Abstract
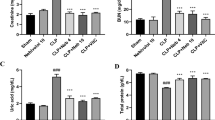
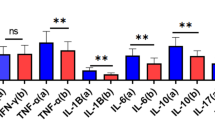
Oxidant/antioxidant imbalance plays an important role in septic shock. The present study examined changes in circulating oxidative components in a neonatal sepsis model. Subjects were 14 newborn mixed-strain piglets randomly divided into two groups: a cecal ligation and perforation (CLP) model (n = 7) and sham (n = 7). Blood samples for total hydroperoxide (TH), biological antioxidant potential (BAP), tumor necrosis factor (TNF) α, interleukin (IL)-6, and IL-10 were collected pre-CLP and at 1, 3, and 6 h post-CLP. TH and BAP levels at 1 h post-CLP were significantly higher in the CLP group than in the sham group. In the CLP group, TH decreased gradually and reached baseline levels by 6 h post-CLP, while BAP remained elevated. Linear correlations were identified between serum TH and BAP at 1 h post-CLP, serum TH and TNF-α at 1 h post-CLP, and BAP and IL-6 at 6 h post-CLP. Changes in and correlations between circulating oxidative and inflammatory state components in a neonatal sepsis model were clarified. This is the first study to reveal that the presence of oxidant/antioxidant imbalance in sepsis and septic shock changes during the disease course.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
biological antioxidant potentials
- CLP:
-
cecal ligation and perforation
- LPS:
-
lipopolysaccharide
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- TH:
-
total hydroperoxide
References
Parravicini E, van de Ven C, Anderson L, Cario MS 2002 Myeloid hematopoietic growth factors and their role in prevention and/or treatment of neonatal sepsis. Transfus Med Rev 16: 11–24
Heumann D, Gallay P, Barras C, Zaech P, Ulevitch RJ, Tobias PS, Glauser MP, Baumgartner JD 1992 Control of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) binding and LPS-induced tumor necrosis factor secretion in human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol 148: 3505–3512
Bone RC, Sprung CL, Sibbald WJ 1992 Definition for sepsis and organ failure. Crit Care Med 20: 724–726
Wolkow PP 1998 Involvement and dual effects of nitric oxide in septic shock. Inflamm Res 47: 152–166
Silveira RC, Procianoy RS 1999 Evaluation of interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta for early diagnosis of neonatal sepsis. Acta Paediatr 88: 647–650
Berner R, Welter P, Brandis M 2002 Cytokine expression of cord and adult blood mononuclear cells in response to Streptococcus agalactiae. Pediatr Res 51: 304–309
Batra S, Seema Kumar R, Seema Kapoor AK, Ray G 2000 Alterations in antioxidant status during neonatal sepsis. Ann Trop Paediatr 20: 27–33
Seema Kumar R, Mandal RN, Tandon A, Randhawa VS, Mehta G, Batra S, Ray GN, Kapoor AK 1999 Serum TNF-alpha free radical scavengers in neonatal septicemia. Indian J Pediatr 66: 511–516
Oldham KM, Bowen PE 1998 Oxidative stress in critical care: is antioxidant supplementation beneficial?. J Am Diet Assoc 98: 1001–1008
Buonocore G, Perrone S, Longini M, Terzuoli L, Bracci R 2000 Total hydroperoxide and advanced oxidation proteins products in preterm hypoxic babies. Pediatr Res 47: 221–224
Dohi K, Satoh K, Ohtaki H, Shioda S, Miyake Y, Shindo M, Aruga T 2005 Elevated plasma levels of bilirubin in patients with neurotrauma reflect its pathophysiological role in free radical scavenging. In Vivo 19: 855–860
Saugstad OD 1996 Mechanisms of tissue injury by oxygen radicals: implications for neonatal disease. Acta Paediatr 85: 1–4
Hara K, Yamashita S, Fujisawa A, Ishiwa S, Ogawa T, Yamamoto Y 1999 Oxidative stress in newborn infants with and without asphyxia as measured by plasma antioxidants and free fatty acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257: 244–248
Gitto E, Karbownik M, Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Cuzzocrea S, Chiurazzi P, Cordaro S, Corona G, Trimarchi G, Barberi I 2001 Effects of melatonin treatment in septic newborns. Pediatr Res 50: 756–760
Kato T, Hussein MH, Sugiura T, Suzuki S, Fukuda S, Tanaka T, Kato I, Togari H 2004 Development and characterization of a novel porcine model of neonatal sepsis. Shock 21: 329–335
Gutteridge JM, Mitchell J 1999 Redox imbalance in the critically ill. Br Med Bull 55: 49–75
Victor VM, Rocha M, De la Fuente M 2004 Immune cells: free radicals and antioxidants in sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 4: 327–347
Macarthur H, Westfall TC, Riley DP, Misko TP, Salvemini D 2000 Inactivation of catecholamines by superoxide gives new insights on the pathogenesis of septic shock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97: 9753–9758
Andrades M, Ritter C, Moreira JC, Dal-Pizzol F 2005 Oxidative parameters differences during non-lethal and lethal sepsis development. J Surg Res 125: 68–72
Victor VM, De la Fuente M 2003 Immune cells redox state from mice with endotoxin-induced oxidative stress. Involvement of NF-kappaB. Free Radic Res 37: 19–27
Ritter C, Andrades M, Frota Junior ML, Bonatto F, Pinho RA, Polydro M, Klamt F, Pinheiro CT, Menna-Barreto SS, Moreira JC, Dal-Pizzol F 2003 Oxidative parameters and mortality in sepsis induced by cecal ligation and perforation. Intensive Care Med 29: 1782–1789
Nijsten MW, de Groot ER, ten Duis HJ, Klasen HJ, Hack CE, Aarden LA 1987 Serum levels of interleukin-6 and acute phase responses. Lancet 2: 921
Tilg H, Trehu E, Atkins MB, Dinarello CA, Mier JW 1994 Interleukin-6 (IL-6) as an anti-inflammatory cytokine: induction of circulating IL-1 receptor antagonist and soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor p55. Blood 83: 113–118
Yu BP 1994 Cellular defenses against damage from reactive oxygen species. Physiol Rev 74: 139–162
Pascual C, Karzai W, Meier-Hellmann A, Oberhoffer M, Horn A, Bredle D, Reinhart K 1998 Total plasma antioxidant capacity is not always decreased in sepsis. Crit Care Med 26: 705–709
Yoshida Y, Maruyama M, Fujita T, Arai N, Hayashi R, Araya J, Matsui S, Yamashita N, Sugiyama E, Kobayashi M 1999 Reactive oxygen intermediates stimulate interleukin-6 production in human bronchial epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 276: L900–L908
Williams JG, Bernstein S, Prager M 1998 Effect of melatonin on activated macrophage TNF, IL-6, and reactive oxygen intermediates. Shock 9: 406–411
Ward NS, Waxman AB, Homer RJ, Mantell LL, Einarsson O, Du Y, Elias JA 2000 Interleukin-6-induced protection in hypoxic acute lung injury. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 22: 535–542
Waxman AB, Mahboubi K, Knickelbein RG, Mantell LL, Manzo N, Pober JS, Elias JA 2003 Interleukin-11 and interleukin-6 protect cultured human endothelial cells from H2O2-induced cell death. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29: 513–522
Tsan MF, White JE, Del Vecchio PJ, Shaffer JB 1992 IL-6 enhances TNF-alpha- and IL-1-induced increase of Mn superoxide dismutase mRNA and O2 tolerance. Am J Physiol 263: L22–L26
Kemp AS, Campbell DE 1996 The neonatal immune system. Semin Neonatol 1: 67–75
Sanlioglu S, Williams CM, Samavati L, Butler NS, Wang G, McCray PB Jr, Ritchie TC, Hunninghake GW, Zandi E, Engelhardt JF 2001 Lipopolysaccharide induces Rac1-dependent reactive oxygen species formation and coordinates tumor necrosis factor-alpha secretion through IKK regulation of NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem 276: 30188–30198
Sozzani S, Bosisio D, Mantovani A, Ghezzi P 2005 Linking stress, oxidation and the chemokine system. Eur J Immunol 35: 3095–3098
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN, Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M, Talalay P 2002 Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 and sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 11908–11913
Holtzclaw WD, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Talalay P 2004 Protection against electrophile and oxidative stress by induction of phase 2 genes: the quest for the elusive sensor that responds to inducers. Adv Enzyme Regul 44: 335–367
Qasimi P, Ming-Lum A, Ghanipour A, Ong CJ, Cox ME, Ihle J, Cacalano N, Yoshimura A, Mui AL 2006 Divergent mechanisms utilized by SOCS3 to mediate interleukin-10 inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha and nitric oxide production by macrophages. J Biol Chem 281: 6316–6324
Ogilvie AC, Groeneveld AB, Straub JP, Thijis LG 1991 Plasma lipid peroxides and antioxidants in human septic shock. Intensive Care Med 17: 40–44
Goode HF, Cowley HC, Walker BE, Howdle PD, Webster NR 1995 Decreased antioxidant status and increased lipid peroxidation in patients with septic shock and secondary organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 23: 646–651
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kakita, H., Hussein, M., Daoud, G. et al. Total Hydroperoxide and Biological Antioxidant Potentials in a Neonatal Sepsis Model. Pediatr Res 60, 675–679 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000245911.79943.8a
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000245911.79943.8a
This article is cited by
-
Increased biological antioxidant potential in the cerebrospinal fluid of transient global amnesia patients
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Endothelin receptor antagonist attenuates oxidative stress in a neonatal sepsis piglet model
Pediatric Research (2012)