Abstract
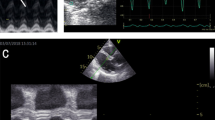
Hurler syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type I [MPS I]) is a uniformly lethal autosomal recessive storage disease caused by absence of the enzyme α-l-iduronidase (IDUA), which is involved in lysosomal degradation of sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). Cardiomyopathy and valvar insufficiency occur as GAGs accumulate in the myocardium, spongiosa of cardiac valves, and myointima of coronary arteries. Here we report the functional, biochemical, and morphologic cardiac findings in the MPS I mouse. We compare the cardiac functional and histopathological findings in the mouse to human MPS I. In MPS I mice, we have noted aortic insufficiency, increased left ventricular size, and decreased ventricular function. Aortic and mitral valves are thickened and the aortic root is dilated. However, murine MPS I is not identical to human MPS I. Myointimal proliferation of epicardial coronary arteries is unique to human MPS I, whereas dilation of aortic root appears unique to murine MPS I. Despite the differences between murine and human MPS I, the murine model provides reliable in vivo outcome parameters, such as thickened and insufficient aortic valves and depressed cardiac function that can be followed to assess the impact of therapeutic interventions in preclinical studies in Hurler syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- GAG:
-
glycosaminoglycan
- IDUA:
-
α-l-iduronidase
- MPS I:
-
mucopolysaccharidosis type I (Hurler)
References
Meikle PJ, Hopwood JJ, Clague AE, Carey WF 1999 Prevalence of lysosomal storage disorders. JAMA 281: 249–254
Neufeld EF, Muenzer J 1997 The mucopolysaccharidoses. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The Metabolic Basis of Inherited Diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 2465–2494
Renteria VG, Ferrans VJ, Roberts WC 1976 The heart in the Hurler syndrome: gross, histologic and ultrastructural observations in five necropsy cases. Am J Cardiol 38: 487–501
Brosius FC 3rd Roberts WC 1981 Coronary artery disease in the Hurler syndrome. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the extent of coronary narrowing at necropsy in six children. Am J Cardiol 47: 649–653
Beesley CE, Meaney CA, Greenland G, Adams V, Vellodi A, Young EP, Winchester BG 2001 Mutational analysis of 85 mucopolysaccharidosis type I families: frequency of known mutations, identification of 17 novel mutations and in vitro expression of missense mutations. Hum Genet 109: 503–511
Matte U, Yogalingam G, Brooks D, Leistner S, Schwartz I, Lima L, Norato DY, Brum JM, Beesley C, Winchester B, Giugliani R, Hopwood JJ 2003 Identification and characterization of 13 new mutations in mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. Mol Genet Metab 78: 37–43
Clarke LA, Russell CS, Pownall S, Warrington CL, Borowski A, Dimmick JE, Toone J, Jirik FR 1997 Murine mucopolysaccharidosis type I: targeted disruption of the murine α-L-iduronidase gene. Hum Mol Genet 6: 503–511
Ohmi K, Greenberg DS, Rajavel KS, Ryazantsev S, Li HH, Neufeld EF 2003 Activated microglia in cortex of mouse models of mucopolysaccharidosis I and IIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100: 1902–1097
Liu Y, Xu L, Hennig AK, Kovacs A, Fu A, Chung S, Lee D, Wang B, Herati RS, Mosinger Ogilvie J, Cai SR, Parker Ponder K 2005 Liver-directed neonatal gene therapy prevents cardiac, bone, ear and eye disease in mucopolysaccharidosis I mice. Mol Ther 11: 35–47
Zheng Y, Rozengurt N, Ryazantsev S, Kohn DB, Satake N, Neufeld EF 2003 Treatment of the mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis I with retrovirally transduced bone marrow. Mol Genet Metab 79: 233–244
Snider AR, Serwer GA 1990 Echocardiography in Pediatric Heart Disease. Year Book Medical Publishers, Chicago, p 23
Yang XP, Liu YH, Rhaleb NE, Kurihara N, Kim HE, Carretero OA 1999 Echocardiographic assessment of cardiac function in conscious and anesthetized mice. Am J Physiol 277: H1967–H1974
Di Domenico C, Villani GR, Di Napoli D, Reyero EG, Lombardo A, Naldini L, Di Natale P 2005 Gene therapy for a mucopolysaccharidosis type I murine model with lentiviral-IDUA vector. Hum Genet Ther 16: 81–90
Hartung SD, Frandsen JL, Pan D, Koniar BL, Graupman P, Gunther R, Low WC, Whitley CB, McIvor RS 2004 Correction of metabolic, craniofacial, and neurologic abnormalities in MPS I mice treated at birth with adeno-associated virus vector transducing the human α-L-iduronidase gene. Mol Ther 9: 866–875
Hobbs JR, Hugh-Jones K, Barrett AJ, Byrom N, Chambers D, Henry K, James DC, Lucas CF, Rogers TR, Benson PF, Tansley LR, Patrick AD, Mossman J, Young EP 2004 Reversal of clinical features of Hurler's disease and biochemical improvement after treatment by bone-marrow transplantation. Lancet 2: 709–712
Vinallonga X, Sanz N, Balaguer A, Miro L, Ortega JJ, Casaldaliga J 1992 Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in mucopolysaccharidosis: regression after bone marrow transplantation. Pediatr Cardiol 13: 107–109
Gatzoulis MA, Vellodi A, Redington AN 1995 Cardiac involvement in mucopolysaccharidosis: effects of allogenic bone marrow transplantation. Arch Dis Child 73: 259–260
Braunlin EA, Stauffer NR, Peters CH, Bass JL, Berry JM, Hopwood JJ, Krivit W 2003 Usefulness of bone marrow transplantation in the Hurler syndrome. Am J Cardiol 92: 882–886
Dangel JH 1998 Cardiovascular changes in children with mucopolysaccharide storage diseases and related disorders - Clinical and echocardiographic findings in 64 patients. Eur J Pediatr 157: 534–538
Gross DM, Williams JC, Caprioli C, Dominguez B, Howell RR 1988 Echocardiographic abnormalities in the mucopolysaccharide storage diseases. Am J Cardiol 61: 170–176
Daugherty A 2002 Mouse models of atherosclerosis. Am J Med Sci 323: 3–10
Stefanovich V, Akiyama K 1970 Comparative studies of aortic acid mucopolysaccharides in fifteen species. Comp Biochem Physiol 34: 125–130
Gardais A, Picard J, Hermelin B 1973 Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) distribution in aortic wall from five species. Comp Biochem Physiol B 44: 507–515
Brown OR, DeMots H, Kloster FE, Roberts A, Menashe VD, Beals RK 1975 Aortic root dilatation and mitral valve prolapse in Marfan's syndrome: an echocardiographic study. Circulation 52: 651–657
Pereira L, Lee SY, Gayraud B, Andrikopoulos K, Shapiro SD, Bunton T, Biery NJ, Dietz HC, Sakai LY, Ramirez F 1999 Pathogenetic sequence for aneurysm revealed in mice underexpressing fibrillin-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96: 3819–3823
Hinek A, Wilson SE 2000 Impaired elastogenesis in Hurler disease. dermatan sulfate accumulation linked to deficiency in elastin-binding protein and elastic fiber assembly. Am J Pathol 156: 925–938
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by Minnesota Medical Foundation, Children's Cancer Research Foundation, University of Minnesota Cancer Center, and NIH RO1 HL49997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braunlin, E., Mackey-Bojack, S., Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A. et al. Cardiac Functional and Histopathologic Findings in Humans and Mice with Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I: Implications for Assessment of Therapeutic Interventions in Hurler Syndrome. Pediatr Res 59, 27–32 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000190579.24054.39
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000190579.24054.39
This article is cited by
-
Neonatal nonviral gene editing with the CRISPR/Cas9 system improves some cardiovascular, respiratory, and bone disease features of the mucopolysaccharidosis I phenotype in mice
Gene Therapy (2020)
-
Angiotensin receptor blockade mediated amelioration of mucopolysaccharidosis type I cardiac and craniofacial pathology
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease (2017)
-
Cardiac QTc interval characteristics before and after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: an analysis of 995 consecutive patients at a single center
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2015)
-
Increased longevity and metabolic correction following syngeneic BMT in a murine model of mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2012)
-
Arterial pathology in canine mucopolysaccharidosis-I and response to therapy
Laboratory Investigation (2011)