Abstract
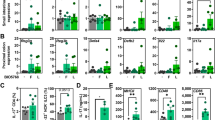
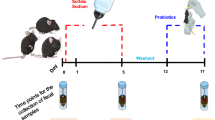
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) is a common pathogen in infantile diarrhea, causing a characteristic histopathologic attaching and effacing (A/E) lesion in the intestinal mucosa. The mouse pathogen Citrobacter rodentium causes a similar A/E lesion in the murine intestine. Like EPEC, C. rodentium infection results in colonic crypt hyperplasia, goblet cell depletion, epithelial proliferation, and mucosal disruption. Using this murine model, we tested the hypothesis that preinoculation of murine gut with Lactobacillus acidophilus early in life can enhance host defense against enteric bacterial infection and attenuate bacteria-mediated colitis. Two-week old BALB/c mice were inoculated with L. acidophilus twice per week for 4 weeks before C. rodentium infection or concomitantly with the exposure to C. rodentium at 6–8 weeks of age. The probiotics were administered twice weekly thereafter. We observed that L. acidophilus inoculation in mice inhibits C. rodentium–induced colitis, which is associated with a decrease in C. rodentium colonization and translocation, an increase in its clearance, and a suppression of colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity. Probiotic treatment also stimulates regulatory cytokine expression in the colon [transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), interleukin (IL)-10]. Preinoculation with L. acidophilus is more effective than concomitant use of probiotics in the induction of intestinal IgA secretion and in the downregulation of proinflammatory cytokine expression [tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), IL-6, and IL-12]. These observations suggest that inoculation with probiotics can effectively prevent bacteria-induced colitis by limiting enteric bacteria infection and promoting mucosal protective regulatory immune responses. This study may have ramifications for prevention of infectious diarrhea in human infants and children, particularly in developing countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- MLN:
-
mesenteric lymph node
- MPO:
-
myeloperoxidase
- TGF-β:
-
transforming growth factor β
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor α
References
Vallance BA, Finlay BB 2000 Exploitation of host cells by enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 8799–8806
Moon HW, Whipp SC, Argenzio RA, Levine MM, Giannella RA 1983 Attaching and effacing activities of rabbit and human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in pig and rabbit intestines. Infect Immun 41: 1340–1351
Schauer DB, Falkow S 1993 The eae gene of Citrobacter freundii biotype 4280 is necessary for colonization in transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Infect Immun 61: 4654–4661
Ghaem-Maghami M, Simmons CP, Daniell S, Pizza M, Lewis D, Frankel G, Dougan G 2001 Intimin-specific immune responses prevent bacterial colonization by the attaching-effacing pathogen Citrobacter rodentium. Infect Immun 69: 5597–5605
Frankel G, Phillips AD, Novakova M, Field H, Candy DC, Schauer DB, Douce G, Dougan G 1996 Intimin from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli restores murine virulence to a Citrobacter rodentium eaeA mutant: induction of an immunoglobulin A response to intimin and EspB. Infect Immun 64: 5315–5325
Nader de Macias ME, Apella MC, Romero NC, Gonzalez SN, Oliver G 1992 Inhibition of Shigella sonnei by Lactobacillus casei and Lact. Acidophilus. J Appl Bacteriol 73: 407–411
Filho-Lima JV, Vieira EC, Nicoli JR 2000 Antagonistic effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus, Saccharomyces boulardii and Escherichia coli combinations against experimental infections with Shigella flexneri and Salmonella enteritidis subsp. Typhimurium in gnotobiotic mice. J Appl Microbiol 88: 365–370
Shu Q, Gill HS 2002 Immune protection mediated by the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (DR20) against Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 34: 59–64
Asahara T, Shimizu K, Nomoto K, Hamabata T, Ozawa A, Takeda Y 2004 Probiotic bifidobacteria protect mice from lethal infection with Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Infect Immun 72: 2240–2247
Varcoe JJ, Krejcarek G, Busta F, Brady L 2003 Prophylactic feeding of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM to mice attenuates overt colonic hyperplasia. J Food Prot 66: 457–465
MacDonald TT, Frankel G, Dougan G, Goncalves NS, Simmons C Host defences to Citrobacter rodentium. Int J Med Microbiol 2003 293: 87–93
Kimura K, McCartney AL, McConnell MA, Tannock GW 1997 Analysis of fecal populations of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli and investigation of the immunological responses of their human hosts to the predominant strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 63: 3394–3398
Ahrne S, Nobaek S, Jeppsson B, Adlerberth I, Wold AE, Molin G 1998 The normal Lactobacillus flora of healthy human rectal and oral mucosa. J Appl Microbiol 85: 88–94
Walter J, Hertel C, Tannock GW, Lis CM, Munro K, Hammes WP 2001 Detection of Lactobacillus, Pediococcus, Leuconostoc, and Weissella species in human feces by using group-specific PCR primers and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67: 2578–2585
Cong Y, Konrad A, Iqbal N, Elson CO 2003 Probiotics and immune regulation of inflammatory bowel diseases. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 2: 145–154
Sanders ME, Klaenhammer TR 2001 Invited review: the scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionally as a probiotic. J Dairy Sci 84: 319–331
Varcoe J, Zook C, Sui J, Leighton S, Busta F, Brady L 2002 Variable response to exogenous Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM consumed in different delivery vehicles. J Appl Microbiol 93: 900–906
Sui J, Leighton S, Busta F, Brady L 2002 16S ribosomal DNA analysis of the faecal lactobacilli composition of human subjects consuming a probiotic strain Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM. J Appl Microbiol 93: 907–912
Shi HN, Liu HY, Nagler-Anderson C 2000 Enteric infection acts as an adjuvant for the response to a model food antigen. J Immunol 165: 6174–6182
Burns RC, Rivera-Nieves J, Moskaluk CA, Matsumoto S, Cominelli F, Ley K 2001 Antibody blockade of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 ameliorates inflammation in the SAMP-1/Yit adoptive transfer model of Crohn's disease in mice. Gastroenterology 121: 1428–1436
Loher F, Schmall K, Freytag P, Landauer N, Hallwachs R, Bauer C, Siegmund B, Rieder F, Lehr HA, Dauer M, Kapp JF, Endres S, Eigler A 2003 The specific type-4 phosphodiesterase inhibitor mesopram alleviates experimental colitis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305: 549–556
Miller MJ, Sadowska-Krowicka H, Chotinaruemol S, Kakkis JL, Clark DA 1993 Amelioration of chronic ileitis by nitric oxide synthase inhibition. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264: 11–16
Wallace JL, MacNaughton WK, Morris GP, Beck PL 1989 Inhibition of leukotriene synthesis markedly accelerates healing in a rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 96: 29–36
Osman N, Adawi D, Ahrne S, Jeppsson B, Molin G 2004 Modulation of the effect of dextran sulfate sodium-induced acute colitis by the administration of different probiotic strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. Dig Dis Sci 49: 320–327
Araki Y, Andoh A, Takizawa J, Takizawa W, Fujiyama Y 2004 Clostridium butyricum, a probiotic derivative, suppresses dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis in rats. Int J Mol Med 13: 577–580
Pavan S, Desreumaux P, Mercenier A 2003 Use of mouse models to evaluate the persistence, safety, and immune modulation capacities of lactic acid bacteria. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 10: 696–701
Lamine F, Fioramonti J, Bueno L, Nepveu F, Cauquil E, Lobysheva I, Eutamene H, Theodorou V 2004 Nitric oxide released by Lactobacillus farciminis improves TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Scand J Gastroenterol 39: 37–45
Rolfe RD 2000 The role of probiotic cultures in the control of gastrointestinal health. J Nutr 130: 396S–402S
Rani B, Khetarpaul N 1998 Probiotic fermented food mixtures: possible applications in clinical anti-diarrhoea usage. Nutr Health 12: 97–105
Tkalcic S, Zhao T, Harmon BG, Doyle MP, Brown CA, Zhao P 2003 Fecal shedding of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli in weaned calves following treatment with probiotic Escherichia coli.. J Food Prot 66: 1184–1189
Shu Q, Qu F, Gill HS 2001 Probiotic treatment using Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 reduces weanling diarrhea associated with rotavirus and Escherichia coli infection in a piglet model. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 33: 171–177
Johnson E, Barthold SW 1979 The ultrastructure of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Am J Pathol 97: 291–313
Higgins LM, Frankel G, Douce G, Dougan G, MacDonald TT 1999 Citrobacter rodentium infection in mice elicits a mucosal Th1 cytokine response and lesions similar to those in murine inflammatory bowel disease. Infect Immun 67: 3031–3039
Perdigon G, Alvarez S, Pesce de Ruiz Holgado A 1991 Immunoadjuvant activity of oral Lactobacillus casei: influence of dose on the secretory immune response and protective capacity in intestinal infections. J Dairy Res 58: 485–496
Kaila M, Isolauri E, Soppi E, Virtanen E, Laine S, Arvilommi H 1992 Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatr Res 32: 141–144
Shu Q, Gill HS 2002 Immune protection mediated by the probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 (DR20) against Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection in mice. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 34: 59–64
Tejada-Simon MV, Lee JH, Ustunol Z, Pestka JJ 1999 Ingestion of yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium to potentiate immunoglobulin A responses to cholera toxin in mice. J Dairy Sci 82: 649–660
Fukushima Y, Kawata Y, Mizumachi K, Kurisaki J, Mitsuoka T 1999 Effect of bifidobacteria feeding on fecal flora and production of immunoglobulins in lactating mouse. Int J Food Microbiol 46: 193–197
Maaser C, Housley MP, Iimura M, Smith JR, Vallance BA, Finlay BB, Schreiber JR, Varki NM, Kagnoff MF, Eckmann L 2004 Clearance of Citrobacter rodentium requires B cells but not secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA) or IgM antibodies. Infect Immun 72: 3315–3324
Defrance T, Vanbervliet B, Briere F, Durand I, Rousset F, Banchereau J 1992 Interleukin 10 and transforming growth factor beta cooperate to induce anti-CD40-activated naive human B cells to secrete immunoglobulin A. J Exp Med 175: 671–782
von der Weid T, Bulliard C, Schiffrin EJ 2001 Induction by a lactic acid bacterium of a population of CD4 (+) T cells with low proliferative capacity that produce transforming growth factor beta and interleukin-10. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 8: 695–701
Pathmakanthan S, Li CK, Cowie J, Hawkey CJ 2004 Lactobacillus plantarum 299: beneficial in vitro immunomodulation in cells extracted from inflamed human colon. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 19: 166–173
Malstrom C, James S 1998 Inhibition of murine splenic and mucosal lymphocyte function by enteric bacterial products. Infect Immun 66: 3120–3127
Kim SH, Yang SJ, Koo HC, Bae WK, Kim JY, Park JH, Baek YJ, Park YH 2001 Inhibitory activity of Bifidobacterium longum HY8001 against Vero cytotoxin of Escherichia coli O157:H7. J Food Prot 64: 1667–1673
Pena JA, Versalovic J 2003 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG decreases TNF-α production in lipopolysaccharide-activated murine macrophages by a contact-independent mechanism. Cell Microbiol 5: 277–285
Karlsson H, Larsson P, Wold AE, Rudin A 2004 Pattern of cytokine responses to gram-positive and gram-negative commensal bacteria is profoundly changed when monocytes differentiate into dendritic cells. Infect Immun 72: 2671–2678
Simmons CP, Goncalves NS, Ghaem-Maghami M, Bajaj-Elliott M, Clare S, Neves B, Frankel G, Dougan G, MacDonald TT 2002 Impaired resistance and enhanced pathology during infection with a noninvasive, attaching-effacing enteric bacterial pathogen, Citrobacter rodentium, in mice lacking IL-12 or IFN-gamma. J Immunol 168: 1804–1812
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Beth McCormick for critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported in part by a Hood Foundation Research Grant, a Career Development Award from the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America (to H.N.S.), by NIH grants RO1-DK070260, PO1-DK-33506 to Dr. Walker, and by the Clinical Nutrition Research Center at Harvard (P30-DK40561). Hai Ning Shi, B.V.M., Ph.D., is a recipient of an NIH KO1 Award (DK059996). Chien-Chang Chen, M.D., is sponsored by the Chang Gung University and Chang Gung Children's Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, CC., Louie, S., Shi, H. et al. Preinoculation With the Probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus Early in Life Effectively Inhibits Murine Citrobacter rodentium Colitis. Pediatr Res 58, 1185–1191 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000183660.39116.83
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000183660.39116.83
This article is cited by
-
Heat-inactivated Lacticaseibacillus paracasei N1115 alleviates the damage due to brain function caused by long-term antibiotic cocktail exposure in mice
BMC Neuroscience (2022)
-
Oral supplementation with selected Lactobacillus acidophilus triggers IL-17-dependent innate defense response, activation of innate lymphoid cells type 3 and improves colitis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Lactobacillus casei protects dextran sodium sulfate- or rapamycin-induced colonic inflammation in the mouse
European Journal of Nutrition (2020)
-
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. lactis (strain CIDCA 133) stimulates murine macrophages infected with Citrobacter rodentium
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (2017)
-
Identification of TLR2/TLR6 signalling lactic acid bacteria for supporting immune regulation
Scientific Reports (2016)