Abstract
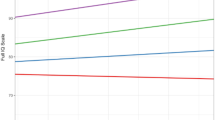
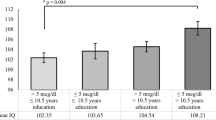
In one study of children in 27 families with maternal retardation, those children with higher intelligence quotient (IQ) were more likely to have multiple behavior problems than those with lower IQ. If true, this result would affect clinical practice, but it has not been replicated. Because the setting of the initial observation is similar to the setting of childhood lead poisoning, we attempted a replication using data from the Treatment of Lead-Exposed Children (TLC) study, in which 780 children aged 12–33 mo with blood lead levels 20–44 μg/dL were randomized to either succimer treatment or placebo and then followed up to 5 y. Of 656 mothers of TLC children with IQ measured, 113 demonstrated mental retardation (IQ <70). Whether maternal IQ was <70 or ≥70, children with IQ ≥85 were rated more favorably on cognitive tests and behavioral questionnaires than children with IQ <85; these measures included Conners' Parent Rating Scale–Revised at age 5, the Developmental Neuropsychological Assessment at ages 5 and 7, and the Behavioral Assessment System for Children at age 7. Among children of mothers with IQ <70, those with IQ ≥85 did not show more severe clinical behavioral problems, nor were they more likely to show multiple behavior problems. Children with higher IQ have fewer behavior problems, irrespective of the mother's IQ. In the special setting of mothers with IQ <70, children with higher IQ are not at greater risk of behavior problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BASC-PRS:
-
Behavioral Assessment System for Children–Parent Rating Scale
- BASC-TRS:
-
Behavioral Assessment System for Children–Teacher Rating Scale
- CPRS-R:
-
Conners' Parent Rating Scale–Revised
- CPT:
-
Conners' Continuous Performance Test
- CVLTC:
-
California Verbal Learning Test for Children
- IQ:
-
intelligence quotient
- NEPSY:
-
Developmental Neuropsychological Assessment
- NESS:
-
Neurological Examination for Subtle Signs
- TLC:
-
Treatment of Lead-Exposed Children Study
- WLPB-R:
-
Woodcock Language Proficiency Battery–Revised
References
Feldman MA, Walton-Allen N 1997 Effects of maternal mental retardation and poverty on intellectual, academic, and behavioral status of school-age children. Am J Ment Retard 101: 352–364
O'Neill AM 1985 Normal and bright children of mentally retarded parents: the Huck Finn syndrome. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 15: 255–268
Goodman R, Simonoff E, Stevenson J 1995 The impact of child IQ, parent IQ and sibling IQ on child behavioural deviance scores. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 36: 409–425
Andersson HW, Sommerfelt K 2001 The relationship between cognitive abilities and maternal ratings of externalizing behaviors in preschool children. Scand J Psychol 42: 437–444
Anselmi L, Piccinini CA, Barros FC, Lopes RS 2004 Psychosocial determinants of behaviour problems in Brazilian preschool children. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 45: 779–788
1998 The Treatment of Lead-exposed Children (TLC) trial: design and recruitment for a study of the effect of oral chelation on growth and development in toddlers. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 12: 313–333
Rogan WJ, Dietrich KN, Ware JH, Dockery DW, Salganik M, Radcliffe J, Jones RL, Ragan NB, Chisolm JJ Jr, Rhoads GG 2001 The effect of chelation therapy with succimer on neuropsychological development in children exposed to lead. N Engl J Med 344: 1421–1426
Dietrich KN, Ware JH, Salganik M, Radcliffe J, Rogan WJ, Rhoads GG, Fay ME, Davoli CT, Denckla MB, Bornschein RL, Schwarz D, Dockery DW, Adubato S, Jones RL, Treatment of Lead-Exposed Children Clinical, Trial Group 2004 Effect of chelation therapy on the neuropsychological and behavioral development of lead-exposed children after school entry. Pediatrics 114: 19–26
Silverstein AB 1985 Two- and four-subtest short forms of the WAIS-R: a closer look at validity and reliability. J Clin Psychol 41: 95–97
Wechsler D 1989 The Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scales of Intelligence–Revised. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Wechsler D 1991 Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children–III. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Korkman M, Kirk U, Kemp S 1998 NEPSY: A Developmental Neuropsychological Assessment: Manual. Rev. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Conners CK 1997 Conners' Rating Scales: Technical Manual. Multi-Health Systems, North Tonawanda, NY
Conners CK 1995 Conners' Continuous Performance Test. Multi-Health Systems, North Tonawanda, NY
Delis DC, Kramer JH, Kaplan E, Ober BA 1994 California Verbal Learning Test–Children's Version. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio, TX
Woodcock RW 1991 Woodcock Language Proficiency Battery–Revised. Riverside Publishing, Itasca, IL
Denckla MB 1985 Revised Neurological Examination for Subtle Signs. Psychopharmacol Bull 21: 773–800
Reynolds CR, Kamphaus RW 1992 Behavior Assessment System for Children. American Guidance Service, Circle Pines, MN
Miller DT, Paschal DC, Gunter EW, Stroud PE, D'Angelo J 1987 Determination of lead in blood using electrothermal atomisation atomic absorption spectrometry with a L'vov platform and matrix modifier. Analyst 112: 1701–1704
Burns JM, Baghurst PA, Sawyer MG, McMichael AJ, Tong SL 1999 Lifetime low-level exposure to environmental lead and children's emotional and behavioral development at ages 11-13 years. The Port Pirie Cohort Study. Am J Epidemiol 149: 740–749
Wasserman GA, Staghezza-Jaramillo B, Shrout P, Popovac D, Graziano J 1998 The effect of lead exposure on behavior problems in preschool children. Am J Public Health 88: 481–486
Sciarillo WG, Alexander G, Farrell KP 1992 Lead exposure and child behavior. Am J Public Health 82: 1356–1360
Bacharach VR, Baumeister AA 1998 Effects of maternal intelligence, marital status, income, and home environment on cognitive development of low birthweight infants. J Pediatr Psychol 23: 197–205
Plomin R 1999 Genetics and general cognitive ability. Nature 402: C25–29.
Stoolmiller M 1999 Implications of the restricted range of family environments for estimates of heritability and nonshared environment in behavior-genetic adoption studies. Psychol Bull 125: 392–409
Dickens WT, Flynn JR 2001 Heritability estimates versus large environmental effects: the IQ paradox resolved. Psychol Rev 108: 346–369
Gillberg C, Geijer-Karlsson M 1983 Children born to mentally retarded women: a 1-21 year follow-up study of 41 cases. Psychol Med 13: 891–894
Feldman MA, Case L, Towns F, Betel J 1985 Parent Education Project. I: development and nurturance of children of mentally retarded parents. Am J Ment Defic 90: 253–258
Schwartz J 1994 Low-level lead exposure and children's IQ: a meta-analysis and search for a threshold. Environ Res 65: 42–55
Pocock SJ, Smith M, Baghurst P 1994 Environmental lead and children's intelligence: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. BMJ 309: 1189–1197
Lanphear BP, Hornung R, Khoury J, Yolton K, Baghurst P, Bellinger DC, Canfield RL, Dietrich KN, Bornschein R, Greene T, Rothenberg SJ, Needleman HL, Schnaas L, Wasserman G, Graziano J, Roberts R 2005 Low-level environmental lead exposure and children's intellectual function: an international pooled analysis. Environ Health Perspect 113: 894–899
Offord DR, Boyle MH, Szatmari P, Rae-Grant NI, Links PS, Cadman DT, Byles JA, Crawford JW, Blum HM, Byrne C, et al. 1987 Ontario Child Health Study. II. Six-month prevalence of disorder and rates of service utilization. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44: 832–836
Deng S, Liu X, Roosa MW 2004 Agreement between parent and teacher reports on behavioral problems among Chinese children. J Dev Behav Pediatr 25: 407–414
Kumpulainen K, Rasanen E, Henttonen I, Moilanen I, Piha J, Puura K, Tamminen T, Almqvist F 1999 Children's behavioural/emotional problems: a comparison of parents' and teachers' reports for elementary school-aged children. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry 8( suppl 4): 41–47
Gagnon C, Vitaro F, Tremblay RE 1992 Parent-teacher agreement on kindergarteners' behavior problems: a research note. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 33: 1255–1261
Harder DW, Greenwald DF 1992 Parent, family interaction, and child predictors of outcome among sons at psychiatric risk. J Clin Psychol 48: 151–164
Greenwald DF 1990 Child functioning predictors of outcome among boys at risk for psychological disorder. J Genet Psychol 151: 139–151
Schachar R, Rutter M, Smith A 1981 The characteristics of situationally and pervasively hyperactive children: implications for syndrome definition. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 22: 375–392
Broman S, Nichols PL, Shaughnessy P, Kennedy W 1987 Retardation in Young Children: A Developmental Study of Cognitive Deficit. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ 24–37
Renick MJ, Harter S 1989 Impact of social comparisons on the developing self-perceptions of learning disabled students. J Educ Psychol 81: 631–638
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented, in part, at the annual meeting of the Pediatric Academic Societies, May 14–17, 2005, Washington, DC.The Treatment of Lead-Exposed Children Trial was supported by the NIEHS in cooperation with the NIH Office of Minority Health, and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Succimer and placebo capsules were gifts from McNeil Labs, Fort Washington, PA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, A., Schwarz, D., Radcliffe, J. et al. Maternal IQ, Child IQ, Behavior, and Achievement in Urban 5–7 Year Olds. Pediatr Res 59, 471–477 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000199910.16681.f0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000199910.16681.f0
This article is cited by
-
Neurodevelopmental profiles of preschool-age children in Flint, Michigan: a latent profile analysis
Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (2021)
-
Spillover Effects of Maternal Chronic Disease on Children’s Quality of Life and Behaviors Among Low-Income Families
The Patient - Patient-Centered Outcomes Research (2018)
-
Maternal mental quality of life mediates the associations between intimate partner abuse against mothers and their children’s behaviours and quality of life in low-income Chinese families
Quality of Life Research (2017)