Abstract
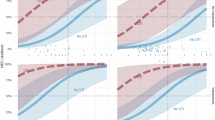
The National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the Digestive Diseases Interagency Coordinating Committee held a workshop, chaired by Dr. W. Allan Walker, on July 10–11, 2006, to identify promising leads in necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) research. The goals of the workshop were to identify new approaches to the prevention and treatment of NEC, to define basic and translational mechanisms of potential approaches to NEC, and to develop recommendations for clinical studies to reduce the incidence of NEC. Workshop participants implicated prematurity, introduction of enteral feedings, gastrointestinal bacterial colonization, gut motility, proinflammatory cytokines, impaired gut blood flow, and various neonatal complications in the pathogenesis of NEC. They concluded that a unifying hypothesis encompassing these pathogenetic factors is the uncontrolled exuberant inflammatory response to bacterial colonization that characterizes the intestine of premature infants. The inflammatory cascade appears to offer multiple targets for interventions with a variety of anti-inflammatory agents, including human milk and probiotics. Because of the rapidity with which the inflammatory response gets out of control in infants with NEC, workshop participants agreed that searching for ways to prevent NEC will be more rewarding than trying to identify ways to treat the condition once it has become established.
Similar content being viewed by others
Log in or create a free account to read this content
Gain free access to this article, as well as selected content from this journal and more on nature.com
or
Abbreviations
- ET-1:
-
endothelin-1
- GLP-2:
-
glucagon-like peptide-2
- HB-EGF:
-
heparin-binding epidermal growth factor
- NEC:
-
necrotizing enterocolitis
- PAF:
-
platelet activating factor
- PPD:
-
primary peritoneal drainage
- RIA:
-
resection-induced adaptation
- SIP:
-
spontaneous intestinal perforation
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- VLBW:
-
very low birth weight (<1500 g)
References
Moss RL, Dimmitt RA, Barnhart DC, Sylvester KG, Brown RL, Powell DM, Islam S, Langer JC, Sato TT, Brandt ML, Lee H, Blakely ML, Lazar EL, Hirschl RB, Kenney BD, Hackam DJ, Zelterman D, Silverman BL 2006 Laparotomy versus peritoneal drainage for necrotizing enterocolitis and perforation. N Engl J Med 354: 2225–2234
Blakely ML, Tyson JE, Lally KP, McDonald S, Stoll BJ, Stevenson DK, Poole WK, Jobe AH, Wright LL, Higgins RD 2006 Laparotomy versus peritoneal drainage for necrotizing enterocolitis or isolated intestinal perforation in extremely low birth weight infants: outcomes through 18 months adjusted age. Pediatrics 117: e680–e687
Wiedmeier SE, Henry E, Baer VL, Stoddard RA, Eggert LD, Lambert DK, Christensen RD 2007 Necrotizing enterocolitis in three level III NICUs within one healthcare system. Am J Perinatol (in press)
Christensen RD, Havranek T, Gerstmann DR, Calhoun DA 2005 Enteral administration of a simulated amniotic fluid to very low birth weight neonates. J Perinatol 25: 380–385
Warner BW, Erwin CR 2006 Critical roles for EGF receptor signaling during resection-induced intestinal adaptation. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 43: S68–S73
Wildhaber BE, Yang H, Spencer AU, Drongowski RA, Teitelbaum DH 2005 Lack of enteral nutrition—effects on the intestinal immune system. J Surg Res 123: 8–16
Li N, Lassman BJ, Liu Z, Liboni K, Neu J 2004 Effects of protein deprivation on growth and small intestinal morphology are not improved by glutamine or glutamate in gastrostomy-fed rat pups. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 39: 28–33
Bartholome AL, Albin DM, Baker DH, Holst JJ, Tappenden KA 2004 Supplementation of total parenteral nutrition with butyrate acutely increases structural aspects of intestinal adaptation after an 80% jejunoileal resection in neonatal piglets. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 28: 210–222
Claud EC, Savidge T, Walker WA 2003 Modulation of human intestinal epithelial cell IL-8 secretion by human milk factors. Pediatr Res 53: 419–425
Neu J, Chen M, Beierle E 2005 Intestinal innate immunity: how does it relate to the pathogenesis of necrotizing enterocolitis?. Semin Pediatr Surg 14: 137–144
Uauy RD, Fanaroff AA, Korones SB, Phillips EA, Philllips JB, Wright LL 1991 Necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants: biodemographic and clinical correlates. J Pediatr 119: 630–638
Martin CR, Walker WA 2006 Intestinal immune defences and the inflammatory response in necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med 11: 369–377
Jilling T, Lu J, Jackson M, Caplan MS 2004 Intestinal epithelial apoptosis initiates gross bowel necrosis in an experimental rat model of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Res 55: 622–629
Claud EC, Lu L, Anton PM, Savidge T, Walker AW, Cherayil BJ 2004 Developmentally regulated IkappaB expression in intestinal epithelium and susceptibility to flagellin-induced inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101: 7404–7408
Jilling T, Simon D, Lu J, Meng FJ, Li D, Schy R, Thomson RB, Soliman A, Arditi M, Caplan MS 2006 The roles of bacteria and TLR4 in rat and murine models of necrotizing enterocolitis. J Immunol 177: 3273–3282
Collier-Hyams LS, Sloane V, Batten BC, Neish AS 2005 Cutting edge: bacterial modulation of epithelial signaling via changes in neddylation of cullin-1. J Immunol 175: 4194–4198
Caplan MS, Simon D, Jilling T 2005 The role of PAF, TLR, and the inflammatory response in neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Semin Pediatr Surg 14: 145–151
Schanler RJ, Lau C, Hurst NM, Smith EO 2005 Randomized trial of donor human milk versus preterm formula as substitutes for mothers' own milk in the feeding of extremely premature infants. Pediatrics 116: 400–406
Heiman H, Schanler RJ 2006 Benefits of maternal and donor human milk for premature infants. Early Hum Devel Epub October 19:2006
Lin HC, Su BH, Chen AC, Lin TW, Tsai CH, Yeh TF, Oh W 2005 Oral probiotics reduce the incidence and severity of necrotizing enterocolitis in very low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 115: 1–4
Kalliomaki MA, Walker WA 2005 Physiologic and pathologic interactions of bacteria with gastrointestinal epithelium. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 34: 383–399
Shin CE, Falcone RA Jr, Stuart L, Erwin CR, Warner BW 2000 Diminished growth factor levels in infants with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 35: 173–176
Dvorak B, Halpern MD, Holubec H, Williams CS, McWilliam DL, Dominguez JA, Stepankova R, Payne CM, McCuskey 2002 Epidermal growth factor reduces the development of necrotizing enterocolitis in a neonatal rat model. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282: G156–G164
Halpern MD, Dominguez JA, Dvorakova K, Holubec H, Williams CS, Meza YG, Ruth MC, Dvorak B 2003 Ileal cytokine dysregulation in experimental necrotizing enterocolitis is reduced by epidermal growth factor. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 36: 126–133
Clark JA, Lane RH, Maclennan NK, Holubec H, Dvorakova K, Halpern MD, Williams CS, Payne CM, Dvorak B 2005 Epidermal growth factor reduces intestinal apoptosis in an experimental model of necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 288: G755–G762
Feng J, El-Assal ON, Besner GE 2006 Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor reduces intestinal apoptosis in neonatal rats with necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr Surg 41: 742–747
Feng J, El-Assal ON, Besner GE 2006 Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor decreases the incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis in neonatal rats. J Pediatr Surg 41: 144–149
Nowicki PT, Dunaway DJ, Nankervis CA, Giannone PJ, Reber KM, Hammond SB, Besner GE, Caniano DA 2005 Endothelin-1 in human intestine resected for necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr 146: 805–810
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The workshop was sponsored by the National Institute of Child Health and Development and the NIDDK.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grave, G., Nelson, S., Walker, W. et al. New Therapies and Preventive Approaches for Necrotizing Enterocolitis: Report of a Research Planning Workshop. Pediatr Res 62, 510–514 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318142580a
Received:
Accepted:
Issue date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1203/PDR.0b013e318142580a
This article is cited by
-
Initial surgical treatment of necrotizing enterocolitis: a meta-analysis of peritoneal drainage versus laparotomy
European Journal of Pediatrics (2022)
-
IL-17-related signature genes linked to human necrotizing enterocolitis
BMC Research Notes (2021)
-
Surfactant protein A reduces TLR4 and inflammatory cytokine mRNA levels in neonatal mouse ileum
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Does red blood cell irradiation and/or anemia trigger intestinal injury in premature infants with birth weight ≤ 1250 g? An observational birth cohort study
BMC Pediatrics (2018)
-
Timing of developmental reduction in epithelial glutathione redox potential is associated with increased epithelial proliferation in the immature murine intestine
Pediatric Research (2017)