Abstract
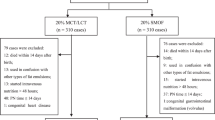
Intragastric fat digestion was investigated by analyzing the products of lipolysis and the gastric lipase (HGL) levels of premature infants fed with a formula enriched with medium chain triglycerides (MCT) and those of infants fed with human milk. Infants were fed using a gastric tube and the gastric contents were aspirated twice a day for 5 d, before and at various times after gavage feeding. HGL levels were measured using the pHstat technique. After extraction, lipids were separated and quantified using thin-layer chromatography coupled to a flame ionization detector. Fatty acid methyl esters were analyzed by gas chromatography. HGL concentration increased during digestion, reaching 77.4 ± 43.1 μg/mL (around 75% of those recorded in adults). Mean HGL output was 115 ± 43 μg for 3 h and the overall intragastric lipolysis was 6.1 ± 2.6%. Although the formula was enriched with octanoic and decanoic acid, the main fatty acids released in the stomach were palmitic (C16:0, 17.03 ± 0.23% wt/wt) and oleic (C18:1 n-9, 28.23 ± 1.26% wt/wt) acid. Similar results were obtained with infants fed with human milk. MCT supplementation has no quantitative or qualitative effects on the intragastric lipolysis, which is not higher in premature infant than in adults.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- BSSL:
-
bile salt-stimulated lipase
- C16:0:
-
palmitic acid
- C18:1:
-
oleic acid
- CCK:
-
cholecystokinin
- DG:
-
diglyceride
- FAME:
-
fatty acid methyl ester
- GE:
-
gastric emptying
- HGL:
-
human gastric lipase
- LCFA:
-
long-chain fatty acid
- MCFA:
-
medium-chain fatty acid
- MCT:
-
medium-chain triglyceride
- MG:
-
monoglyceride
- TG:
-
triglyceride
References
Zoppi G, Andreotti G, Pajno-Ferrara F, Njai DM, Gaburro D 1972 Exocrine pancreas function in premature and full term neonates. Pediatr Res 6: 880–886
Fredrikzon B, Olivecrona T 1978 Decrease of lipase and esterase activities in intestinal contents of newborn infants during test meals. Pediatr Res 12: 631–634
Watkins JB, Ingall D, Szczepanik P, Klein PD, Lester R 1973 Bile-salt metabolism in the newborn. Measurement of pool size and synthesis by stable isotope technic. N Engl J Med 288: 431–434
Murphy GM, Signer E 1974 Bile acid metabolism in infants and children. Gut 15: 151–163
Bernback S, Blackberg L, Hernell O 1990 The complete digestion of human milk triacylglycerol in vitro requires gastric lipase, pancreatic colipase-dependent lipase, and bile salt-stimulated lipase. J Clin Invest 85: 1221–1226
Sarles J, Moreau H, Verger R 1992 Human gastric lipase: ontogeny and variations in children. Acta Paediatr 81: 511–513
Bernbäck S, Bläckberg L, Hernell O 1989 Fatty acids generated by gastric lipase promote human milk triacylglycerol digestion by pancreatic colipase-dependent lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1001: 286–291
Armand M, Hamosh M, Mehta NR, Angelus PA, Philpott JR, Henderson TR, Dwyer NK, Lairon D, Hamosh P 1996 Effect of human milk or formula on gastric function and fat digestion in the premature infant. Pediatr Res 40: 429–437
Armand M, Hamosh M, Dipalma JS, Gallagher J, Benjamin SB, Philpott JR, Lairon D, Hamosh P 1995 Dietary fat modulates gastric lipase activity in healthy humans. Am J Clin Nutr 62: 74–80
Carrière F, Barrowman JA, Verger R, Laugier R 1993 Secretion and contribution to lipolysis of gastric and pancreatic lipases during a test meal in humans. Gastroenterology 105: 876–888
Lengsfeld H, Beaumier-Gallon G, Chahinian H, De Caro A, Verger R, Laugier R, Carrière F 2004 Physiology of gastrointestinal lipolysis and therapeutical use of lipases and digestive lipase inhibitors. In: Müller G, Petry S (eds) Lipases and Phospholipases in Drug Development. Wiley, Weinheim, 195–229.
Ville E, Carriere F, Renou C, Laugier R 2002 Physiological study of pH stability and sensitivity to pepsin of human gastric lipase. Digestion 65: 73–81
Roulet M, Weber AM, Paradis Y, Roy CC, Chartraud L, Lasalle R, Morin CL 1980 Gastric emptying and lingual lipase activity in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Res 14: 1360–1362
Moreau J, Bouisson M, Balas D, Ravaud A, Stupnik S, Buscail L, Vaysse N, Ribet A 1990 Gastric lipase in alcoholic pancreatitis. Comparison of secretive profiles following pentagastrin stimulation in normal adults and patients with pancreatic insufficiency. Gastroenterology 99: 175–180
Carrière F, Grandval P, Renou C, Palomba A, Priéri F, Giallo J, Henniges F, Sander-Struckmeier S, Laugier R 2005 Quantitative study of digestive enzyme secretion and gastrointestinal lipolysis in chronic pancreatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3: 28–38
Schanler RJ, Shulman RJ, Lau C 1999 Feeding strategies for premature infants: beneficial outcomes of feeding fortified human milk versus preterm formula. Pediatrics 103: 1150–1157
Hamosh M, Bitman J, Liao TH, Mehta NR, Buczek RJ, Wood DL, Grylack LJ, Hamosh P 1989 Gastric lipolysis and fat absorption in preterm infants: effect of medium-chain triglyceride or long-chain triglyceride-containing formulas. Pediatrics 83: 86–92
Villeneuve P, Pina M, Montet D, Graille J 1995 Determination of lipase specificities through the use of chiral triglycerides and their racemics. Chem Phys Lipids 76: 109–113
Fredrikzon B, Hernell O 1977 Role of feeding on lipase activity in gastric contents. Acta Paediatr Scand 66: 479–484
Siegel M, Lebenthal E, Topper W, Krantz B, Li PK 1982 Gastric emptying in prematures of isocaloric feedings with differing osmolalities. Pediatr Res 16: 141–147
Carriere F, Renou C, Ransac S, Lopez V, De Caro J, Ferrato F, De Caro A, Fleury A, Sanwald-Ducray P, Lengsfeld H, Beglinger C, Hadvary P, Verger R, Laugier R 2001 Inhibition of gastrointestinal lipolysis by Orlistat during digestion of test meals in healthy volunteers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 281: G16–G28
Carrière F, Rogalska E, Cudrey C, Ferrato F, Laugier R, Verger R 1997 In vivo and in vitro studies on the stereoselective hydrolysis of tri- and diglycerides by gastric and pancreatic lipases. Bioorg Med Chem 5: 429–435
Straarup EM, Lauritzen L, Faerk J, Hoy Deceased CE, Michaelsen KF 2006 The stereospecific triacylglycerol structures and fatty acid profiles of human milk and infant formulas. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 42: 293–299
Patton JS, Rigler MW, Liao H, Hamosh P, Hamosh M 1982 Hydrolysis of triacylglycerol emulsions by lingual lipase. A microscopic study. Biochim Biophys Acta 712: 400–407
Hamosh M, Bitman J, Liao T, Mehta NR, Buczek RJ, Wood DL, Grylack LJ, Hamosh P 1989 Gastric lipolysis and fat absorption in preterm infants: effect of medium chain triglyceride or long chain triglyceride containing formulas. Pediatrics 83: 86–92
Myher JJ, Kuksis A, Steiner G 1984 Milk fat structure of a patient with type 1 hyperlipidemia. Lipids 19: 673–682
Winter CH, Hoving EB, Muskiet FA 1993 Fatty acid composition of human milk triglyceride species. Possible consequences for optimal structures of infant formula triglycerides. J Chromatogr 616: 9–24
Staggers JE, Fernando-Warnakulasuriya GJ, Wells MA 1981 Studies on fat digestion, absorption, and transport in the suckling rat. II. Triacylglycerols: molecular species, stereospecific analysis, and specificity of hydrolysis by lingual lipase. J Lipid Res 22: 675–679
Fernando-Warnakulasuriya GJ, Staggers JE, Frost SC, Wells MA 1981 Studies on fat digestion, absorption, and transport in the suckling rat. I. Fatty acid composition and concentrations of major lipid components. J Lipid Res 22: 668–674
Hildebrand P, Petrig C, Burckhardt B, Ketterer S, Lengsfeld H, Fleury A, Hadvary P, Beglinger C 1998 Hydrolysis of dietary fat by pancreatic lipase stimulates cholecystokinin release. Gastroenterology 114: 123–129
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Nathalie Barouh and Bruno Barrea (CIRAD, Montpellier, France) for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roman, C., Carriere, F., Villeneuve, P. et al. Quantitative and Qualitative Study of Gastric Lipolysis in Premature Infants: Do MCT-Enriched Infant Formulas Improve Fat Digestion?. Pediatr Res 61, 83–88 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000250199.24107.fb
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/01.pdr.0000250199.24107.fb
This article is cited by
-
Fatty acid composition and phospholipid types used in infant formulas modifies the establishment of human gut bacteria in germ-free mice
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
The impact of lactoferrin with different levels of metal saturation on the intestinal epithelial barrier function and mucosal inflammation
BioMetals (2016)
-
Pancreatic lipase–related protein 2 digests fats in human milk and formula in concert with gastric lipase and carboxyl ester lipase
Pediatric Research (2013)
-
Digested formula but not digested fresh human milk causes death of intestinal cells in vitro: implications for necrotizing enterocolitis
Pediatric Research (2012)
-
Development of the Digestive System—Experimental Challenges and Approaches of Infant Lipid Digestion
Food Digestion (2012)