis. Therefore, we conclude that treatment of preterm infants with EPO might reduce the risk of developing BPD.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BPD:
-
bronchopulmonary dysplasia
- EPO:
-
erythropoietin
- rhEPO:
-
human recombinant erythropoietin
- SMA:
-
smooth muscle actin
References
Welty SE 2001 Is there a role for antioxidant therapy in bronchopulmonary dysplasia?. J Nutr 131: 947S–950S
Coalson JJ 2003 Pathology of new bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol 8: 73–81
Saugstad OD 2003 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia-oxidative stress and antioxidants. Semin Neonatol 8: 39–49
Vaucher YE 2002 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: an enduring challenge. Pediatr Rev 23: 349–358
Juul SE 2000 Nonerythropoietic roles of erythropoietin in the fetus and neonate. Clin Perinatol 27: 527–541
Ohls RK 2000 The use of erythropoietin in neonates. Clin Perinatol 27: 681–696
Bany-Mohammad FM, Slivka S, Hallman M 1996 Recombinant human erythropoietin: possible role as an antioxidant in premature rabbits. Pediatr Res 40: 381–387
Stocker JT 1986 Pathologic features of long-standing “healed” bronchopulmonary dysplasia: a study of 28 3- to 40-month-old infants. Hum Pathol 17: 943–961
Veness-Meehan KA, Moats-Staats BM, Price WA, Stiles AD 1997 Re-emergence of a fetal pattern of insulin-like growth factor expression during hyperoxic rat lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 16: 538–548
Veness-Meehan KA, Bottone FG Jr, Stiles AD 2000 Effects of retinoic acid on airspace development and lung collagen in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats. Pediatr Res 48: 434–444
Ozer E, Sis B, Ozen E, Sakizli M, Canda T, Sarioglu S 2000 BRCA1, c-erbB-2 and H-ras gene expressions in young woman with breast cancer. An immunohistochemical study. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 8: 12–18
Costello P, McCann A, Carney DN, Dervan PA 1995 Prognostic significance of microvessel density in lymph node negative breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 26: 1181–1184
Abman SH 2001 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: “A vascular hypothesis.”. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164: 1755–1756
Bancalari E, Claure N, Sosenko IR 2003 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia: changes in pathogenesis, epidemiology and definition. Semin Neonatol 8: 63–71
Sasaki R, Masuda S, Nagao M 2000 Erythropoietin: multiple physiological functions and regulation of biosynthesis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64: 1775–1793
Kumral A, Baskin H, Duman N, Yilmaz O, Tatli M, Ozer E, Gokmen N, Genc S, Ozkan H 2003 Erythropoietin protects against necrotizing enterocolitis of newborn rats by the inhibiting nitric oxide formation. Biol Neonate 84: 325–329
Speer CP 2003 Inflammation and bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Semin Neonatol 8: 29–38
Siren AL, Fratelli M, Brines M, Goemans C, Casagrande S, Lewczuk P, Keenan S, Gleiter C, Pasquali C, Caobianco A, Mennini T, Heumann R, Cerami A, Ehrenreich H, Ghezzi P 2001 Erythropoietin prevents neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia and metabolic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98: 4044–4049
Wen TC, Sadamoto Y, Tanaka J, Zhu PX, Nakata K, Ma YJ, Hata R, Sakanaka M 2002 Erythropoietin protects neurons against chemical hypoxia and cerebral ischemic injury by up-regulating Bcl-xL expression. J Neurosci Res 67: 795–803
Jakkula M, Le Cras TD, Gebb S, Hirth KP, Tuder RM, Voelkel NF, Abman SH 2000 Inhibition of angiogenesis decreases alveolarization in the developing rat lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279: L600–L607
Marti HH 2004 Erythropoietin and the hypoxic brain. J Exp Biol 207: 3233–3242
Zipursky A 2002 The risk of hematopoietic growth factor therapy in newborn infants. Pediatr Res 51: 549
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Rachel Cooper, M.D., of Cookridge Hospital, Leeds, UK, and Michael Ashworth, M.D., of Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, Liverpool, UK, for English language corrections.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozer, E., Kumral, A., Ozer, E. et al. Effects of Erythropoietin on Hyperoxic Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats. Pediatr Res 58, 38–41 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000163391.75389.52
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.PDR.0000163391.75389.52
This article is cited by
-
Erythropoietin as candidate for supportive treatment of severe COVID-19
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine, a DNA methylation inhibitor, attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung fibrosis via re-expression of P16 in neonatal rats
Pediatric Research (2018)
-
Transient vascular and long-term alveolar deficits following a hyperoxic injury to neonatal mouse lung
BMC Pulmonary Medicine (2014)
-
Combined effects of maternal inflammation and neonatal hyperoxia on lung fibrosis and RAGE expression in newborn rats
Pediatric Research (2014)
-
Erythropoetin as a novel agent with pleiotropic effects against acute lung injury
European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology (2011)