Abstract
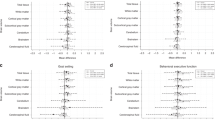
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the differences in whole brain white matter (WM) volume and anisotropy between preterm and term children and to determine the relationships with cognitive outcome. Twenty-five low birth weight (BW), preterm, neurologically normal children between 8.8 and 11.5 y of age were recruited for volumetric and diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging (DTI), together with 13 age-matched term control subjects. Subsequent intelligence quotient (IQ) testing was performed for 21 preterm children within 6 mo of imaging studies. We computed the mean volume and fractional anisotropy (FA) of the whole brain WM and compared the differences between the two groups. Mean WM volume and FA were significantly lower in the preterm group (p = 0.014 and p < 0.001, respectively). Multiple regression analysis found both WM volume and FA to be independent variables significantly affecting full scale IQ (FSIQ) (r2 = 0.407, p = 0.021 and r2 = 0.496, p = 0.005, respectively) after adjusting for BW, gestational age (GA), and gender. In the evaluation of the whole brain WM of preterm children, we found that both volume and FA remain reduced at late childhood with both parameters significantly affecting long-term cognitive outcome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BW:
-
birth weight
- DTI:
-
diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging
- FA:
-
fractional anisotropy
- FSIQ:
-
full scale IQ
- GM:
-
gray matter
- M-U:
-
Mann-Whitney U test
- VLBW:
-
very low birth weight
- WM:
-
white matter
- WMI:
-
white matter injury
- 3D SPGR:
-
three-dimensional spoiled gradient recalled
References
Volpe JJ 2001 Neurobiology of periventricular leukomalacia in the premature infant. Pediatr Res 50: 553–562
Pinto-Martin JA, Whitaker AH, Feldman JF, Van Rossem R, Paneth N 1999 Relation of cranial ultrasound abnormalities in low-birthweight infants to motor or cognitive performance at ages 2, 6, and 9 years. Dev Med Child Neurol 41: 826–833
Latal-Hajnal B, von Siebenthal K, Kovari H, Bucher HU, Largo RH 2003 Postnatal growth in VLBW infants: significant association with neurodevelopmental outcome. J Pediatr 143: 163–170
Foulder-Hughes LA, Cooke RW 2003 Motor, cognitive, and behavioural disorders in children born very preterm. Dev Med Child Neurol 45: 97–103
Bhutta AT, Cleves MA, Casey PH, Cradock MM, Anand KJ 2002 Cognitive and behavioral outcomes of school-aged children who were born preterm: a meta-analysis. JAMA 288: 728–737
McCarton CM, Brooks-Gunn J, Wallace IF, Bauer CR, Bennett FC, Bernbaum JC, Broyles RS, Casey PH, McCormick MC, Scott DT, Tyson J, Tonascia J, Meinert CL 1997 Results at age 8 years of early intervention for low-birth-weight premature infants. The Infant Health and Development Program. JAMA 277: 126–132
Ajayi-Obe M, Saeed N, Cowan FM, Rutherford MA, Edwards AD 2000 Reduced development of cerebral cortex in extremely preterm infants. Lancet 356: 1162–1163
Vasileiadis GT, Gelman N, Han VK, Williams LA, Mann R, Bureau Y, Thompson RT 2004 Uncomplicated intraventricular hemorrhage is followed by reduced cortical volume at near-term age. Pediatrics 114: e367–e372
Lodygensky GA, Rademaker K, Zimine S, Gex-Fabry M, Lieftink AF, Lazeyras F, Groenendaal F, de Vries LS, Huppi PS 2005 Structural and functional brain development after hydrocortisone treatment for neonatal chronic lung disease. Pediatrics 116: 1–7
Martinussen M, Fischl B, Larsson HB, Skranes J, Kulseng S, Vangberg TR, Vik T, Brubakk AM, Haraldseth O, Dale AM 2005 Cerebral cortex thickness in 15-year-old adolescents with low birth weight measured by an automated MRI-based method. Brain 128: 2588–2596
Reiss AL, Kesler SR, Vohr B, Duncan CC, Katz KH, Pajot S, Schneider KC, Makuch RW, Ment LR 2004 Sex differences in cerebral volumes of 8-year-olds born preterm. J Pediatr 145: 242–249
Nosarti C, Al-Asady MH, Frangou S, Stewart AL, Rifkin L, Murray RM 2002 Adolescents who were born very preterm have decreased brain volumes. Brain 125: 1616–1623
Inder TE, Warfield SK, Wang H, Huppi PS, Volpe JJ 2005 Abnormal cerebral structure is present at term in premature infants. Pediatrics 115: 286–294
Peterson BS, Vohr B, Staib LH, Cannistraci CJ, Dolberg A, Schneider KC, Katz KH, Westerveld M, Sparrow S, Anderson AW, Duncan CC, Makuch RW, Gore JC, Ment LR 2000 Regional brain volume abnormalities and long-term cognitive outcome in preterm infants. JAMA 284: 1939–1947
Abernethy LJ, Palaniappan M, Cooke RW 2002 Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in survivors of very low birth weight. Arch Dis Child 87: 279–283
Abernethy LJ, Cooke RW, Foulder-Hughes L 2004 Caudate and hippocampal volumes, intelligence, and motor impairment in 7-year-old children who were born preterm. Pediatr Res 55: 884–893
Inder TE, Wells SJ, Mogridge NB, Spencer C, Volpe JJ 2003 Defining the nature of the cerebral abnormalities in the premature infant: a qualitative magnetic resonance imaging study. J Pediatr 143: 171–179
Gimenez M, Junque C, Narberhaus A, Bargallo N, Botet F, Mercader JM 2006 White matter volume and concentration reductions in adolescents with history of very preterm birth: a voxel-based morphometry study. Neuroimage 32: 1485–1498
Isaacs EB, Edmonds CJ, Chong WK, Lucas A, Morley R, Gadian DG 2004 Brain morphometry and IQ measurements in preterm children. Brain 127: 2595–2607
Nosarti C, Rushe TM, Woodruff PW, Stewart AL, Rifkin L, Murray RM 2004 Corpus callosum size and very preterm birth: relationship to neuropsychological outcome. Brain 127: 2080–2089
Peterson BS, Anderson AW, Ehrenkranz R, Staib LH, Tageldin M, Colson E, Gore JC, Duncan CC, Makuch R, Ment LR 2003 Regional brain volumes and their later neurodevelopmental correlates in term and preterm infants. Pediatrics 111: 939–948
Beaulieu C 2002 The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system - a technical review. NMR Biomed 15: 435–455
Counsell SJ, Boardman JP 2005 Differential brain growth in the infant born preterm: current knowledge and future developments from brain imaging. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 10: 403–410
Partridge SC, Mukherjee P, Henry RG, Miller SP, Berman JI, Jin H, Lu Y, Glenn OA, Ferriero DM, Barkovich AJ, Vigneron DB 2004 Diffusion tensor imaging: serial quantitation of white matter tract maturity in premature newborns. Neuroimage 22: 1302–1314
Huppi PS, Maier SE, Peled S, Zientara GP, Barnes PD, Jolesz FA, Volpe JJ 1998 Microstructural development of human newborn cerebral white matter assessed in vivo by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Res 44: 584–590
Huppi PS, Murphy B, Maier SE, Zientara GP, Inder TE, Barnes PD, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA, Volpe JJ 2001 Microstructural brain development after perinatal cerebral white matter injury assessed by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatrics 107: 455–460
Miller SP, Vigneron DB, Henry RG, Bohland MA, Ceppi-Cozzio C, Hoffman C, Newton N, Partridge JC, Ferriero DM, Barkovich AJ 2002 Serial quantitative diffusion tensor MRI of the premature brain: development in newborns with and without injury. J Magn Reson Imaging 16: 621–632
Nagy Z, Westerberg H, Skare S, Andersson JL, Lilja A, Flodmark O, Fernell E, Holmberg K, Bohm B, Forssberg H, Lagercrantz H, Klingberg T 2003 Preterm children have disturbances of white matter at 11 years of age as shown by diffusion tensor imaging. Pediatr Res 54: 672–679
Vangberg TR, Skranes J, Dale AM, Martinussen M, Brubakk AM, Haraldseth O 2006 Changes in white matter diffusion anisotropy in adolescents born prematurely. Neuroimage 32: 1538–1548
Hong Kong: Education and Manpower Bureau 1981 Hong Kong Wechsler Intelligence Scale for children. Translated and adapted from Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children by permission of New York: The Psychological Corporation
Wilke M, Schmithorst VJ, Holland SK 2002 Assessment of spatial normalization of whole-brain magnetic resonance images in children. Hum Brain Mapp 17: 48–60
Khong PL, Leung LH, Fung AS, Fong DY, Qiu D, Kwong DL, Ooi GC, McAlanon G, Cao G, Chan GC 2006 White matter anisotropy in post-treatment childhood cancer survivors: preliminary evidence of association with neurocognitive function. J Clin Oncol 24: 884–890
du Plessis AJ, Volpe JJ 2002 Perinatal brain injury in the preterm and term newborn. Curr Opin Neurol 15: 151–157
Yoshioka A, Bacskai B, Pleasure D 1996 Pathophysiology of oligodendroglial excitotoxicity. J Neurosci Res 46: 427–437
Oka A, Belliveau MJ, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ 1993 Vulnerability of oligodendroglia to glutamate: pharmacology, mechanisms, and prevention. J Neurosci 13: 1441–1453
Inder T, Neil J, Yoder B, Rees S 2005 Patterns of cerebral injury in a primate model of preterm birth and neonatal intensive care. J Child Neurol 20: 965–967
Inder TE, Huppi PS, Warfield S, Kikinis R, Zientara GP, Barnes PD, Jolesz F, Volpe JJ 1999 Periventricular white matter injury in the premature infant is followed by reduced cerebral cortical gray matter volume at term. Ann Neurol 46: 755–760
Allin M, Henderson M, Suckling J, Nosarti C, Rushe T, Fearon P, Stewart AL, Bullmore ET, Rifkin L, Murray R 2004 Effects of very low birthweight on brain structure in adulthood. Dev Med Child Neurol 46: 46–53
Fearon P, O'Connell P, Frangou S, Aquino P, Nosarti C, Allin M, Taylor M, Stewart A, Rifkin L, Murray R 2004 Brain volumes in adult survivors of very low birth weight: a sibling-controlled study. Pediatrics 114: 367–371
Kesler SR, Ment LR, Vohr B, Pajot SK, Schneider KC, Katz KH, Ebbitt TB, Duncan CC, Makuch RW, Reiss AL 2004 Volumetric analysis of regional cerebral development in preterm children. Pediatr Neurol 31: 318–325
Counsell SJ, Shen Y, Boardman JP, Larkman DJ, Kapellou O, Ward P, Allsop JM, Cowan FM, Hajnal JV, Edwards AD, Rutherford MA 2006 Axial and radial diffusivity in preterm infants who have diffuse white matter changes on magnetic resonance imaging at term-equivalent age. Pediatrics 117: 376–386
Nagy Z, Westerberg H, Klingberg T 2004 Maturation of white matter is associated with the development of cognitive functions during childhood. J Cogn Neurosci 16: 1227–1233
Peng SS, Tseng WY, Chien YH, Hwu WL, Liu HM 2004 Diffusion tensor images in children with early-treated, chronic, malignant phenylketonuric: correlation with intelligence assessment. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25: 1569–1574
Kantarci K, Jack CR Jr, Xu YC, Campeau NG, O'Brien PC, Smith GE, Ivnik RJ, Boeve BF, Kokmen E, Tangalos EG, Petersen RC 2001 Mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease: regional diffusivity of water. Radiology 219: 101–107
O'sullivan M, Morris RG, Huckstep B, Jones DK, Williams SC, Markus HS 2004 Diffusion tensor MRI correlates with executive dysfunction in patients with ischaemic leukoaraiosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75: 441–447
Rovaris M, Iannucci G, Falautano M, Possa F, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M 2002 Cognitive dysfunction in patients with mildly disabling relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: an exploratory study with diffusion tensor MR imaging. J Neurol Sci 195: 103–109
Schmithorst VJ, Wilke M, Dardzinski BJ, Holland SK 2005 Cognitive functions correlate with white matter architecture in a normal pediatric population: a diffusion tensor MRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 26: 139–147
Ment LR, Peterson BS, Meltzer JA, Vohr B, Allan W, Katz KH, Lacadie C, Schneider KC, Duncan CC, Makuch RW, Constable RT 2006 A functional magnetic resonance imaging study of the long-term influences of early indomethacin exposure on language processing in the brains of prematurely born children. Pediatrics 118: 961–970
Hindmarsh GJ, O'Callaghan MJ, Mohay HA, Rogers YM 2000 Gender differences in cognitive abilities at 2 years in ELBW infants. Extremely low birth weight. Early Hum Dev 60: 115–122
Johnson EO, Breslau N 2000 Increased risk of learning disabilities in low birth weight boys at age 11 years. Biol Psychiatry 47: 490–500
Hack M, Flannery DJ, Schluchter M, Cartar L, Borawski E, Klein N 2002 Outcomes in young adulthood for very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med 346: 149–157
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by the University of Hong Kong Committee on Research and Conference grants (CRCG).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yung, A., Poon, G., Qiu, DQ. et al. White Matter Volume and Anisotropy in Preterm Children: A Pilot Study of Neurocognitive Correlates. Pediatr Res 61, 732–736 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/pdr.0b013e31805365db
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/pdr.0b013e31805365db
This article is cited by
-
Functional and structural connectivity of the brain in very preterm babies: relationship with gestational age and body and brain growth
Pediatric Radiology (2019)
-
Neuroimaging in former preterm children who received erythropoiesis stimulating agents
Pediatric Research (2017)
-
Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging in preterm brain injury
Neuroradiology (2013)
-
Associations between regional brain volumes at term-equivalent age and development at 2 years of age in preterm children
Pediatric Radiology (2011)
-
Neuro-developmental outcome at 18 months in premature infants with diffuse excessive high signal intensity on MR imaging of the brain
Pediatric Radiology (2011)